The NCCPA™ Musculoskeletal Content Blueprint infectious diseases (PEARLS)
Acute and chronic osteomyelitis (ReelDx)
ReelDx Virtual Rounds (Osteomyelitis)
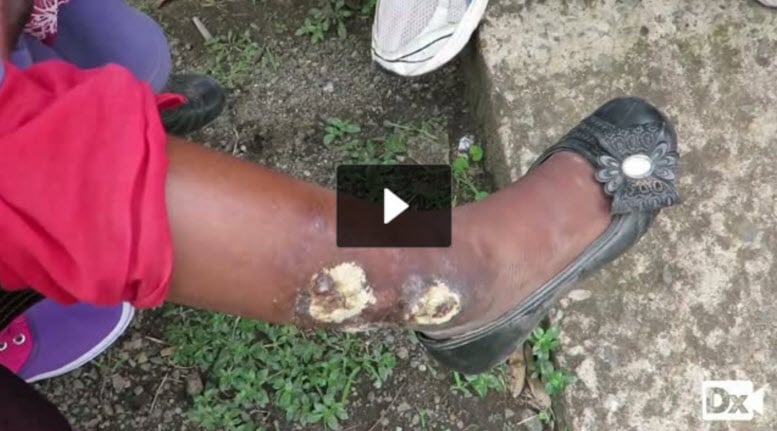
Osteomyelitis is an acute or chronic infection and inflammation of bone and bone marrow – it can occur as a result of hematogenous seeding, the contiguous spread of infection, or direct inoculation into intact bone (trauma/surgery)
- Fever, restriction of movement of the involved extremity, or refusal to bear weight
Acute osteomyelitis is most commonly seen in children with S. aureus as the most common organism
- Sickle cell disease - Salmonella is pathognomonic
Chronic osteomyelitis is most common in adults secondary to open injury of bone and surrounding soft tissue
- S. aureus is the most common organism (80%)
- Staph epidermidis in prosthetic joints
- Gram-negative pseudomonas in IVDU
- Pasteurella is seen in cases caused by cat/dog bites
- Mycobacterium TB is seen in vertebral involvement (Potts DZ)
DX: bone aspiration = gold standard
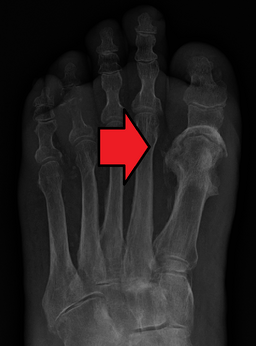
- X-ray triad: demineralization, periosteal reaction, bone destruction (lags behind symptoms 7-10 days); MRI shows changes before X-ray
- Labs: CRP elevated for 4-6 weeks, WBC and ESR high in most cases
- Definitive diagnosis = blood culture or by needle aspiration/bone biopsy
TX: Treat initially with a broad-spectrum antibiotic regimen. Base treatment on the results of cultured bone tissue to obtain the best outcome.
- Duration of therapy: 4–6 weeks for acute osteomyelitis and generally >8 weeks for chronic osteomyelitis or MRSA infection
- Newborn (<4 months) - Group B Strep - nafcillin or oxacillin + 3rd gen cephalosporin
- > 4 months - S. aureus - MSSA - Nafcillin + Ancef. MRSA - Vancomycin or Linezolid
- Sickle cell - Salmonella - 3rd gen cephalosporin or FQ (Cipro)
- Puncture wound - Pseudomonas - Cipro or levofloxacin
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate
ReelDx Virtual Rounds (Septic arthritis)
Septic arthritis is a direct bacterial invasion of joint space - a most dangerous form of acute arthritis. It is a medical emergency!
- A single, swollen, warm, painful joint that is tender to palpation + constitutional symptoms (fever, sweats, myalgia, malaise, pain)
- MC = knee and hip
- Caused by: hematogenous spread, direct inoculation, contiguous spread
- S. aureus is most common (40-50%); N. gonorrhea in sexually active young adults, streptococci; pseudomonas in IVDU
DX: Diagnose with arthrocentesis: joint fluid aspirate for definitive diagnosis (WBC > 50,000 primarily PMNs)
- WBC > 1000 is positive in pt with prosthetic joints
TX: Treatment is based on gram stain- 2-4 week course of antibiotics + arthrotomy with joint drainage
- Staph aureus = Vanco/nafcillin (Vanco or Clindamycin if PCN allergic)
- Gonorrhea = ceftriaxone
- IVDU = Cipro/Levaquin
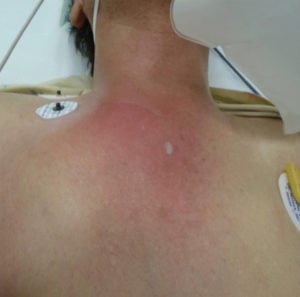
Image: 'Sternoclavicular joint septic arthritis with chest wall abscess in a healthy adult: a case report' by Tanaka Y, Kato H, Shirai K, Nakajima Y, Yamada N, Okada H, Yoshida T, Toyoda I, Ogura S. License: CC BY 4.0
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate