Patient will present as → a 32-year-old female presents with fever, chills, nausea, and flank pain for 24 hours. She developed dysuria and urinary frequency 3 days prior and states that both have worsened. On physical exam, you note suprapubic abdominal pain and CVA tenderness. The urinalysis reveals white blood cell casts.
To watch this and all of Joe Gilboy PA-C's video lessons you must be a member. Members can log in here or join now.
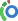
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is any infection of the urinary tract, which includes the upper portion of the tract—the kidneys and the ureters, and the lower portion of the tract—the bladder and urethra. Acute pyelonephritis is a type of upper urinary tract infection that results in inflammation of the kidney that develops relatively quickly, usually because of a bacterial infection.
- Irritative voiding + fever + flank Pain + nausea and vomiting + CVA tenderness
- Organism ⇒ E. coli
- If severe symptoms or unable to take PO will need to be hospitalized
Urinalysis:
- Pyuria, hematuria, bacteriuria, and WBC casts (pathognomonic pyelonephritis and interstitial nephritis)
- Leukocyte esterase, nitrites, hematuria
- Culture and sensitivity need to be done
- If complicated pyelonephritis order a renal ultrasound may show hydronephrosis secondary to obstruction
An oral regimen is considered the best initial outpatient treatment (7 days of outpatient treatment is equivalent to longer treatment regimens)
- Ciprofloxacin: 500 mg BID for 7 days
- Ciprofloxacin XR: 1,000 mg/day for 7 days
- Levofloxacin: 750 mg/day for 5 days
- Cephalexin 500 mg PO QID for 10-14 days
IV antibiotics are indicated for inpatients who are toxic or unable to tolerate oral antibiotics
- Ceftriaxone 1 g IV once daily
Management of acute pyelonephritis in pregnant women includes hospital admission for parenteral antibiotics.
- Empiric therapy includes IV/IM ceftriaxone
"The decision to hospitalize a patient is usually clear in the setting of critical illness or sepsis. Otherwise, general indications for inpatient management include persistently high fever (eg, >101°F/>38.4°C) or pain, marked debility, inability to maintain oral hydration, or take oral medications, suspected urinary tract obstruction, and concerns regarding adherence to therapy."
 Osmosis Osmosis |
|
 |
 Pyelonephritis is inflammation in an area of the kidney called the renal parenchyma. This condition is caused by a bacterial infection that begins in the lower urinary tract and travels upward and into the kidney(s). Patients with vesicoureteral reflux, urinary obstruction, or patients who are pregnant are at an increased risk of developing pyelonephritis. Presenting symptoms include fatigue, fever, chills, flank pain, nausea, vomiting, dysuria, and possible hematuria. Treatment of this condition involves antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain, and increased fluid intake. In some cases, a short stay in the hospital may be necessary for intravenous antibiotic administration.
Pyelonephritis is inflammation in an area of the kidney called the renal parenchyma. This condition is caused by a bacterial infection that begins in the lower urinary tract and travels upward and into the kidney(s). Patients with vesicoureteral reflux, urinary obstruction, or patients who are pregnant are at an increased risk of developing pyelonephritis. Presenting symptoms include fatigue, fever, chills, flank pain, nausea, vomiting, dysuria, and possible hematuria. Treatment of this condition involves antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain, and increased fluid intake. In some cases, a short stay in the hospital may be necessary for intravenous antibiotic administration.
| Pyelonephritis Assessment | Play Video + Quiz |
| Pyelonephritis interventions | Play Video + Quiz |
| Acute abdomen differential diagnosis (lower quadrants) | Play Video + Quiz |
| E. coli overview | Play Video + Quiz |
Question 1 |
Oral ciprofloxacin (Cipro) Hint: See B for explanation. | |
Oral trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim) Hint: The fluoroquinolones and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole are contraindicated in pregnancy. | |
IV gentamicin (Garamycin) Hint: Gentamicin is not indicated as first line therapy in the treatment of pyelonephritis in a pregnant patient | |
IV ceftriaxone (Rocephin) |
Question 2 |
acute salpingitis Hint: Acute salpingitis would be suggested if pelvic exam abnormalities were present. | |
nephrolithiasis Hint: Nephrolithiasis does not usually present with fever or casts. Urinalysis will have RBCs present. | |
acute pyelonephritis | |
appendicitis Hint: This scenario is consistent with acute pyelonephritis, not acute appendicitis. |
Question 3 |
Ciprofloxacin | |
Erythromycin Hint: See A for explanation. | |
Doxycycline Hint: See A for explanation. | |
Amoxicillin Hint: See A for explanation. |
Question 4 |
Hyaline casts Hint: Hyaline casts may be found in concentrated urine and are not indicative of renal disease. | |
Red cell casts Hint: Red cell casts are indicative of glomerulonephritis. | |
White cell casts | |
Granular casts Hint: Granular casts are non-specific and may be seen in acute tubular necrosis |
|
List |
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate


 Lecture
Lecture

