| DSM-5 Trauma and Stressor-Related Disorders
Items in bold are covered as part of the NCCPA PANCE/PANRE Psychiatry Blueprint and will be covered here. Additional topics may be covered in the PAEA EOR™ Psychiatry Topic List. |
|
|
|
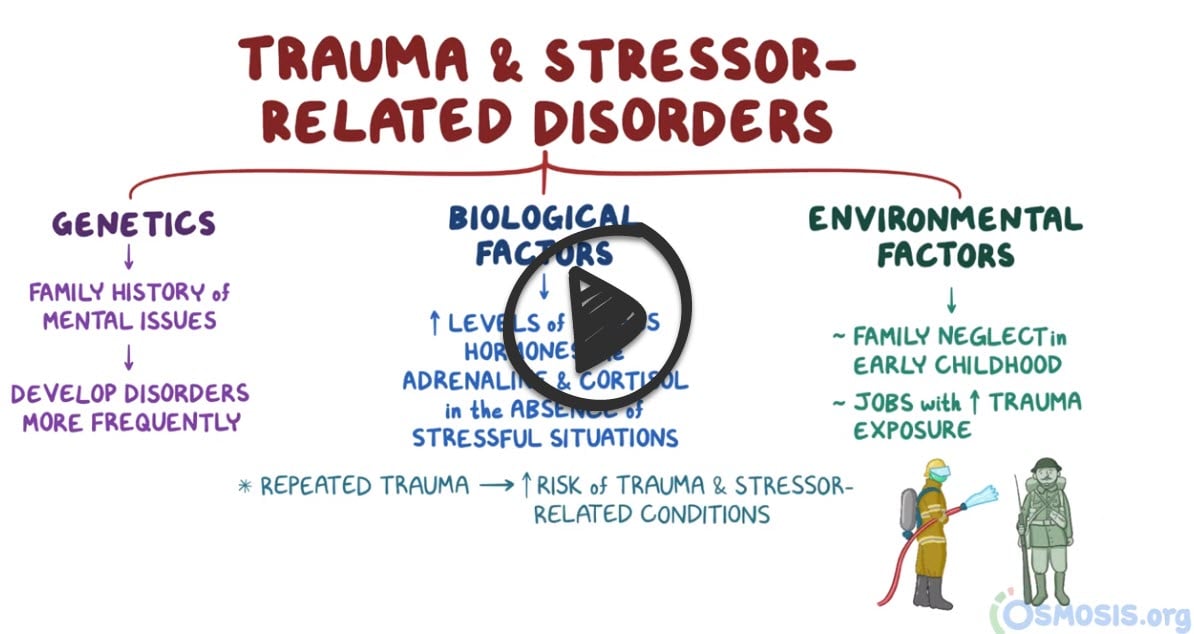
Trauma and stressor-related disorders
 |
|
| Adjustment disorders | Prolonged negative emotional reaction following a major life stressor (e.g., divorce, moving, new job) |
| Post-traumatic stress disorder | An anxiety disorder characterized by haunting memories, nightmares, social withdrawal, jumpy anxiety, and/or insomnia that lingers for four weeks or more after a traumatic experience |
| Acute stress disorder (ASD) | Acute stress disorder is a period of intrusive recollections that occurs after witnessing or experiencing a traumatic event. ASD occurs within one month of the traumatic event and lasts from three days up to one month |
| Adjustment disorders | Patient will present as → a 35-year-old woman who comes to your office with a 3-month history of feeling “depressed.” She feels “extremely distressed at work” and tells you that she is “burned out.” You discover that she moved into a managerial position at work 3 months ago and is having a great deal of difficulty (interpersonal conflict) with two of her employees. The patient has no history of psychiatric illness. She has no other symptoms. She is not taking any medications. The disproportionate response to a stressor that would normally be expected (ex. job loss, physical illness) which begin within 3 months of the stressor and end within 6 months after the stressor resolved
Stressors:
|
| Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) | Patient will present as → 33-year-old male presents with difficulty sleeping. The patient states that these symptoms began approximately 3 months ago when he lost his close friend while they were both in combat. He re-experiences this loss during the day and in his dreams. The patient reports anxiety and depression. The patient has experienced a traumatic event that causes an acute stress reaction. Once the symptoms persist past 1 month it is now considered post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) Treatment: SSRIs are considered first-line along with cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) |
| Acute stress disorder (ASD) | Patient will present as → a 25-year-old individual who was involved in a severe car accident three weeks ago. They report experiencing recurrent, involuntary, and intrusive distressing memories of the car accident. They have been feeling on edge, have difficulty sleeping, and actively avoid reminders of the accident. They also feel a sense of detachment from others and a loss of interest in activities they used to enjoy. Acute Stress Disorder (ASD) is characterized by the development of severe anxiety, dissociation, and other symptoms that occur within one month after exposure to an extreme traumatic stressor PTSD vs. ASD
Acute stress disorder is a period of intrusive recollections that occurs after witnessing or experiencing a traumatic event. The characteristics of this disorder differ from those of posttraumatic stress disorder in that ASD occurs within one month of the traumatic event and lasts from three days up to one month, whereas PTSD symptoms must last more than one month. Diagnosis is based on clinical criteria from the DSM-5, which requires the presence of nine or more symptoms from any of the five categories of intrusion, negative mood, dissociation, avoidance, and arousal, beginning or worsening after the traumatic event and lasting for three days to one month Treatment: Early intervention is crucial. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), specifically Trauma-focused cognitive-behavioral therapy (TF-CBT), is the most effective treatment for ASD |

