Encephalopathic disorders
| Encephalopathic disorders |
| Spongiform encephalopathy |
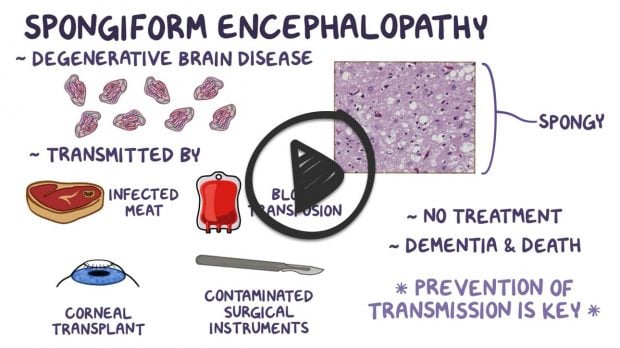
Group of progressive, invariably fatal, conditions that affect the brain are caused by the accumulation of misfolded prion proteins giving the brain a "spongy" appearance
- Transmitted by infected meat, blood transfusions, corneal transplants, and contaminated surgical instruments
- Symptoms may not show for decades then progress rapidly and may cause death
- Ataxia, poor memory, behavioral changes, dementia, myoclonus
- Diagnosed on MRI
- Lumbar puncture ↑ levels of 14-3-3 protein
- Definitive diagnosis with brain biopsy
- Currently, no treatments, genetic counseling for familial form, restrict blood transfusions
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD) which has four main forms
- Familial CJD - Mutation in PRNP Gene
- Variant CJD - Eating the meat of cows with prions in muscle tissue (mad cows disease)
- Iatrogenic CJD - caused by medical procedures
- Sporadic CJD - no clear cause
KURU - caused by cannibalism of infected flesh
Fatal Familial Insomnia - mutation in PRNP gene, prion proteins build up in thalamus and affect sleep, patients develop insomnia, exaggerated startle response
"Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), commonly known as mad cow disease, is an incurable and invariably fatal neurodegenerative disease of cattle. Symptoms include abnormal behavior, trouble walking, and weight loss. Later in the course of the disease, the cow becomes unable to function normally. The time between infection and onset of symptoms is generally four to five years. Spread to humans is believed to result in variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (vCJD)"
|
| Hashimoto encephalopathy (HE) |
Hashimoto encephalopathy (HE) is a syndrome of acute or subacute encephalopathy that is associated with elevated anti-thyroid antibody titers
- The presence of elevated antithyroid antibody titers and the exclusion of other causes of encephalopathy support the diagnosis of HE
- Treated with corticosteroids
|
| Wernicke encephalopathy (WE) and Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome |
A complication of thiamine (vitamin B1) deficiency
The term refers to two different syndromes, each representing a different stage of the disease:
- Wernicke encephalopathy (WE) is an acute syndrome requiring emergent treatment to prevent death and neurologic morbidity
- Ophthalmoplegia - weakness or paralysis of eye muscles
- Ataxia - unsteady gait
- Changes in mental state - confusion, apathy, difficulty concentrating
- Coma and death
- Korsakoff syndrome (KS) refers to a chronic neurologic condition that usually occurs as a consequence of WE
- Severe memory impairment
- Confabulation - creates stories to fill gaps in memory
Most often associated with chronic alcoholism
- WE occurs also in the setting of poor nutrition caused by malabsorption, poor dietary intake (anorexia), increased metabolic requirement (eg, during systemic illnesses), or increased loss of the water-soluble vitamin thiamine (eg, in renal dialysis)
Diagnose - thiamine levels and LFTs, confirmed by MRI - degeneration of mammillary bodies
TX: medical emergency, infusion of thiamine over a few days to normalized thiamine levels
- Given with glucose ** Must normalize thiamine levels first or will cause metabolic acidosis due to increased lactic acid

|
| Hepatic encephalopathy |
Occurs in individuals with chronic liver disease such as cirrhosis or hepatitis
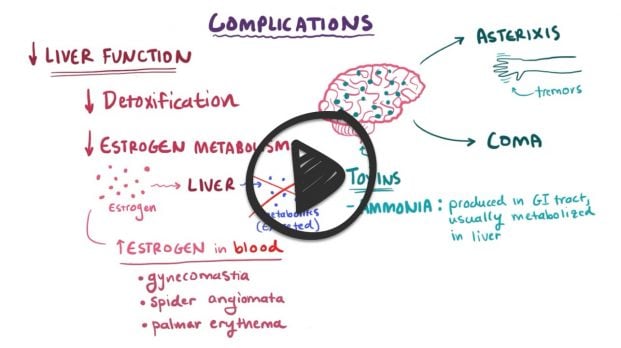
- Toxins that are produced by the digestive breakdown of proteins, such as ammonia, and normally cleared in the liver accumulate in the blood eventually traveling to and damaging the brain
- Triggers include infection and dehydration.
- Early symptoms include forgetfulness, confusion, and breath with a sweet or musty odor
- Advanced symptoms include shaking of the hands or arms (asterixis), disorientation, and slurred speech, and coma
Treatment includes removing toxic substances from the intestine
- Lactulose (to increase NH4 generation) and rifaximin (decrease intraluminal NH3 production)
|
Back to PANCE Blueprint Neurology (7%)





