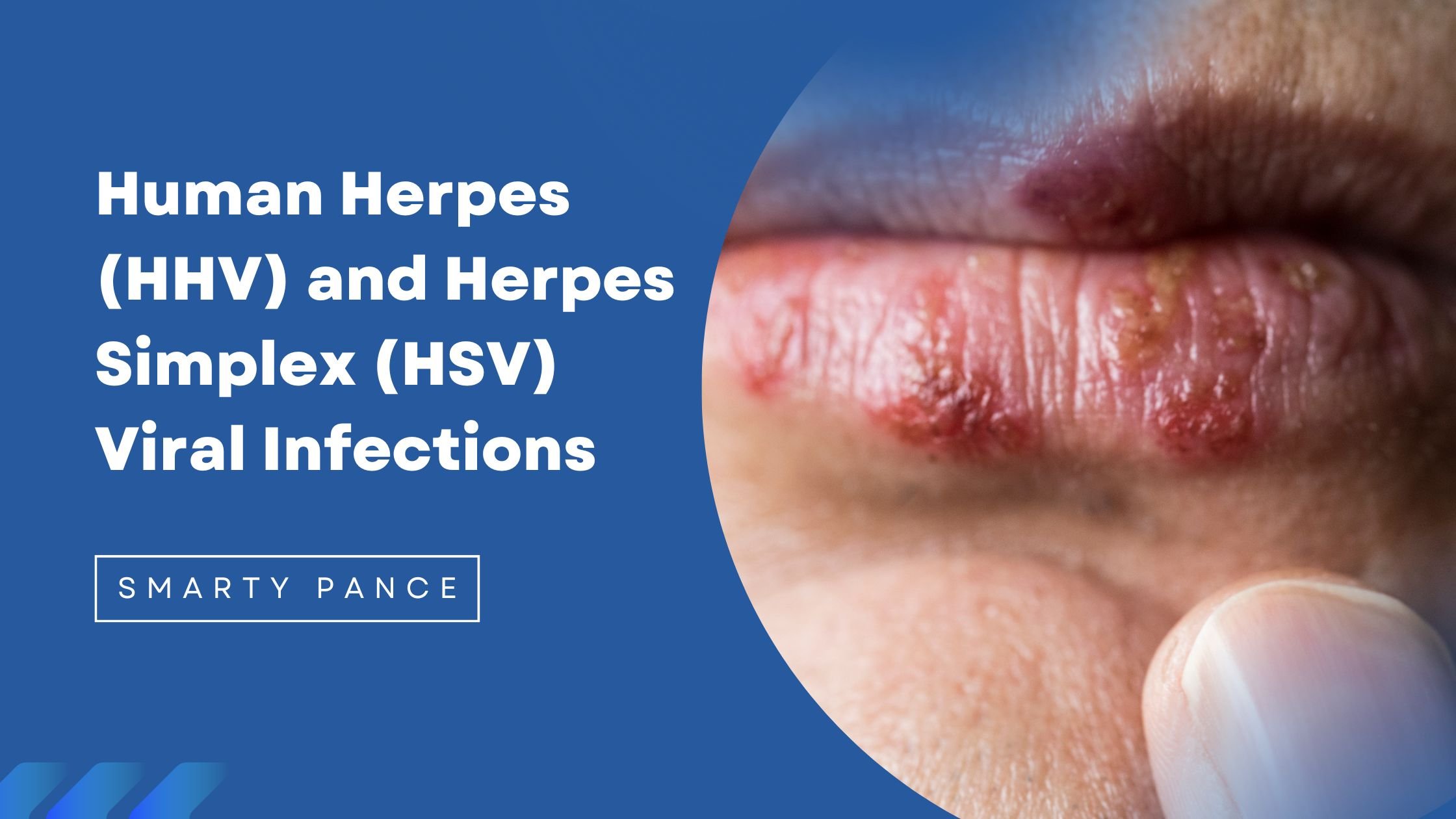
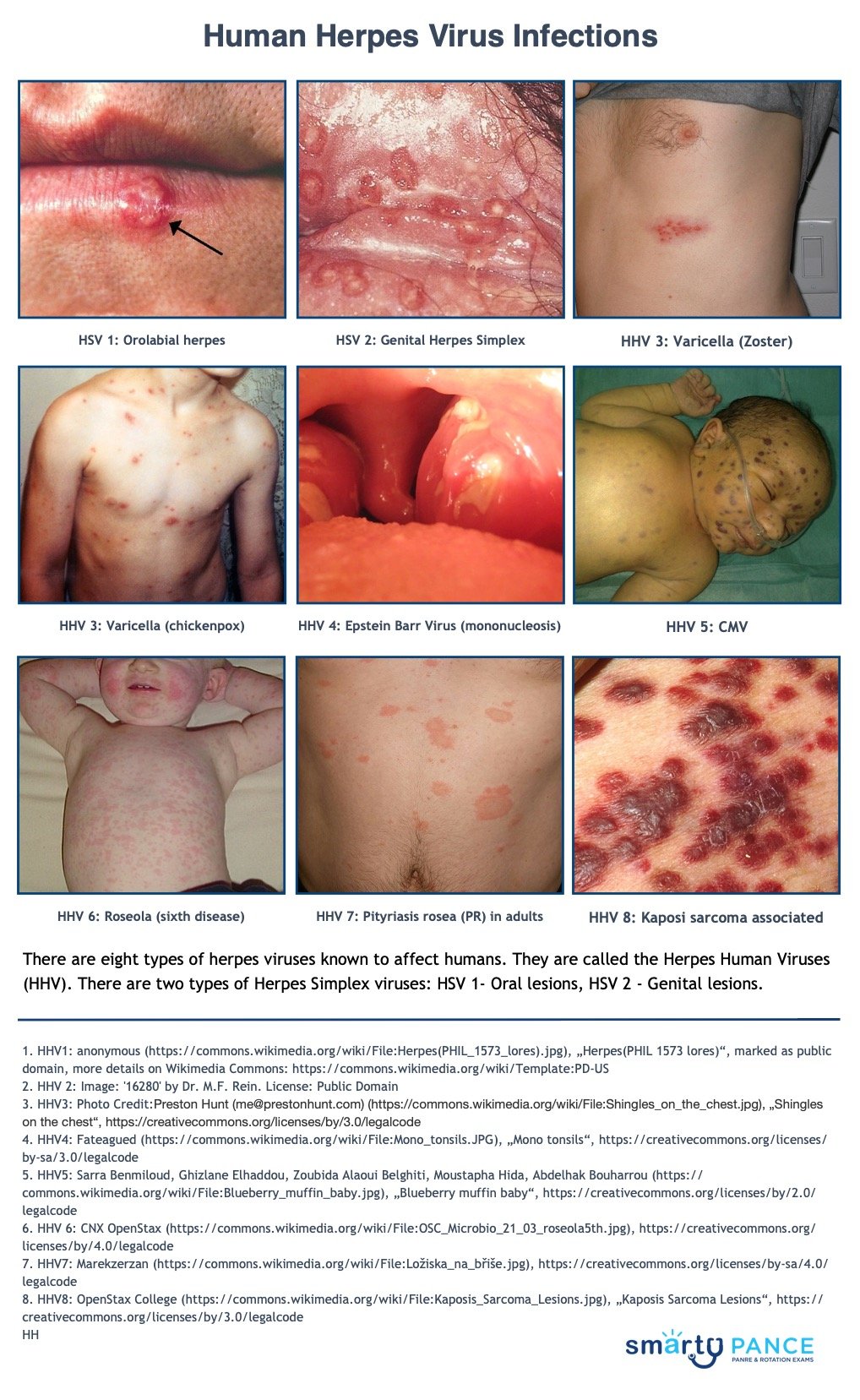
There are eight types of herpes viruses known to affect humans.
They are called the Herpes Human Viruses (HHV). There are two types of Herpes Simplex viruses: HSV 1- Oral lesions and HSV 2 - Genital lesions.
Herpes Simplex Viruses:
- HSV 1 - Oral lesions commonly called cold sores (tongue, lips, etc.)
- HSV 2 - Genital lesions (vulva, vagina, cervix, glans, prepuce, and penile shaft)
Herpes Human Viruses:
- HHV 3 - Varicella zoster virus (VZV) causes two diseases: 1. chickenpox (varicella) and 2. herpes zoster (shingles)
- HHV 4 - EBV - Epstein Barr Virus is commonly known as infectious mononucleosis (mono or glandular fever)
- HHV 5 - CMV (Cytomegalovirus is the most common virus transmitted to a pregnant woman's unborn child)
- HHV 6 - Roseolovirus is more commonly known as the 6th disease or Roseola Infantum
- HHV 7 - Similar to HHV6 (not yet classified) - may cause roseola in children and pityriasis rosea as well as CMV in adults
- HHV 8 - A type of rhadinovirus known as the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV)
After initial infection, all herpes viruses remain latent within specific host cells and may subsequently reactivate. Herpesviruses do not survive long outside a host; thus, the transmission usually requires intimate contact, although varicella-zoster virus (VZV) may spread by aerosol. In people with latent infection, the virus can reactivate without causing symptoms; in such cases, asymptomatic shedding occurs and people can transmit infection. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and human herpesvirus type 8 (HHV-8), also known as Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), can cause certain cancers.
| Human herpesvirus 1 | Gingivostomatitis, keratoconjunctivitis, cutaneous herpes, genital herpes, encephalitis, herpes labialis, esophagitis*, pneumonia*, hepatitis* | |
| Herpes simplex virus type 2 | Human herpesvirus 2 |
Genital herpes, cutaneous herpes, gingivostomatitis, neonatal herpes, aseptic meningitis, disseminated infection*, hepatitis* |
| Varicella-zoster virus |
Human herpesvirus 3 |
Chickenpox, herpes zoster, disseminated herpes zoster* |
|
Human herpesvirus 4 |
Infectious mononucleosis, hepatitis, encephalitis, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, Burkitt lymphoma, lymphoproliferative syndromes*, oral hairy leukoplakia* |
|
|
Human herpesvirus 5 |
Infectious mononucleosis, hepatitis, congenital cytomegalic inclusion disease, hepatitis*, retinitis*, pneumonia*, colitis* |
|
|
— |
Roseola infantum, otitis media with fever; encephalitis |
|
|
— |
Roseola infantum and pityriasis rosea, as well as CMV in adults |
|
|
Human herpesvirus 8 |
Not a known cause of acute illness but has a causative role in Kaposi sarcoma* and AIDS-related non-Hodgkin lymphomas that grow primarily in the pleural, pericardial, or abdominal cavities as lymphomatous effusions Also linked with multicentric Castleman disease |
|
|
*In immunocompromised hosts |
||
View more images of herpes simplex virus infections (HSV1) and (HSV2)