Cranial Nerve Palsies
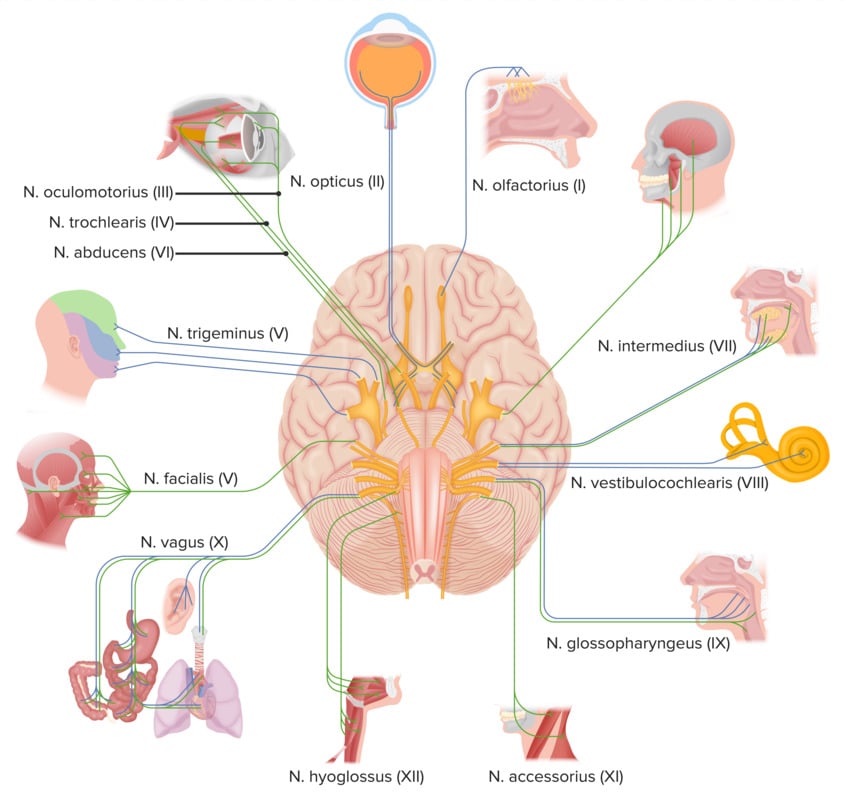 |
| Muscles Innervated by Cranial Nerves |
| Cranial Nerve |
Muscle(s) |
Lesion(s) |
| Olfactory nerve (CN I)
|
Sensory |
- Anosmia (inability to smell), hyposmia (reduced ability to smell), Dysomia, smells become mixed up
|
| Optic nerve (CN II) |
Sensory |
- Scotomas (blind spots) are a defect of vision in a defined area in one or both eyes. Optical neuropathologies show up as a partial or complete loss of vision
|
| Oculomotor nerve (CN III) |
- Extraocular muscles innervated by CN III are
- superior rectus (SR)
- inferior rectus (IR)
- medial rectus (MR)
- inferior oblique (IO)
- Levator palpebrae superioris
- Ciliary muscle
- Sphincter pupillae
|
- Diplopia
- Ptosis
- Loss of accommodation
- Pupillary involvement
- in compressive lesions the pupil becomes dilated and non-reactive
- in ischemic lesions (e.g., diabetes mellitus) the pupil is spared
|
| Trochlear nerve (CN IV) |
|
- Difficulty looking down
- Head tilt away from the side of the lesion
|
| Mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V3) |
- Muscles of mastication include
- masseter
- temporalis
- lateral and medial pterygoid
- Anterior belly of the digastric muscle
- Mylohyoid muscle
- Tensor palati
- Tensor tympani
|
- Jaw deviation towards the side of the lesion
|
| Abducens nerve (CN VI) |
|
|
| Facial nerve (CN VII) |
- Muscles of facial expression
- Posterior belly of digastric muscle
- Stylohyoid muscle
- Stapedius muscle
|
- Bell's palsy
- Loss of blink reflex
- Hyperacusis (when the stapedius is involved)
|
| Vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) |
Sensory
- It divides into the vestibular nerve which is responsible for balance/equilibrium and visual fixation during movement and the cochlear nerve which is responsible for hearing
|
- Deafness, tinnitus, vertigo, dizziness, nausea, nystagmus, loss of balance and ataxia
|
| Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) |
|
-
|
| Vagus nerve (CN X) |
- Muscles of the palate and pharynx except
- tensor palati muscle (CN V3)
- Stylopharyngeus muscle (CN IX)
- All muscles of the larynx
|
- Palate droop
- Dysphagia
- Deviation of the uvula away from the side of the lesion
- Loss of gag reflex (the sensory component of this reflex is mostly via CN IX)
|
| Accessory nerve (CN XI) |
- Sternocleidomastoid muscle
- Trapezius muscle
|
- Weakness with turning of the head
- Shoulder droop
|
| Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) |
- Muscles of the tongue except for the
|
- Tongue deviation towards the side of the lesion
|
 Osmosis Osmosis |
 |
| Picmonic |
 |
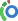
There are 12 cranial nerves, which have nuclei located in the tegmentum of the brain stem. These nerves classified as either sensory, motor, or both.
Play Video + Quiz
|
> |
Cranial nerve I, also known as the olfactory nerve, is a special sensory nerve that is responsible for the smell. It travels through the olfactory tract and bulbs and exits through the foramina in the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone.
Play Video + Quiz
|
 |
CN II, also known as the optic nerve, is a special sensory nerve responsible for vision. It partially decussates in the optic chiasm and exits the cranium through the optic canal.
Play Video + Quiz
|
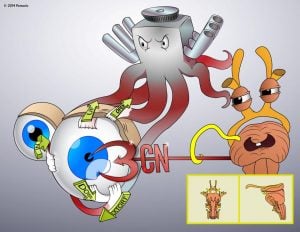 |
CN III, also known as the oculomotor nerve. It is a motor neuron that controls most of the eye's movements, along with accommodation, eyelid opening, and pupillary constriction.
Play Video + Quiz
|
 |
CN IV, also known as the trochlear nerve. It is a motor nerve that controls the superior oblique extraocular muscle.
Play Video + Quiz
|
 |
CN V, also known as the trigeminal nerve. CN V is the largest cranial nerve and has both motor and sensory functions.
Play Video + Quiz
|
 |
CN VI is lso known as the abducens nerve. CN VI controls the lateral rectus extraocular muscle.
Play Video + Quiz
|
 |
CN VII (Seven) is also known as the facial nerve and it has both motor and sensory functions. It's sensory functions include being responsible for taste from the anterior 2/3 of the tongue. It's motor functions include control of the muscles of facial expression, the stapedius muscle in the middle ear and closing of the eyelid
Play Video + Quiz
|
 |
CN VIII is a sensory nerve that is also known as the vestibulocochlear nerve. It divides into the vestibular nerve which is responsible for balance/equilibrium and visual fixation during movement and the cochlear nerve which is responsible for hearing.
Play Video + Quiz
|
 |
CN IX is also known as the glossopharyngeal nerve. It is a motor and sensory nerve that has various functions including swallowing and taste sensation for the posterior 1/3 of the tongue. It is also important for regulation of heart rate via baroreceptors in the carotid sinus and regulation of respiratory drive via chemoreceptors in the carotid body.
Play Video + Quiz
|
 |
CN X is also known as the vagus nerve. it is a motor, sensory and visceral nerve with several functions such as heart rate regulation, respiratory drive regulation, palate elevation, swallowing and talking. It is clinically assessed by checking for ability to swallow, elevate the palate and maintain a midline uvula.
Play Video + Quiz
|
 |
CN XI, also known as the accessory nerve. This is a motor nerve that is responsible for head-turning and shoulder shrugging via innervation of the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles.
Play Video + Quiz
|
 |
CN XII is also known as the hypoglossal nerve. This is a motor nerve that is responsible for tongue movement. It should be noted that unilateral damage will lead to tongue deviation TOWARD the affected side.
Play Video + Quiz
|
Back to PANCE Blueprint Neurology (7%)

 Osmosis
Osmosis















