The NCCPA™ PANCE and PANRE Dermatology Content Blueprint covers two disorders under Eczematous Eruptions
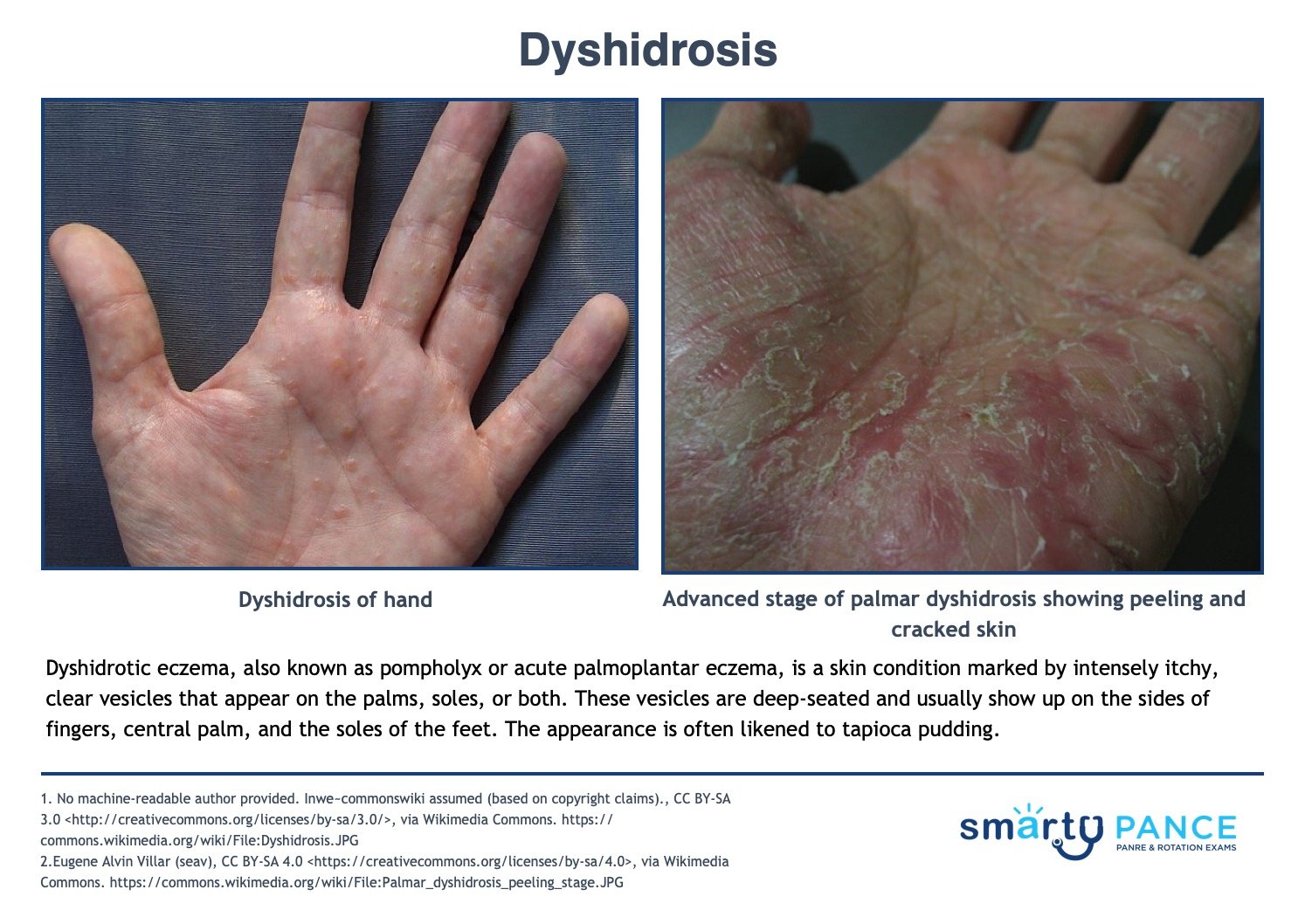
| Dyshidrosis | Patient will present as → a 13-year-old with a pruritic vesicular eruption comprised of clear, deep-seated vesicles without erythema erupting on the lateral aspects of fingers, the central palm, and plantar surfaces. Characterized by a pruritic vesicular eruption comprised of clear, deep-seated vesicles without erythema erupting on the lateral aspects of fingers, the central palm, and plantar surfaces.
Treatment: petroleum jelly, moisturizer, cold compresses, and topical steroids View more images of dyshidrosis |
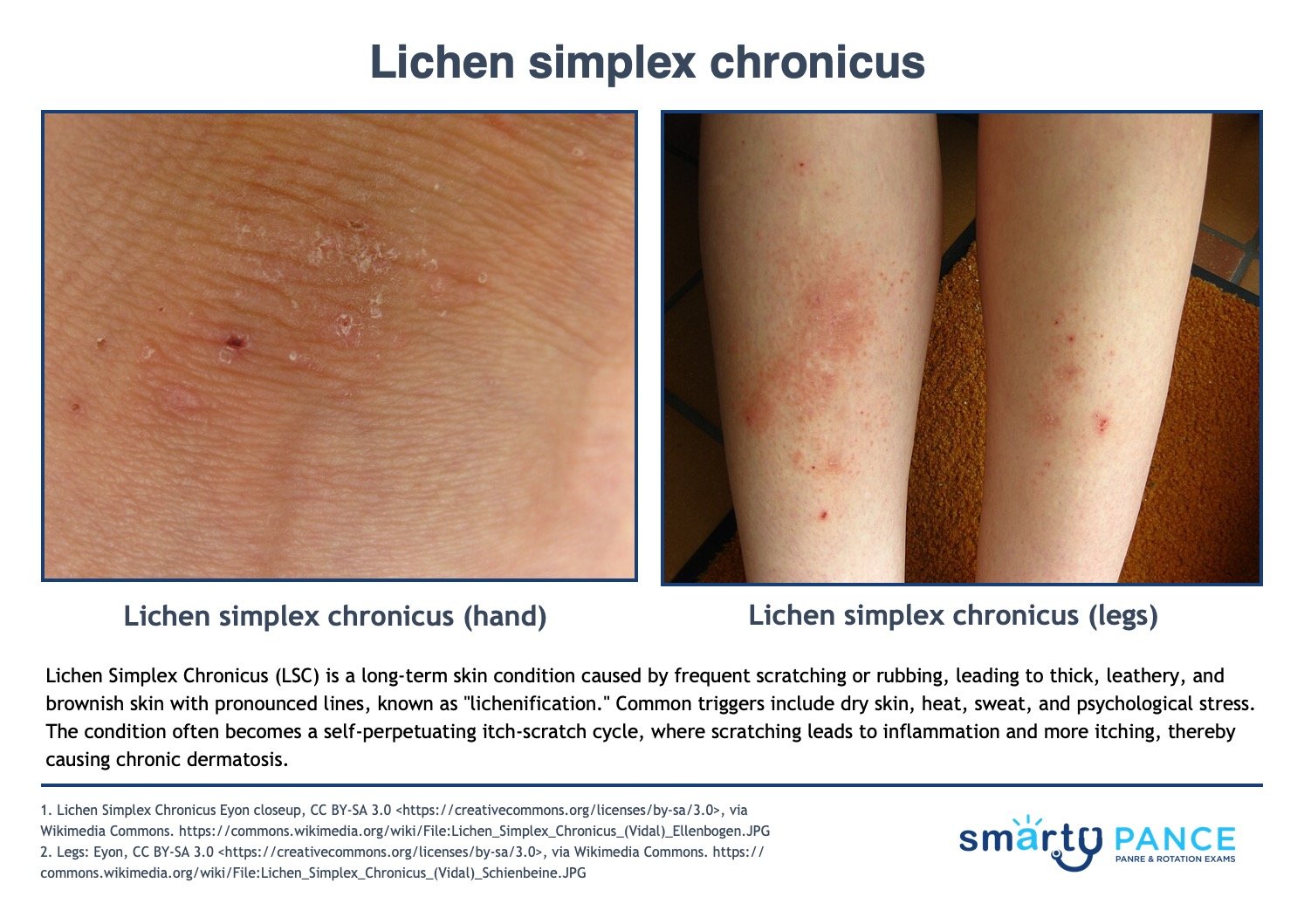
| Lichen simplex chronicus | Patient will present as → a 34-year-old male with a very itchy skin lesion on the front of the ankle of his left foot. The itching is paroxysmal and severe. On examination, there is a well-defined, thickened and hyperpigmented large plaque spreading across the front of the left ankle. Lichen simplex chronicus (LSC) is a chronic dermatitis resulting from chronic, repeated rubbing or scratching of the skin. Skin becomes thickened with accentuated lines (“lichenification”). The constant scratching causes thick, leathery, brownish skin
Treatment: Break the itch-scratch cycle (antihistamines, occlusive dressing) View more images of lichen simplex |