Patient will present as → a 27-year-old female who has been experiencing postprandial bloating, flatulence, diarrhea, and abdominal pain for one year. Symptoms occur following the ingestion of milk products
To watch this and all of Joe-Gilboy PA-C's video lessons you must be a member. Members can log in here or join now.
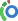
Lactose intolerant individuals have insufficient levels of lactase, an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of lactose into glucose and galactose, in their digestive system.
- In most cases, this causes symptoms that may include abdominal bloating and cramps, flatulence, diarrhea, nausea, borborygmi (rumbling stomach), or vomiting after consuming significant amounts of lactose
- Clinical symptoms typically appear within 30 minutes but may take up to two hours, depending on other foods and activities
- Patients may need calcium supplementation
The diagnosis of lactose intolerance should be considered in patients with bloating, flatulence, abdominal pain, and/or chronic diarrhea
- A presumptive diagnosis of lactose intolerance can be made in patients with mild symptoms that occur with significant lactose ingestion (eg, >2 servings of dairy/day or >1 serving in a single dose that is not associated with a meal) and resolve after five to seven days of avoidance of lactose-containing foods, with recurrence on rechallenge
Definitive diagnosis is with lactose breath hydrogen test
- The patient drinks a liquid that has lactose in it. Then they breathe into a special machine every 30 minutes. The machine measures how much hydrogen they breathe out.
- People who have lactose intolerance breathe out more hydrogen than normal
- The hydrogen breath test is positive for lactose malabsorption if the post-lactose breath hydrogen value rises greater than 20 ppm over the baseline measurement
Stool acidity test (Fecal PH Test)
- Human feces are normally alkaline. An acidic stool can indicate a digestive problem such as lactose intolerance or a contagion such as E. coli or rotavirus, or overgrowth of the acid-producing bacteria
Treatment focuses on the avoidance of dairy products, the use of lactose-free products, or the use of lactase supplements
 Osmosis Osmosis |
|
 |
Lactose intolerance is due to lactase deficiency, which leads to a decrease in lactose absorption and increased osmotic load. This can manifest as abdominal pain, flatulence, and diarrhea. Lactose intolerance can be diagnosed with a positive hydrogen breath test and decreased stool pH. It can be treated by avoiding dairy products and lactase supplementation.
Play Video + QuizQuestion 1 |
Giardiasis Hint: Is due to ingestion of contaminated water. Can cause lactose intolerance.v | |
Celiac disease Hint: Causes chronic diarrhea. Usually due to sensitivity to gluten containing food. Can also cause lactose intolerance. | |
Lactose intolerance | |
Gastrinoma Hint: In addition to diarrhea, patient will also have ulcer symptoms. Can cause lactose intolerance. |
Question 2 |
urea breath test Hint: Urea breath test is used in diagnosing H. pylori infection. | |
hydrogen breath test | |
endoscopy Hint: Endoscopy and biopsy of the small intestine is done to diagnose celiac disease. | |
ileocolonoscopy Hint: Ileocolonoscopy is the diagnostic tool of choice to diagnose Crohn’s disease. |
Question 3 |
Osteopenia is a possible complication. Hint: See C for explanation | |
Hydrogen breath test is the diagnostic test of choice. Hint: See C for explanation | |
The congenital form is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait. | |
May be secondarily due to Crohn’s disease. Hint: See C for explanation |
Question 4 |
Supplemental calcium Hint: See D for explanation | |
Lactase enzyme preparations Hint: See D for explanation | |
Pre-hydrolyzed milk Hint: See D for explanation | |
Promethazine |
Question 5 |
Glucose and galactose | |
Glucose and sucrose Hint: See A for explanation | |
Fructose and galactose Hint: See A for explanation | |
Glucose and fructose Hint: See A for explanation |
|
List |
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate


 Lecture
Lecture

