41-year-old with acute abdominal pain
Patient will present as → a 43-year-old woman who comes to the emergency department with a 12-hour history of right upper quadrant (RUQ) abdominal pain. The pain is severe now but waxes and wanes and is associated with nausea and some episodes of vomiting. The pain sometimes radiates through to the back. She feels warm but has not checked her temperature. There is no diarrhea. Her last bowel movement was 1 day ago and was normal. The patient has no similar history in the past. On examination, the patient is an obese young woman in some discomfort. Her vital signs reveal a temperature of 100 ° F and a pulse of 102 beats per minute. Her blood pressure is 130/70 mmHg, and her respirations are 18 breaths/minute. There is no scleral icterus. The chest is clear, and the cardiovascular examination is normal. Abdominal examination reveals marked upper abdominal tenderness with guarding, especially in the RUQ. On palpation of the RUQ of the abdomen, when the patient is asked to take a deep breath, there is a marked increase in pain. The bowel sounds are present but seem slightly sluggish. The patient has no drug allergies and is not taking any medications at present.
To watch this and all of Joe-Gilboy PA-C's video lessons you must be a member. Members can log in here or join now.
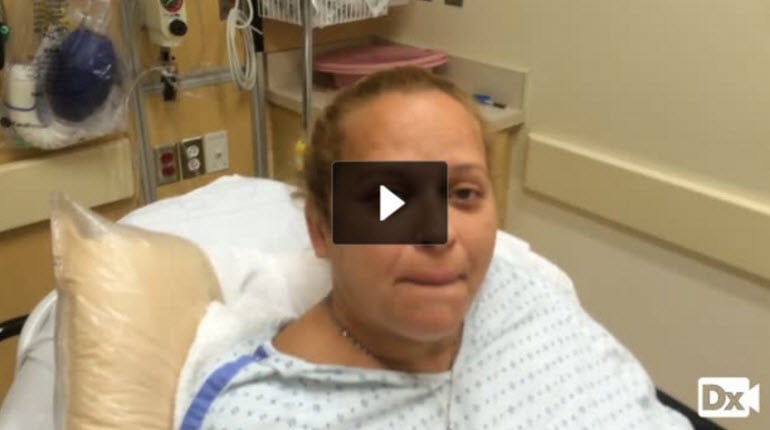
Cholelithiasis refers to stones in the gallbladder (i.e., gallstones) without inflammation
- Most cases are asymptomatic, and the majority of patients found to have incidental gallstones will remain asymptomatic
- Cholesterol stones account for > 85% of gallstones in the Western world - (Fat, female, forty, and fertile) OCPs, chronic hemolysis, cirrhosis, infection, rapid weight loss, IBD, TPN, fibrates, increased triglycerides
- 10% are pigmented - black, brown and mixed
Biliary colic is the cardinal symptom of gallstones and is due to temporary obstruction of the cystic duct by a gallstone. Pain occurs as the gallbladder contracts against this obstruction
- Classically presents as right upper quadrant pain that begins abruptly, continues in duration, resolves slowly, lasting 20 min to several hours, is associated with nausea and precipitated by fatty foods and large meals
- Boas sign—referred right subscapular pain of biliary colic
Complications of cholelithiasis:
- Cholecystitis: cystic duct obstruction by gallstones
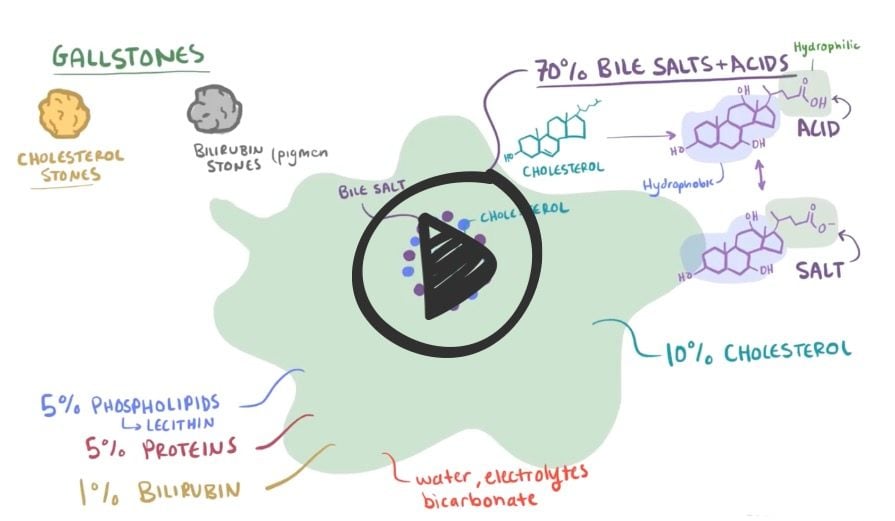
- Choledocholithiasis: gallstones in the biliary tree – associated with ductal dilation and biliary colic or jaundice. Treat with stone extraction via ERCP
- Cholangitis: biliary tract infection secondary to obstruction by gallstones. Diagnose with ERCP
The diagnostic procedure of choice in this patient is abdominal ultrasonography
- Ultrasound examination should be done after 8 hours of fasting because gallstones are visualized better in a distended, bile-filled gallbladder
Alkaline phosphatase (ALK-P): Not specific to the liver—also found in bone, gut, and placenta
- ALK-P is elevated when there is an obstruction to bile flow (e.g., cholestasis) in any part of the biliary tree. Normal levels make cholestasis unlikely.
Bilirubin
GGT is often used to confirm that the ALK-P elevation is of hepatic origin
Albumin—decreased in chronic liver disease, nephrotic syndrome, malnutrition, and inflammatory states (e.g., burns, sepsis, trauma)
Prothrombin time
- The liver synthesizes clotting factors I, II, V, VII, IX, X, XII, and XIII, the function of which is reflected by PT.
- PT is not prolonged until most of the liver’s synthetic capacity is lost, which corresponds to advanced liver disease.
If asymptomatic, may observe or use oral bile dissolution treatment
- Cholecystectomy (usually laparoscopic) in symptomatic patients
Question 1 |
Pregnancy Hint: High progesterone levels of pregnancy reduces gallbladder contractility leading to prolonged retention and greater concentration of bile in the gallbladder. | |
Obesity Hint: Obesity is associated with increased hepatic cholesterol secretion. | |
Sickle cell anemia | |
Estrogen Hint: Estrogen administered for contraception increase the risk of cholesterol gallstones by increasing biliary cholesterol secretion |
Question 2 |
Gallstone disease is responsible for about 10,000 deaths per year in the United States. Hint: See answer for explanation | |
Consumption of caffeinated coffee appears to protect against gallstones in women. Hint: See answer for explanation | |
Acute pancreatitis is a possible complication of cholelithiasis Hint: See answer for explanation | |
Gallstones are more common in men than women. |
Question 3 |
Cholesterol stones Hint: Cholesterol or mixed stones contain 51–99% pure cholesterol plus an admixture of calcium salts, bile acids, bile pigments and phospholipids. | |
Cystine stones | |
Pigment stones Hint: Pigment stone is the name used for stones containing less than 30% cholesterol. There are two types – black and brown. | |
Mixed stones Hint: Cholesterol or mixed stones contain 51–99% pure cholesterol plus an admixture of calcium salts, bile acids, bile pigments and phospholipids. |
Question 4 |
Intestinal obstruction Hint: Gallstone ileus is an uncommon (but possible) cause of small bowel obstruction. | |
Acute cholangitis | |
Gallbladder empyema Hint: Acute cholecystitis in the presence of bacteria-containing bile may progress to suppurative infection in which the gallbladder fills with purulent material, a condition referred to as empyema of the gallbladder. | |
Pyelonephritis |
Question 5 |
Amoxicillin | |
Ciprofloxacin | |
Ceftriaxone | |
Doxycycline |
|
List |
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate


 Lecture
Lecture