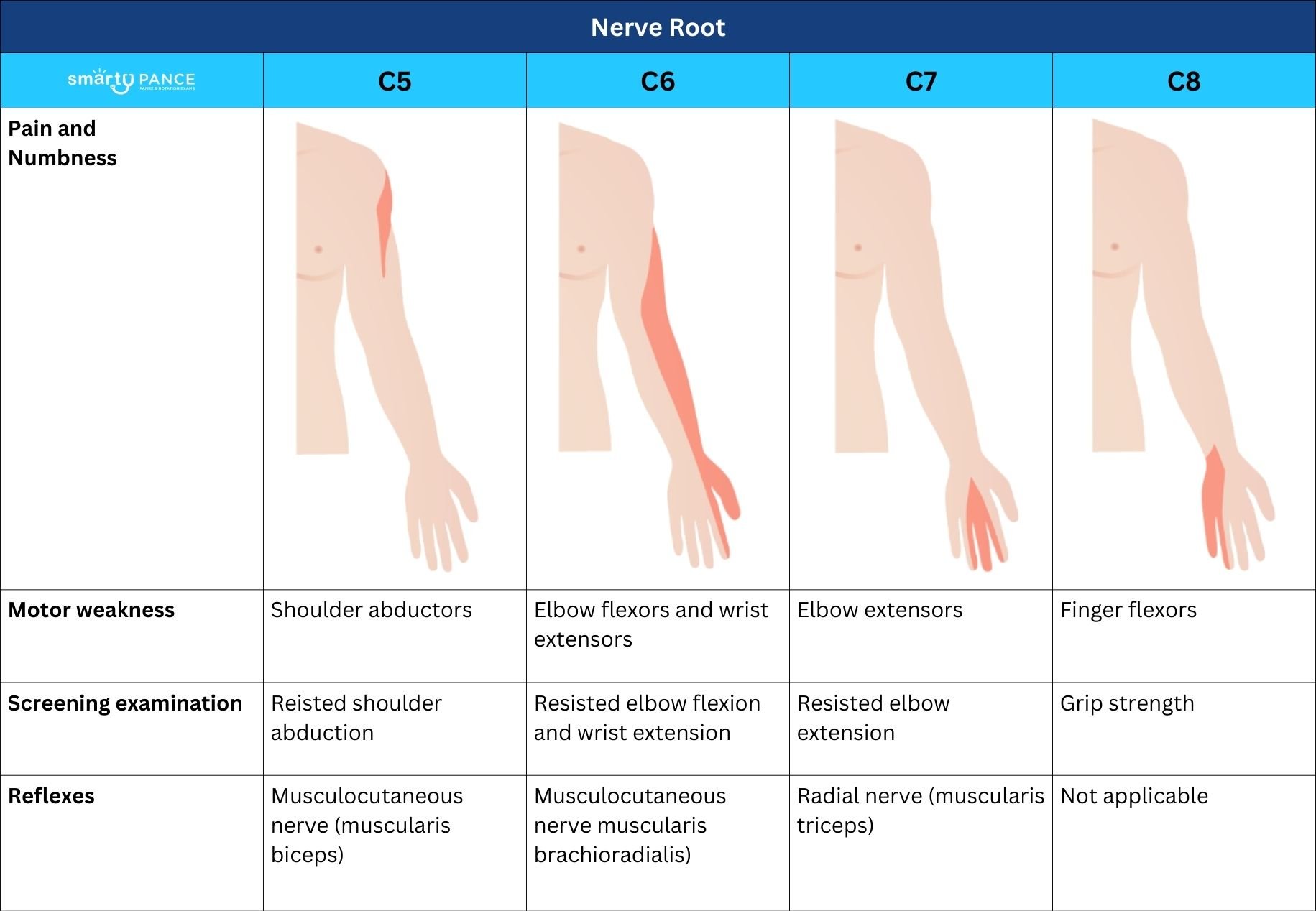
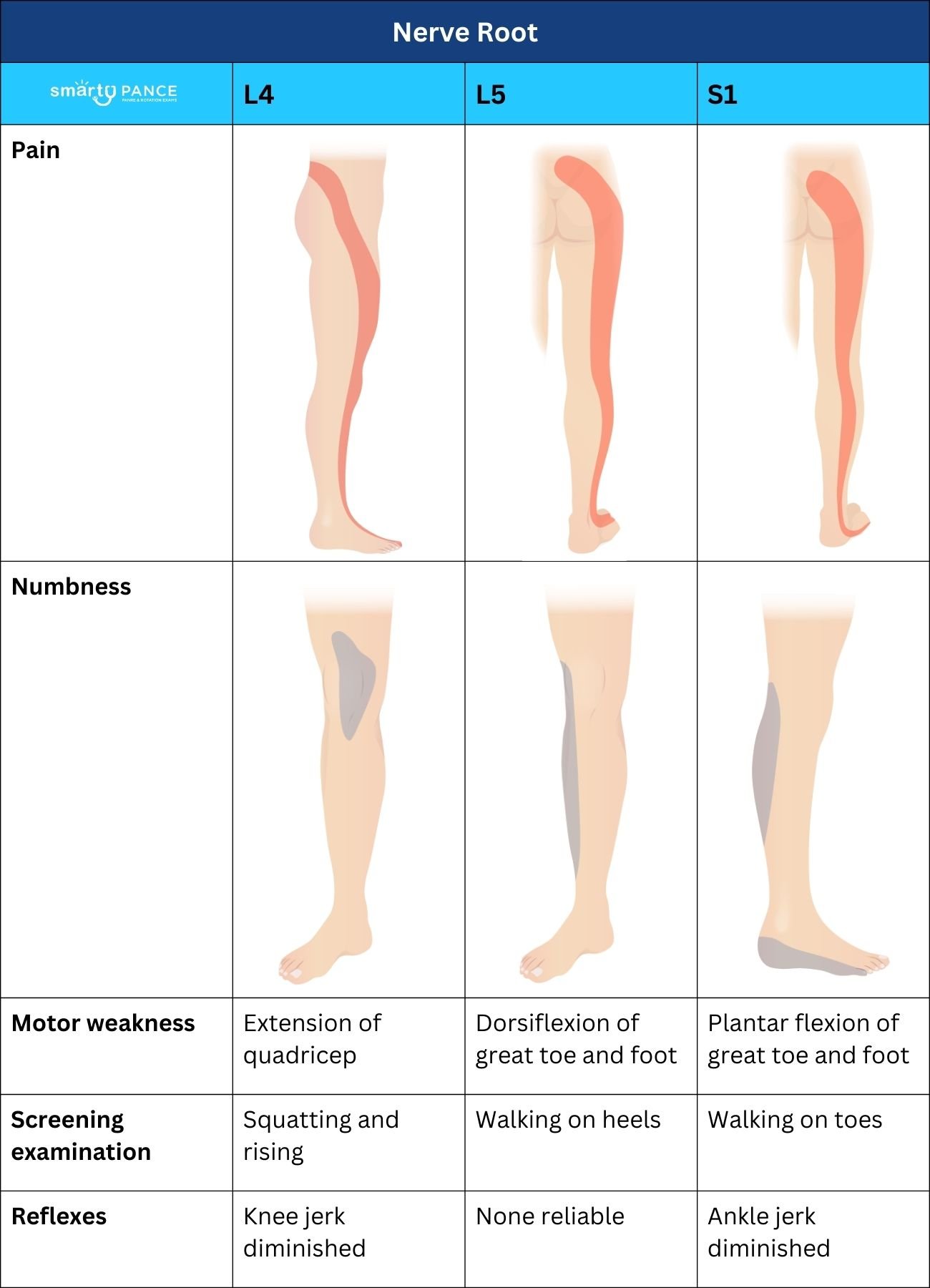
Symptoms will follow a dermatomal distribution
Cervical Spine
Cervical herniated diskPatient will present as → a 42-year-old female presents to the clinic with neck pain and numbness in her left arm, which has been worsening over the past month. She reports that the pain often radiates down to her left thumb and index finger. She recalls lifting heavy boxes several weeks ago, after which the symptoms started. She denies any recent trauma or falls. On examination, she has decreased range of motion in her neck due to pain, and there is tenderness over the cervical spine. Neurological examination reveals diminished sensation in the left C6 dermatome and weakness in the left biceps and wrist extensor muscles. Deep tendon reflexes are normal. A cervical spine MRI is ordered, which reveals a herniated disk at the C5-C6 level, compressing the left C6 nerve root. The patient is diagnosed with a cervical herniated disk. She is started on a course of oral steroids for inflammation, physical therapy focusing on neck strengthening and flexibility exercises, and advised to use heat and ice therapy for pain relief. She is also educated on proper body mechanics to prevent future injuries. A follow-up appointment is scheduled to assess her response to conservative management and to discuss further treatment options, including possible surgical intervention if her symptoms do not improve. |
Usually posterolateral at C5-C6, C6-C7
Cervical radiculopathy
|
| Disk space | Nerve root | Muscle | Reflex | Sensory |
| C4-5 | C5 | Deltoid, supraspinatus, infraspinatus | Biceps | Lateral arm |
| C5-C6 | C6 | Biceps, wrist extensors | Biceps, brachioradialis | Radial forearm, thumb, index finger |
| C6-7 | C7 | Triceps, wrist flexors, finger extensors | Triceps | Middle finger |
| C7-T11 | C8 | Finger flexors | None | Fourth and fifth fingers |
| T1-2 | T1 | Finger abductors | None | Ulnar forearm |
Lumbar Spine
Lumbar herniated diskTo watch this and all of Joe Gilboy PA-C's video lessons you must be a member. Members can log in here or join now. |
Patient will present as → a 35-year-old male construction worker presents to the clinic with low back pain radiating down his right leg, which has been worsening over the past two weeks. He describes the pain as a sharp, shooting sensation that extends to his right foot. He also reports numbness in the right lateral foot and big toe. The pain is exacerbated by sitting for long periods and improves slightly when walking. He denies any recent trauma but mentions that his job involves frequent heavy lifting. On examination, there is tenderness over the lower lumbar spine. A positive straight leg raise test is noted on the right side, exacerbating the leg pain at 40 degrees of elevation. Neurological examination reveals decreased sensation in the right L5 dermatome and weakness in the right extensor hallucis longus muscle. An MRI of the lumbar spine is performed, revealing a herniated disk at the L4-L5 level compressing the right L5 nerve root. The patient is diagnosed with a lumbar herniated disk. He is advised to avoid heavy lifting and twisting movements and is prescribed a course of oral NSAIDs for pain relief. Physical therapy focusing on core strengthening and lumbar stabilization exercises is initiated. He is also counseled on ergonomic adjustments at work to prevent further injury. A follow-up appointment is scheduled to monitor his progress and to consider additional interventions, such as epidural steroid injections or surgical options, if there is no improvement. |
| Diagnosis of Lumbar Disk Herniation
Pain in a dermatomal pattern - increases with coughing, straining, bending, and sitting
Clinical Manifestations
Diagnosis
Treatment
Look for "red-flag" symptoms:
Lumbar radiculopathy most commonly involves either the L5 or S1 root.
|
| L4 | L5 | S1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensory |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weakness |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflex Diminished |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Which of the following statements about lumbar disc disease is true?
Question 1 Explanation: Lumbar disc disease usually results from posterior herniation of the nucleus pulposus that impinges on the spinal cord. The most common site is the L5-S1 interspace, which affects the first sacral nerve root. Patients typically recall a precipitating event such as lifting a heavy object. Symptoms include severe back pain that radiates to the legs and is aggravated by coughing, sneezing, or forward flexion of the trunk. The condition is the most common cause of sciatica. Examination may show decreased sensation in a dermatome pattern, weakness, decreased reflexes, and a positive straight leg-raising test. In severe cases, patients may experience bowel or bladder incontinence. Radiographs and laboratory tests are generally unnecessary, except in the few patients in whom a serious cause is suspected on the basis of a comprehensive history and physical examination. Surgical evaluation is indicated in patients with worsening neurologic deficits or intractable pain that is resistant to conservative treatment. Bed rest should not be recommended for patients with nonspecific acute low back pain. Moderate quality evidence suggests that bed rest is less effective at reducing pain and improving function at 3 to 12 weeks than advice to stay active. Prolonged bed rest can also cause adverse effects such as joint stiffness, muscle wasting, loss of bone mineral density, pressure ulcers, and venous thromboembolism (VTE). The treatment plan should be reassessed in patients who do not return to normal activity within 4 to 6 weeks. Most mild cases can be treated with the limitation of aggravating activity, anti-inflammatory agents, and muscle relaxants.
A 26-year-old male was lifting a heavy object two weeks ago when he felt a sudden onset of low back pain. He describes pain in the low mid back at the belt line aggravated with movement. Radicular symptoms are noted in the left buttock down the leg to the dorsal aspect of the foot. He denies any urine or bowel complaints His examination demonstrates an inability to stand on his toes and a positive straight leg raise. Which of the following is most appropriate diagnostic study in this patient?
Question 2 Explanation: MRI is the diagnostic study of choice in a patient with suspected disc herniation.
What spinal nerve root is most likely affected in a patient with weak wrist extension, thumb and index finger paresthesias and diminished triceps reflex?
Question 3 Explanation: In contrast, cervical 5 would be associated with deltoid and biceps weakness and diminished biceps reflex while cervical 7 would result in triceps weakness and paresthesias in the middle finger and diminished brachioradialis reflex.
Review Topic: Herniated nucleus pulposus
A 65-year-old male presents with back pain two days after he was shoveling snow. The patient complains of pain in his low back that radiates into his buttocks, posterior thigh and calf, and the bottom of his foot. There is associated numbness of his lateral and plantar surface of his foot. Which of the following disc herniations is most likely to be affected?
Question 4 Explanation: The S1 nerve root impingement is most likely to occur from the herniation of the L5-S1 disc space. The S1 disc affects Achilles' reflex, the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles, and the abductor hallucis and gluteus maximus
muscles.
Review Topic: Herniated nucleus pulposus
There are 4 questions to complete.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Osmosis Osmosis |
|
 |
 A herniated disk also referred to as a herniated nucleus pulposus (HNP), is a structural deterioration of the intervertebral discs that provide shock absorption for the spine. Also known as “slipped disc,” damage to the disc enables the nucleus pulposus to seep through the torn or stretched annulus and bulge outward between the vertebrae. HNP frequently occurs between L5-S1 or the fourth and fifth lumbar vertebrae. Causes of HNP include natural degeneration, spine trauma, and spinal stenosis. Assessment findings include radiating pain, lower extremity weakness, and bowel/bladder incontinence. Diagnostic studies to determine structural defects and locate damaged sites include x-rays, myelogram, MRI, and CT scan. Interventions for HNP include wearing a brace to support the spine. Medications include NSAIDs, opioids, analgesics, epidural corticosteroids, muscle relaxants, and antidepressants. Invasive procedures indicated for patients with HNP include intradiscal electrothermal plasty (IDET), interspinous process decompression, laminectomy, discectomy, spinal fusion, and artificial disc replacement.
A herniated disk also referred to as a herniated nucleus pulposus (HNP), is a structural deterioration of the intervertebral discs that provide shock absorption for the spine. Also known as “slipped disc,” damage to the disc enables the nucleus pulposus to seep through the torn or stretched annulus and bulge outward between the vertebrae. HNP frequently occurs between L5-S1 or the fourth and fifth lumbar vertebrae. Causes of HNP include natural degeneration, spine trauma, and spinal stenosis. Assessment findings include radiating pain, lower extremity weakness, and bowel/bladder incontinence. Diagnostic studies to determine structural defects and locate damaged sites include x-rays, myelogram, MRI, and CT scan. Interventions for HNP include wearing a brace to support the spine. Medications include NSAIDs, opioids, analgesics, epidural corticosteroids, muscle relaxants, and antidepressants. Invasive procedures indicated for patients with HNP include intradiscal electrothermal plasty (IDET), interspinous process decompression, laminectomy, discectomy, spinal fusion, and artificial disc replacement.
| Herniated Nucleus Pulposus | Play Video + Quiz |
Dermatomes
The skin’s surface is divided into specific areas called dermatomes, which are mainly supplied by a single spinal. There are 8 cervical nerves (C1 being an exception with no dermatome), 12 thoracic nerves, 5 lumbar nerves, and 5 sacral nerves. Each of these nerves relays sensation (and pain) from a particular region of the skin to the brain.
| Dermatomes – Cervical | Play Video + Quiz |
| Dermatomes – Thoracic | Play Video + Quiz |
| Dermatomes – Lumbosacral | Play Video + Quiz |