The NCCPA™ Musculoskeletal Content Blueprint upper extremity disorders (PEARLS) includes a condensed summary of the following:
Upper extremity disorders
Shoulder Fractures/dislocations
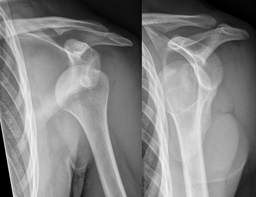
Shoulder FracturesPatient will present as → a 30-year-old male arrives at the emergency room after a motor vehicle accident. Upon arrival, he has difficulty breathing and reports shoulder pain. On physical exam, he has decreased breath sounds on the right side and significant tenderness of his right shoulder. There is overlying ecchymosis, swelling, and erythema over his right scapula and limited range of motion.
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate Shoulder DislocationPatient will present as → an 80-year-old woman arrives at the emergency room with severe right shoulder pain and immobility. She fell down the steps outside her house and landed on her right side two hours prior to presentation. On exam, her right arm is abducted and externally rotated. She has decreased sensation to touch over the lateral aspect of her right shoulder. Radiographs demonstrate an anterior shoulder dislocation. Mode of injury: fall on an outstretched arm (full abduction and extension)
Anterior dislocation is the most common - 95% (Remember ARM = ANTERIOR)
Presentation: In anterior dislocation, the arm is abducted and externally rotated
Radiographs are indicated in any patient in whom a shoulder dislocation is suspected
Associated conditions
Treatment:
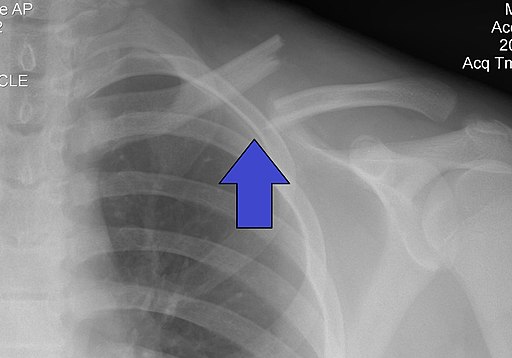
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate Clavicle FracturesPatient will present as → a 23-year-old woman arrives at the emergency room after a biking accident. She reports acute pain after falling on her shoulder. On physical exam, there is swelling, erythema, and tenderness on the anterior aspect of her right shoulder. No tenting of the skin is noted. Distal pulses are intact, and there is no motor or sensory deficits. She is sent for further imaging. Method of injury: most commonly from direct fall on the shoulder (adults and children)
Classified based on location (medial third, middle third, and lateral third)
Physical exam:
Treatment:
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate |
|
Soft tissue injuries of the shoulder
AC Joint SeparationPatient will present as → a 25-year-old male, a recreational soccer player, presents with acute pain in his right shoulder following a fall onto his outstretched hand during a soccer match two days ago. He reports immediate pain and swelling in the shoulder, with difficulty lifting his arm due to pain. He has not experienced any numbness or tingling in the arm. On physical examination, there is noticeable swelling and tenderness over the acromioclavicular (AC) joint. There is a visible step-off at the AC joint, suggestive of a possible separation. Pain is exacerbated with cross-body adduction and during the O’Brien’s test. Range of motion is limited, especially with abduction and forward elevation due to pain. Neurovascular examination of the upper extremity is normal. Radiographic imaging of the shoulder reveals widening of the AC joint space. The patient is diagnosed with a Grade II AC joint separation. Management includes a brief period of immobilization with a sling to allow for pain control and healing, followed by early range-of-motion exercises as tolerated. Patient will present after → fall directly to the shoulder or outstretched hand
DX: To appropriately grade acromioclavicular separations, an x-ray is taken with the patient holding a weight to assess the level of injury to the joint. TX: Conservative management is possible for mild to moderate injuries because they can be managed with a sling and analgesia
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate Biceps TendonitisPatient will present as → a 33-year-old man who complains of left anterior shoulder pain for 4 weeks. The pain is made worse with overhead activities. On examination, you note maximal pain in the shoulder with palpation between the greater and lesser tubercle. Pain in the shoulder is exacerbated when the arm is held at the side, elbow flexed to 90 degrees, and the patient is asked to supinate and flex the forearm against your resistance.
DX: X-ray to r/o fracture and MRI to r/o rotator cuff tear Yergason’s test:
Speed's test:
TX: Treat with NSAIDs, PT strengthening, and steroid injections
A "Popeye" deformity - indicates a biceps tendon rupture References: Merck Manual · UpToDate Rotator cuff tendinopathy/tearPatient will present as → a 69-year-old male with right shoulder pain for the past several months. He reports that he cannot reach above his head without severe pain. As a retired carpenter, he reports that this has significantly impacted his quality of life. Additionally, he is unable to lie on his left side at night due to shoulder pain. On physical exam, there is focal tenderness over the left anterolateral shoulder. Radiography reveals reduced space between the acromion and humeral head.
DX: Radiography for all patients as initial imaging - loss of subacromial space due to upward migration of humeral head
TX: Treat with physical therapy (for all patients), NSAIDs, steroid injections, and surgical repair for patients with complete tears or for those who fail 3-6 months of conservative management Four Muscles of the rotator cuff: Rotator cuff inflammation/impingement:
Supraspinatus tear or inflammation:
Subscapularis tear or inflammation:
Teres minor/infraspinatus tear or inflammation:
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate Adhesive Capsulitis - AKA frozen shoulderPatient will present as → a 52-year-old female presents with a six-month history of progressive shoulder pain and stiffness. She reports that the pain is constant, worsens at night, and is aggravated by movements, especially when reaching overhead or behind her back. She also notes a significant reduction in her shoulder’s range of motion. The patient mentions a history of type 2 diabetes and a sedentary lifestyle. On examination, there is noticeable restriction in both active and passive range of motion of her left shoulder, particularly in external rotation and abduction. There is no apparent joint instability or muscle weakness, and the neurovascular examination is normal. No history of trauma or prior shoulder pathology is reported. Based on these findings, a diagnosis of adhesive capsulitis, also known as frozen shoulder, is considered. The patient is advised to begin a regimen of physical therapy focusing on shoulder mobilization exercises and stretching. She is also prescribed nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain management. The importance of diabetes control and regular follow-up is emphasized to monitor her progress and modify the treatment plan as necessary. Frozen shoulder, also called adhesive capsulitis, is a painful condition in which the movement of the shoulder becomes limited. A frozen shoulder occurs when the strong connective tissue surrounding the shoulder joint (called the shoulder joint capsule) becomes thick, stiff, and inflamed
DX: Frozen shoulder is a clinical diagnosis made on the basis of medical history and physical examination
TX: NSAIDs, physical therapy, and intra-articular steroid injections
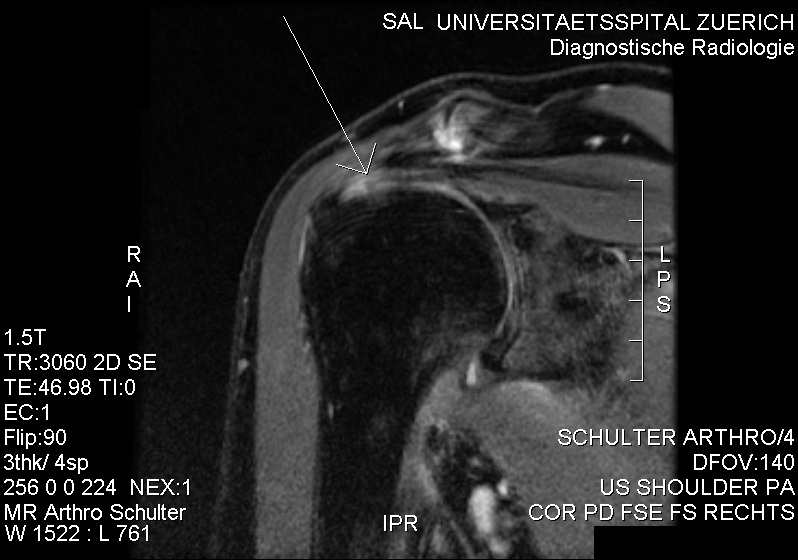 MRI with suspicion of frozen shoulder due to minor intraarticularly injectable contrast agent. No contrast agent at the bursa subacromialis and subdeltoidea. References: UpToDate ImpingementPatient will present as → a 70-year-old male with an insidious onset of left shoulder pain that is exacerbated by overhead activities and while lifting objects away from his body. He is a retired mechanic of 35 years. The patient reports that over the last several months, he has been having difficulty sleeping because of the pain. On physical examination, there is notable tenderness over the left anterolateral shoulder, and passive forward flexion >90° causes severe pain. An x-ray reveals proximal migration of the humeral head and calcification of the coracoacromial ligament. Based on these findings, a diagnosis of shoulder impingement syndrome is considered. Conservative management is initiated with NSAIDs for pain relief, rest, and modification of activities to avoid overhead motions. The patient is referred to physical therapy for rotator cuff and scapular stabilizer strengthening exercises, and postural correction. Instructions are given on the importance of gradual return to sports and the potential need for further intervention, such as a subacromial injection or, rarely, surgical decompression, if symptoms do not improve with conservative management. A follow-up appointment is scheduled to assess progress and response to treatment. Subacromial impingement syndrome (SAIS) refers to the inflammation and irritation of the rotator cuff tendons as they pass through the subacromial space
DX: X-ray may show tendonc calcification or a subacromial spur
TX: Treatment involves rest, ice, activity modification, NSAIDs, and corticosteroid injections
References: UpToDate Subacromial BursitisPatient will present as → a 45-year-old male, an avid tennis player, presents with a three-month history of right shoulder pain. He describes the pain as a constant, dull ache, worsening with overhead activities and at night, especially when lying on the affected side. He denies any history of trauma but mentions that his pain began after intensifying his tennis training. On physical examination, there is tenderness to palpation over the lateral aspect of the right shoulder, and pain is exacerbated by abduction and internal rotation of the arm. The Neer and Hawkins tests elicit pain, while the rotator cuff strength remains intact. There is no evidence of joint instability or neurological deficits. Based on the clinical presentation, a diagnosis of subacromial bursitis is suspected. Subacromial bursitis is a common etiology of shoulder pain. It results from inflammation of the bursa, a sac of tissue present under the acromion process of the shoulder
DX: Diagnosis is by history and physical examination, including provocative maneuvers
TX: Includes prevention of the precipitating factors, rest, and NSAIDs. Cortisone injections can be helpful 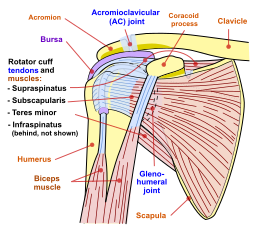 The subacromial bursa sits in a tight space under the acromion process of the shoulder, making it susceptible to overuse injury References: Merck Manual · UpToDate Glenohumeral joint OsteoarthritisPatient will present as → a 67-year-old female with a history of type 2 diabetes and hypertension presents complaining of progressive right shoulder pain over the past year. She describes the pain as a deep, aching sensation, worsening with movement and at night, leading to disturbed sleep. She notes decreased range of motion and difficulty in performing daily activities, such as reaching overhead and behind her back. She denies any history of injury to the shoulder. On examination, there is noticeable crepitus with passive movement of the right shoulder, tenderness to palpation over the glenohumeral joint, and a limited range of motion, particularly in external rotation and abduction. There are no signs of acute inflammation or systemic illness. Radiographic imaging of the shoulder reveals joint space narrowing, osteophyte formation, and subchondral sclerosis, consistent with osteoarthritis. Based on these findings, a diagnosis of primary glenohumeral joint osteoarthritis is made. Degenerative shoulder (glenohumeral) osteoarthritis is characterized by degeneration of articular cartilage and subchondral bone with narrowing of the glenohumeral joint
DX: Radiographs demonstrate joint space narrowing, subchondral sclerosis, and osteophytes at the inferior aspect of the humeral head
TX: NSAIDs, physical therapy, corticosteroid injections
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate |
Disorders of the Forearm, Wrist and Hand
| Fractures and dislocations of the forearm, wrist and hand | ||
Greenstick Fractures
Torus (Buckle) Fractures
|
|
|
Upper Arm |
||
| Humerus Fractures
Patient presents as → a 60-year-old female with a history of osteoporosis presents with severe left arm pain and swelling following a fall at home. She reports losing her balance and landing directly on her left shoulder. On examination, her left arm appears shortened and externally rotated, with notable swelling and tenderness around the mid-shaft of the humerus. X-rays reveal a mid-shaft, transverse fracture of the humerus. Given her osteoporosis, she is referred to an orthopedic surgeon for evaluation of surgical versus conservative management. In the interim, her arm is immobilized in a sling, and she is prescribed analgesics for pain management. She is also advised to follow up with her primary care provider to address her osteoporosis to prevent future fractures. |
||
A humerus fracture is a break in the large bone of the upper arm. There are several types of humerus fractures, depending on the location of the break - they can occur proximally, at the shaft, or distally (less common)
DX: Plain x-rays
TX: Treatment depends on the location of the fracture
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate |
||
Elbow Fractures and Dislocations |
||
| Supracondylar fracture
Patient presents as → a 7-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department after falling off the monkey bars at a playground. He complains of severe pain in his left elbow and is holding his arm close to his body. On examination, there is noticeable swelling and deformity around the elbow, and he is unable to move the elbow without significant pain. X-rays of the elbow reveal a displaced supracondylar fracture. Due to the risk of neurovascular compromise, the orthopedic team is immediately consulted. The child is given pain relief, and his arm is immobilized. He undergoes closed reduction and pinning of the fracture under anesthesia. Postoperatively, he is monitored for signs of compartment syndrome and nerve injury. |
||
A supracondylar fracture is an injury to the distal humerus at its narrowest point, just above the elbow
DX: Diagnosis is made via X-ray showing elbow effusion, an anterior fat pad sign, and a posterior fat pad sign (sail sign) seen as dark area on either side of the bone
TX: Long arm posterior splint followed by long arm casting - open reduction with internal fixation for all displaced fractures. References: Merck Manual · UpToDate |
||
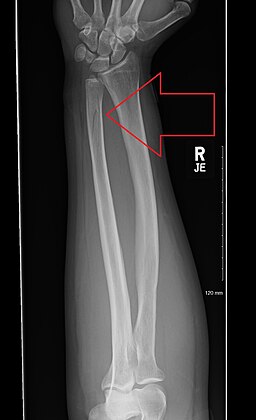
| Radial Head Fracture
Patient presents as → a 32-year-old female presents to the clinic after slipping on ice and landing on her outstretched right hand. She complains of pain and swelling in her right elbow, particularly with rotation of the forearm. Physical examination reveals tenderness over the lateral aspect of the elbow, limited range of motion, especially during pronation and supination, and pain exacerbated by forearm rotation. There is no apparent deformity or open wound. Radiographic imaging of the elbow shows a fracture of the radial head. The patient is managed with a long-arm splint to immobilize the elbow and referred for orthopedic evaluation. |
||
A radial head fracture is a fracture in the section of the radius near the elbow. This injury is the most common elbow joint fracture in adults. The fracture is caused by falling onto the hand with the arm straight or slightly bent.
DX: It may be difficult to see on X-rays!
TX: Treat with sling, long arm splint at 90 degrees, open reduction, and internal fixation
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate |
||
| Radial head subluxation (Nursemaid's elbow)
Patient presents as → a 4-year-old girl is brought to the clinic by her parents with a complaint of left arm pain. The parents report that the pain started suddenly after the child was lifted by her left arm while playing. The child refuses to use her left arm and holds it in a slightly bent position close to her body. On examination, there is no visible swelling or deformity, but the child shows discomfort when her left elbow is touched or moved. No bruising or skin changes are observed. A gentle manipulation, known as a reduction maneuver, is performed, resulting in an audible click and immediate relief of pain. The child starts using her arm soon after the procedure. |
||
Nursemaid's elbow occurs when the radius slips out of place from where it normally attaches to the elbow joint. It is a common condition in children younger than 4 years of age. It is also called pulled elbow, slipped elbow, or toddler's elbow.
DX: Physical examination - Plain radiographs are rarely indicated (carefully palpate arm and wrist to r/o fracture prior to treatment) TX: The supination-flexion technique is the classic method of reducing a subluxed radial head. It has a success rate of 80-92%
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate |
||
Forearm fractures |
||
|
13-year-old with severe pain in left mid-forearm after falling awkwardly on an outstretched left arm, unable to move the left arm without significant pain (watch video) |
||
Ulnar forearm fractures |
||
| Nightstick Fracture (isolated fracture of the ulna)
Patient presents as → a 26-year-old male presents to the emergency room after a fall while playing basketball. He reports landing on his outstretched arm and experiencing immediate pain in his forearm. He denies any other injuries. On examination, the patient exhibits tenderness, swelling, and bruising along the ulnar side of his forearm. He has limited range of motion in his wrist and elbow due to pain. The radial pulse is intact, and there are no sensory or motor deficits. X-rays of the forearm reveal a transverse fracture of the ulna shaft, consistent with a nightstick fracture. There is no displacement or involvement of the radial bone. The patient’s arm is immobilized in a long arm splint, and he is referred to an orthopedic specialist for further management. |
||
Nightstick Fractures are isolated fractures of the ulna, typically transverse and located in the mid-diaphysis and usually resulting from a direct blow
DX: Radial and ulnar shaft fractures are generally diagnosed with anteroposterior and lateral X-rays
TX: For isolated ulnar shaft fractures, closed reduction and splinting with outpatient orthopedic follow-up
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate |
||
| Monteggia Fracture (proximal ulnar shaft fracture with radial head dislocation)
Patient presents as → a 34-year-old female arrives at the emergency department following a high-impact car accident. She complains of severe pain in her left forearm and difficulty in moving her left hand. Examination reveals significant swelling, deformity, and tenderness along the proximal forearm. She also has a limited range of motion in her elbow and wrist. Sensation and circulation in her hand are intact. Radiographic evaluation shows a fracture of the proximal third of the ulna with anterior dislocation of the radial head, consistent with a Monteggia fracture. The patient is given pain medication, and her arm is temporarily immobilized. She is urgently referred to an orthopedic surgeon for definitive management, likely requiring open reduction and internal fixation of the ulnar fracture. |
||
A Monteggia fracture is a traumatic injury to the elbow and forearm characterized by the presence of two bony injuries: proximal ulnar shaft fracture and radial head dislocation
DX: Anteroposterior and lateral x-rays. If a fracture is suspected, the elbow and wrist should also be examined and, when appropriate, x-rayed TX: All Monteggia fractures are unstable and require surgical treatment - Treat with open reduction and internal fixation  Monteggia fracture in a child. In addition to the easily recognizable fracture of the ulna, there is a dislocation of the radius to the lateral volar side. The not-yet-ossified radial head (blue arrow) should be exactly opposite the bone core of the capitellum humeri (red arrow). References: Merck Manual · UpToDate |
||
Radial forearm fractures |
||
| Galeazzi Fracture (distal radial shaft fractures with dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint)
Patient presents as → a 23-year-old male with severe left arm pain. One hour prior to presentation, he was climbing a tree to retrieve a kite and fell 6 feet onto the ground. He landed on his pronated outstretched left arm and developed immediate-onset pain and swelling. On exam, he is tender to palpation with a notable deformity characterized by radial wrist angulation. The distal ulna is palpable. Radiographs demonstrate a fracture of the distal radial diaphysis with associated dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint. |
||
Galeazzi fractures are distal radial shaft fractures + dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint
DX: Anteroposterior and lateral x-rays. If a fracture is suspected, the elbow and wrist should also be examined and, when appropriate, x-rayed TX: Unstable fracture needs ORIF, long arm splint  Galeazzi fracture in the AP and lateral X-ray. In the side view, you can clearly see the dorsal dislocation of the distal ulna (joint lines traced in blue). "GRUesome MURder => G: Galeazzi R: radius fracture U: ulna dislocation. M: Monteggia U: ulna fracture R: radial head dislocation" References: Merck Manual · UpToDate |
||
Wrist Fractures |
||
|
15-year-old with "fall to an outstretched hand" now with acute onset wrist swelling. |
||
| Colles Fracture - Distal Radial Fracture (posterior angulation "dinner fork")
Patient presents as → a 65-year-old female presents to the clinic after falling onto her outstretched right hand during a walk. She reports immediate onset of pain, swelling, and deformity around her wrist. Physical examination reveals tenderness over the distal radius, prominent swelling, and a “dinner fork” deformity, suggesting a Colles fracture. She denies any numbness or tingling in her fingers. Radiographic imaging by lateral X-ray confirms a fracture of the distal radius with dorsal angulation and displacement. The patient is managed with closed reduction under local anesthesia, followed by immobilization in a plaster cast. |
||
"Colles fractures" refer to dorsally (upward) angulated extra-articular distal radius fractures
DX: Need lateral X-ray to make the correct diagnosis; may cause extensor pollicis longus tendon rupture. TX: Treat with a volar splint or sugar tong splint/cast at 15 to 30° of wrist extension  An X-ray image of a fractured radius showing the characteristic Colle's fracture with displacement and angulation of the distal end of the radius. References: Merck Manual · UpToDate |
||
| Smith Fracture - Distal Radial Fracture (anterior angulation "garden spade")
Patient presents as → a 30-year-old male presents to the emergency department after falling on a flexed wrist while skateboarding. He complains of severe pain and deformity in his left wrist. On examination, the wrist appears swollen and tender, with an abnormal volar angulation. He reports no previous injuries to the area and has no significant medical history. X-rays reveal a fracture of the distal radius with volar displacement, consistent with a Smith fracture. The patient’s neurovascular status is intact, with no evidence of median nerve compression. He undergoes closed reduction and casting in the emergency department. |
||
A Smith fracture, sometimes referred to as a reverse Colles fracture, is an extra-articular metaphysical fracture of the radius with volar (downward) angulation and displacement of the radius - garden spade deformity
DX: Need lateral X-ray to make the correct diagnosis; may cause extensor pollicis longus tendon rupture. TX: Treat with a volar splint or sugar tong splint/cast at 15 to 30° of wrist extension References: Merck Manual · UpToDate |
||
| Scaphoid (Navicular) Fracture (snuffbox tenderness)
Patient presents as → a 25-year-old male skateboarder presents to the clinic with wrist pain following a fall on an outstretched hand. He complains of significant tenderness in the anatomical snuffbox and reports the pain has persisted for two days. The patient denies any previous wrist injuries or chronic conditions. Physical examination reveals swelling and pronounced tenderness in the snuffbox region. There is no apparent deformity, but wrist motion, especially extension and radial deviation, exacerbates the pain. Initial X-rays of the wrist are inconclusive. Given the high clinical suspicion, a scaphoid fracture is considered, and the patient is immobilized in a thumb spica splint. MRI or bone scan is recommended to confirm the diagnosis due to the initial negative X-rays. The patient is advised to avoid activities that could worsen the injury and is prescribed analgesics for pain management. He is scheduled for a follow-up appointment in one week to review advanced imaging results and to discuss further treatment options, which may include prolonged immobilization or surgery, depending on the fracture’s characteristics. Additionally, the patient is educated on the importance of proper healing and the risks associated with scaphoid fractures, including non-union and avascular necrosis. |
||
A scaphoid (navicular) fracture is a break in one of the small bones of the wrist
DX: Initially, plain X-rays (anteroposterior, lateral, and oblique views) are taken but are often normal -> The fracture may not be evident for up to 2 weeks
DX: Treat with 6-8 weeks of casting with a thumb spica splint - Return to sport in ~ 11 weeks
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate |
||
Hand Fractures |
||

13-year-old with pain and edema over the 5th metacarpal |
||
| Boxer's Fracture
Patient presents as → a 30-year-old male presents to the emergency department with pain and swelling in his right hand after punching a wall during an argument. He reports immediate pain post-injury and difficulty moving his fingers. Physical examination reveals swelling and tenderness over the fifth metacarpal with a noticeable deformity and bruising. The patient’s skin is intact, and there is no evidence of neurovascular compromise. Finger range of motion is limited due to pain. X-ray of the hand confirms a comminuted fracture of the neck of the fifth metacarpal, consistent with a boxer’s fracture. The patient is provided with pain relief and the fractured hand is immobilized in an ulnar gutter splint. |
||
A boxer's fracture is a break in the neck of the 5th metacarpal bone of the hand
DX: X-rays - anteroposterior, lateral, and oblique views are diagnostic
TX: Treat boxer's fractures with an ulnar gutter splint with joints at least 60 degrees flexion References: Merck Manual · UpToDate |
||
| Base of the thumb metacarpal fractures | ||
| Bennett fracture (intra-articular)
Patient presents as → a 25-year-old male, right-hand dominant, presents to the clinic with severe pain and swelling in his right thumb after falling onto his outstretched hand while skateboarding. He reports immediate pain and difficulty in thumb movement since the accident. Physical examination reveals tenderness at the base of the thumb, significant swelling, and limited range of motion due to pain. There’s no skin laceration or sign of open injury, but slight bruising is noted. Neurovascular examination of the hand is intact. Radiographic imaging of the hand shows an intra-articular fracture at the base of the first metacarpal with slight displacement, characteristic of a Bennett fracture. The patient’s hand is immobilized in a thumb spica splint, and he is given pain medication and ice application instructions to manage swelling. |
||
A Bennett fracture is an intra-articular fracture through the base of the 1st metacarpal (thumb) with a large distal fragment dislocated radially and dorsally by the abductor pollicis longus muscle
DX: X-ray - In addition to lateral and oblique views, a true anteroposterior AP (Robert view) should be taken TX: This is an unstable fracture that requires open reduction and internal fixation  Bennett fracture is an intra-articular fracture through the base of the 1st metacarpal (thumb) with a large distal fragment dislocated radially and dorsally(red arrow) by the abductor pollicis longus muscle References: UpToDate |
||
| Rolando fracture (intra-articular comminuted)
Patient presents as → a 30-year-old female presents with severe pain and swelling in her left thumb following a fall while hiking. She recalls landing directly on her thumb and felt immediate pain. On examination, her thumb base is tender, swollen, and shows a limited range of motion due to pain. There is no open wound, but bruising is evident. Neurovascular assessment of her hand is normal. X-rays reveal a comminuted intra-articular fracture at the base of the first metacarpal, consistent with a Rolando fracture. Given the complexity of the fracture, she is advised for immediate orthopedic referral. The thumb is temporarily immobilized in a thumb spica splint, and she is prescribed analgesics for pain management. |
||
The Rolando fracture is a comminuted intra-articular fracture of the base of the 1st metacarpal characterized by intra-articular comminution
DX: X-ray - In addition to lateral and oblique views, a true anteroposterior AP (Robert view) should be taken TX: This is an unstable fracture that requires open reduction and internal fixation References: UpToDate |
||
| Soft tissue injuries of the forearm, wrist, and hand (ReelDx) | ||
| Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer's/Pitcher's elbow)
Patient presents as → a 42-year-old male, an avid golfer, presents with a 3-month history of progressive pain on the inner side of his right elbow. He reports that the pain is exacerbated while playing golf and when lifting objects with a palm-down position. On examination, there is tenderness over the medial epicondyle, and pain is reproduced with resisted wrist flexion and pronation. There is no apparent swelling, and elbow range of motion is preserved. Neurovascular assessment of the arm is unremarkable. The patient denies any recent trauma or systemic symptoms. The clinical presentation is consistent with medial epicondylitis, commonly known as “golfer’s elbow.” |
|
An overuse syndrome that results in pain in the myotendinous junction between the wrist flexors and medial epicondyle, also known as "golfer's elbow"
DX: Provocative testing - Pain is elicited with resisted wrist flexion while the elbow is fully extended TX: Treat with activity modification, physical therapy, corticosteroid injections - orthopedic surgery in patients who failed physical therapy for 4-6 months Medical illustration of medial epicondylitis, also known as golfer's elbow, baseball elbow, suitcase elbow, or forehand tennis elbow. It's characterized by pain from the elbow to the wrist on the inside (medial side) of the elbow. References: Merck Manual · UpToDate |
| Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis elbow)
Patient presents as → a 35-year-old female office worker with a history of playing tennis on weekends presents with a 4-month history of pain on the outer aspect of her right elbow. She reports the pain worsens with gripping activities and when lifting objects with her palm down. Physical examination reveals tenderness over the lateral epicondyle, and pain is elicited with resisted wrist extension and supination. There is no visible swelling, and the range of motion in the elbow is intact. Neurovascular examination of the arm is normal. She denies any history of direct trauma to the elbow. The clinical findings are suggestive of lateral epicondylitis, commonly referred to as “tennis elbow.” |
|
An overuse syndrome that results in pain in the myotendinous junction between the wrist extensors and lateral epicondyle, also known as "tennis elbow"
DX: Provocative testing - Pain is elicited with resisted wrist extension while the elbow is fully extended TX: Treat with activity modification, counterforce bracing, physical therapy, and corticosteroid injections - orthopedic surgery in patients who failed physical therapy for 4-6 months References: Merck Manual · UpToDate |
| Olecranon Bursitis (Scholar's Elbow)
69 y/o with three days of edema and erythema of the left arm Patient presents as → a 50-year-old male carpenter presents with a two-week history of swelling and pain at the back of his left elbow. He recalls hitting his elbow on a hard surface a few days prior to the onset of symptoms. The patient reports mild discomfort and stiffness but no significant functional impairment. Physical examination reveals a swollen, fluctuant, and tender area over the olecranon process, consistent with olecranon bursitis. There is no overlying erythema or warmth, and the range of motion of the elbow is preserved. The patient denies fever, chills, or any other systemic symptoms. Aspiration of the bursal fluid is performed, which shows no evidence of infection or crystal-induced arthritis. The patient is advised to avoid repetitive elbow movements and direct pressure on the affected area. Conservative management includes the application of ice packs, the use of an elbow pad for cushioning, and NSAIDs for pain relief. |
|
Elbow (Olecranon) Bursitis occurs in the olecranon bursa, a thin, fluid-filled sac that is located at the bony tip of the elbow (the olecranon)
DX: The diagnosis of olecranon bursitis is often made by clinical evaluation alone without the aid of objective diagnostic testing.
TX: Treat with PT, rest and ice, systemic antibiotics based on culture if septic, NSAIDS, injected corticosteroids, and joint, operative bursectomy References: Merck Manual · UpToDate |
| Cubital/Ulnar Tunnel Syndrome
Patient presents as → a 38-year-old female graphic designer presents with a four-month history of numbness and tingling in her right little finger and the ulnar half of the ring finger. She reports that her symptoms worsen while working at her computer and at night. The patient denies any trauma but mentions a habit of resting her elbow on the desk frequently. Physical examination reveals tenderness over the ulnar nerve at the elbow, positive Tinel’s sign at Guyon’s canal, and mild weakness in finger abduction. No atrophy of the hypothenar muscles is noted. Nerve conduction studies confirm the presence of ulnar nerve compression at the wrist. The diagnosis of ulnar tunnel syndrome is made based on clinical and electrophysiological findings. |
|
Cubital tunnel syndrome happens when the ulnar nerve, which passes through the cubital tunnel (a tunnel of muscle, ligament, and bone) on the inside of the elbow, is injured and becomes inflamed, swollen, and irritated.
Ulnar tunnel syndrome is caused by ulnar nerve compression at the wrist in Guyon's canal
Symptoms are the same for both cubital and ulnar tunnel syndrome
DX: Diagnosis is suggested by symptoms and signs, and sometimes nerve conduction studies TX: Treat with NSAIDs, activity modification, and nighttime bracing. Operative - ulnar nerve decompression. References: Merck Manual · UpToDate |
| Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Patient presents as → a 52-year-old male office worker presents with a three-month history of progressive numbness, tingling, and occasional burning pain in his right thumb, index, and middle fingers. He mentions that the symptoms often wake him up at night, and he has to shake his hand to get relief. The patient has a history of type 2 diabetes and hypothyroidism. On examination, there is a positive Tinel’s sign over the carpal tunnel and a positive Phalen’s test. Grip strength is slightly reduced, and there is mild atrophy of the thenar eminence. Nerve conduction studies demonstrate slowed conduction in the median nerve across the carpal tunnel. Based on the clinical findings and supporting investigations, a diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome is made. |
|
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the palm of the hand, becomes pressed or squeezed at the wrist
DX: The diagnosis can be clinically made; however, it is confirmed by nerve conduction studies Provocative maneuvers: + Phalen (pushing backs of hands together) and + Tinel test (tapping over nerve) TX: Splint (particularly at night), corticosteroid (oral or injection), surgical decompression for severe median nerve injury  Tingling, burning, and pain in the median nerve distribution (the first 3 digits and the radial half of the 4th digit) References: Merck Manual · UpToDate |
| De Quervain's Tenosynovitis
Patient presents as → a 38-year-old female, an avid gardener and new mother, presents with a four-week history of pain on the thumb side of her right wrist, exacerbated by thumb movement and wrist rotation. She reports the pain started shortly after she began regularly lifting her baby. On examination, there is localized swelling and tenderness over the radial styloid. Finkelstein’s test elicits sharp pain along the affected tendons. No numbness or tingling in the thumb or fingers is noted, and thumb movements are painful but not restricted. Based on the clinical presentation, a diagnosis of De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is made. |
|
De Quervain's tenosynovitis is a painful condition affecting the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist that is caused by constriction or pinching of the wrist tendons at the base of the thumb
DX: + Finkelstein (make a fist with the thumb inside, then ulnar deviate) - Finkelstein's test is commonly confused with Eichhoff's test, but on most exam questions, the confusion remains (read more about this here)
TX: Thumb spica splint x 3 weeks, NSAIDs x 10-14 days, steroid injections, and PT References: Merck Manual · UpToDate |
| Thumb Collateral Ligament Injury - Gamekeeper's Thumb & Skier's Thumb | |

23-year-old with right thumb pain |
|
Patient presents as → a 25-year-old male, an avid skier, presents with pain and swelling over the thumb’s metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint following a fall on an outstretched hand with his ski pole in hand. He reports immediate pain and difficulty gripping objects. On examination, there is notable tenderness over the ulnar aspect of the MCP joint of the thumb. A positive valgus stress test at 30 degrees of thumb flexion suggests instability, and there is significant pain on applying radial deviation to the thumb. No numbness or weakness in the thumb is observed. Radiographs are obtained to rule out avulsion fractures, showing no bony injury. Based on the clinical findings, a diagnosis of a thumb collateral ligament injury, specifically Skier’s Thumb, is considered. |
|
Skier's or gamekeeper's thumb is a tear of the ulnar collateral ligament
DX: Radiographs to evaluate for avulsion injury. MRI can aid in diagnosis if the exam is equivocal TX: Immobilization (thumb spica splint) for 4 to 6 weeks for partial tears. May need surgery for ligament repair  Avulsion fracture of the thumb as a result of a fall while skiing. The ulnar collateral ligament inserts along the medial (ulnar) aspect of the proximal phalanx of the thumb. Hence, an avulsion fracture may be present in the setting of ulnar collateral ligament injury. References: Merck Manual · UpToDate |
|
Dupuytren Contracture Patient presents as → a 60-year-old male with a history of diabetes and smoking presents with progressive difficulty in straightening his fingers, particularly affecting the ring and little fingers of his right hand. He reports that this issue has been gradually worsening over the past year, and it’s now interfering with his daily activities like typing and holding objects. On examination, thickened cords and nodules are palpable in the palm, extending into the affected fingers. The ring finger demonstrates a flexion contracture at the metacarpophalangeal joint, and passive extension is limited. There is no sensory deficit or weakness in the hand. The patient’s family history reveals that his father had a similar condition. Based on these findings, a diagnosis of Dupuytren’s contracture is made. |
|
Dupuytren Contracture is a gradual thickening and tightening of tissue under the skin in the hand
DX: The diagnosis of Dupuytren's contracture is clinical
TX: First-line therapies include injected collagenase and/or steroids. Fasciotomy or fasciectomy if patients are refractory to first-line therapies References: Merck Manual · UpToDate |
| Mallet (BASEBALL) finger - Extensor tendon injury of the distal interphalangeal joint
Patient presents as → a 35-year-old female presents to the clinic with a drooping of the tip of her right ring finger, which she noticed immediately after accidentally striking her finger against a door two days ago. She reports an inability to straighten the distal part of her finger and mild pain around the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint. On examination, there is obvious flexion deformity at the DIP joint, and the patient is unable to actively extend the fingertip. There is tenderness over the dorsal aspect of the DIP joint, but no laceration or open wound. Radiographs of the finger are obtained, revealing a small avulsion fracture at the base of the distal phalanx, consistent with a mallet finger injury. The patient is informed that this injury is due to the disruption of the extensor tendon at the DIP joint. She is fitted with a splint to keep the DIP joint in continuous extension for 6-8 weeks to allow for proper healing. |
|
Mallet finger is a flexion deformity of the fingertip caused by avulsion of the extensor tendon (which straightens the finger), with or without fracture, from the proximal end of the distal phalanx
DX: Radiographs - usually see bony avulsion of the distal phalanx TX: Splint DIP in uninterrupted extension x 6-8 weeks or surgical pinning References: Merck Manual · UpToDate |
| Boutonniere Deformity - Tear at PIP joint (jammed finger)
Patient presents as → a 34-year-old female, avid basketball player, presents with acute pain and deformity in her right ring finger following a basketball game injury a week ago. She reports immediate swelling and difficulty in straightening her finger post-injury. On examination, her ring finger shows a classic boutonniere deformity with flexion at the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint and hyperextension at the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint. There is significant tenderness and swelling around the PIP joint, suggestive of a possible tear in the extensor mechanism. The patient demonstrates limited range of motion and discomfort upon attempted extension of the PIP joint. Radiographs of the finger rule out fractures but indicate soft tissue swelling. The diagnosis of a boutonniere deformity secondary to a traumatic tear at the PIP joint is made. |
|
Boutonnière deformity is the result of an injury to the tendons that straightens (extends) the middle joint of the finger. The result is that the middle (PIP) joint of the injured finger will not straighten, while the fingertip bends back
DX: Elson test: bend PIP 90° over the edge of a table and extend the middle phalanx against resistance. In the presence of a central slip injury, there will be a weak PIP extension, and the DIP will go rigid
TX: Splint PIP in extension x 4-6 weeks with hand surgeon evaluation References: Merck Manual · UpToDate |
| Digital Flexor Tendinitis and Tenosynovitis (Trigger Finger)
Patient presents as → a 52-year-old male, a long-time construction worker with a history of type II DM, presents with complaints of pain and a ‘locking’ sensation in his right thumb, worsening over the past six months. He describes difficulty in straightening the thumb, especially in the mornings or after periods of rest, and a painful clicking sensation when it finally straightens. The patient denies any recent trauma but reports increased manual work involving repetitive thumb movements. On examination, the patient demonstrates the ‘triggering’ phenomenon upon flexion and extension of the thumb, with noticeable snapping. No signs of inflammation or infection are evident. The diagnosis of trigger finger, likely due to repetitive strain causing inflammation of the flexor tendon sheath of the thumb, is made. |
|
Trigger finger is one of the most common causes of hand pain in adults. It is caused by a disparity in the size of the flexor tendons and the surrounding retinacular pulley system, which overlies the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint.
DX: The diagnosis of trigger finger is primarily based upon physical examination and a history of locking or clicking during finger movement
TX: Treatment includes splinting, medications (NSAIDs) and corticosteroid injections, and surgery References: Merck Manual · UpToDate |
| Infections of the hand
Patient will present as→ a 28-year-old female, a dental hygienist, presents with a painful lesion on her right index finger. She reports the onset of symptoms a week ago, beginning with tingling and mild discomfort, progressing to severe pain and the appearance of small, grouped vesicles on an erythematous base. She denies any fever or systemic symptoms but admits to significant discomfort while performing tasks at work. She recalls treating a patient with active oral herpes lesions approximately two weeks prior, during which she sustained a minor cut on the same finger. Examination reveals a cluster of vesicles with some crusting and serous discharge, located near the distal phalanx of the index finger. No lymphadenopathy is noted. Based on her occupational exposure and clinical presentation, a diagnosis of herpetic whitlow is made, suspected to be a result of inoculation of herpes simplex virus during her professional activity. |
References: UpToDate |
| Ganglion cyst
Patient will present as→ a 35-year-old female presents to the clinic with a painless lump on her left wrist, which she first noticed a few months ago. She reports that the lump has gradually increased in size and is now causing discomfort when she bends her wrist or lifts heavy objects. She works as a graphic designer and mentions that prolonged typing exacerbates the discomfort. On examination, a firm, round, mobile mass approximately 2 cm in diameter is palpated on the dorsal aspect of her left wrist. The lump is translucent when illuminated with a light source. There is no overlying skin discoloration or warmth, and the range of motion of the wrist is full but uncomfortable at extremes. A diagnosis of a ganglion cyst is made. |
|
A ganglion is a noncancerous mucin-filled synovial cyst caused by either trauma, mucoid degeneration, or synovial herniation
DX: Ultrasound: useful for differentiating a cyst from a vascular aneurysm, may provide image localization for aspiration while avoiding artery
TX: Most ganglia do not require treatment. However, if the patient is disturbed by its appearance or if the ganglion is painful or tender, a single aspiration with a large-bore needle is effective in about 50% of patients
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate |
 |
There are 8 carpal bones, which can easily be remembered with the mnemonic, “Some Lovers Try Positions That They Can’t Handle,” representing the scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate and hamate bones. Play Video + Quiz |
 |
The humerus is the largest bone in the upper extremity and has many important landmarks that serve as sites of muscle attachment and action. The greater and lesser tubercles serve as the insertion sites for the muscles of the rotator cuff, while the deltoid inserts on the deltoid tuberosity. Distally, the medial and lateral epicondyles are attachment points for muscles that act on the wrist. Several structures on the humerus also act to stabilize both the shoulder and elbow joint. The olecranon fossa, coronoid fossa, capitulum, and trochlea are all bony structures that contribute to the stability of the elbow joint. Play Video + Quiz |
 |
The ulna and radius are the two distal bones of the arm. While the ulna sits medially, the radius is named for its lateral positioning when the body is prone. Important landmarks of the ulna include the olecranon process, coronoid process, trochlear notch, radial notch, styloid process and ulnar head. Meanwhile, important radius landmarks include the radial head and neck, the radial tuberosity, the styloid process, the ulnar notch, and Lister’s tubercle. Play Video + Quiz |
 |
The hand muscles can be divided into the thenar, hypothenar and intrinsic muscles. The thenar muscles include the opponens pollicis, abductor pollicis brevis, flexor pollicis brevis and adductor pollicis. The hypothenar muscles include the flexor digiti minimi brevis, abductor digiti minimi, opponens digiti minimi and the palmaris brevis. The intrinsic muscles include the interossei and lumbrical muscles. Play Video + Quiz |