Patient will present as → a 4-month-old boy is brought to your office by his parents, who are concerned about his episodes of turning blue, especially during feeding or crying. The parents also report that he seems to get tired more quickly than other infants his age. On examination, you note the baby has a mild cyanotic hue, particularly around his lips and fingertips. The infant's growth is slightly below the expected percentile for his age. Auscultation reveals a harsh systolic ejection murmur best heard at the left upper sternal border. A CXR shows a small boot-shaped heart and decreased pulmonary vascular markings. You suspect a congenital heart defect and order an echocardiogram, which confirms the diagnosis of Tetralogy of Fallot, characterized by four cardiac abnormalities: ventricular septal defect, overriding aorta, pulmonary stenosis, and right ventricular hypertrophy. You generate an urgent referral to a pediatric cardiologist for further management, including surgical intervention to correct the defect and improve oxygenation, which is typically performed within the first year of life to prevent complications and promote normal development.
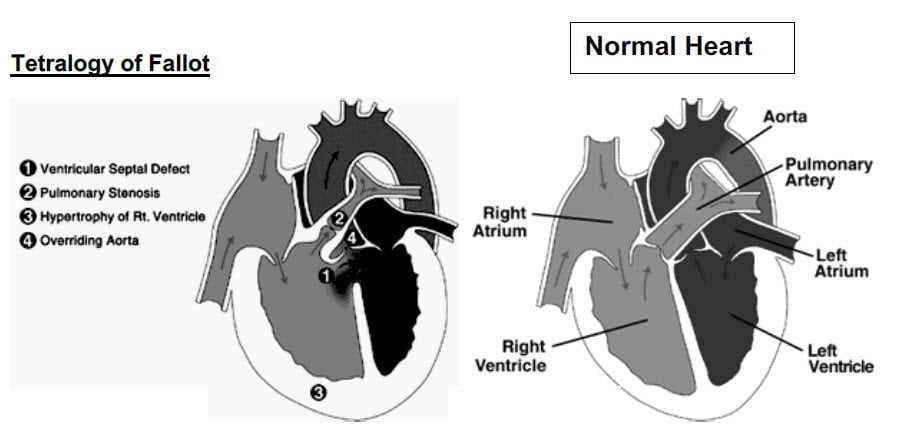
Cyanotic heart disorder that is characterized by four defects (tetra = 4) that together cause oxygen-deficient blood to flow out of the heart and into the rest of the body
Four features: PROVe
- P ulmonary Stenosis
- R ight ventricular hypertrophy
- O verriding aorta
- V entricular septal defect
The pulmonary stenosis causes a right to left shunt through the VSD, thereby causing cyanosis.
- TET SPELLS: hypercyanotic episodes that develop during crying or feeding
The murmur is classically described as a harsh systolic ejection murmur heard best at the left sternal border
- The murmur is usually present at birth
- The murmur may get louder during exercise or crying
Echocardiography is the diagnostic modality of choice. This test can clearly define the four abnormalities as well as provide important information about aortic arch anatomy
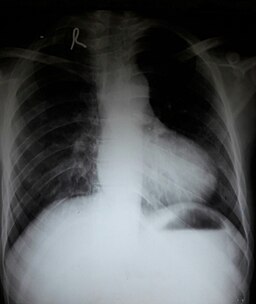
- A chest x-ray classically shows a boot-shaped heart
- EKG may show enlarged Right Atria and Right Ventricle. Check the width of QRS annually via ECG to reduce the risk of sudden cardiac death
- Cardiac catheterization may be required in some patients to fully define the anatomy
- Squatting decreases the cyanosis in tetralogy of Fallot
Treatment is surgical. Most patients have surgery within the first year of life
- Twenty-year survival rates after surgery are above 80%. The most common causes of death are sudden cardiac death and heart failure
- Complications after surgery include arrhythmias, pulmonary regurgitation, residual outflow obstruction, and heart failure
 Osmosis Osmosis |
|
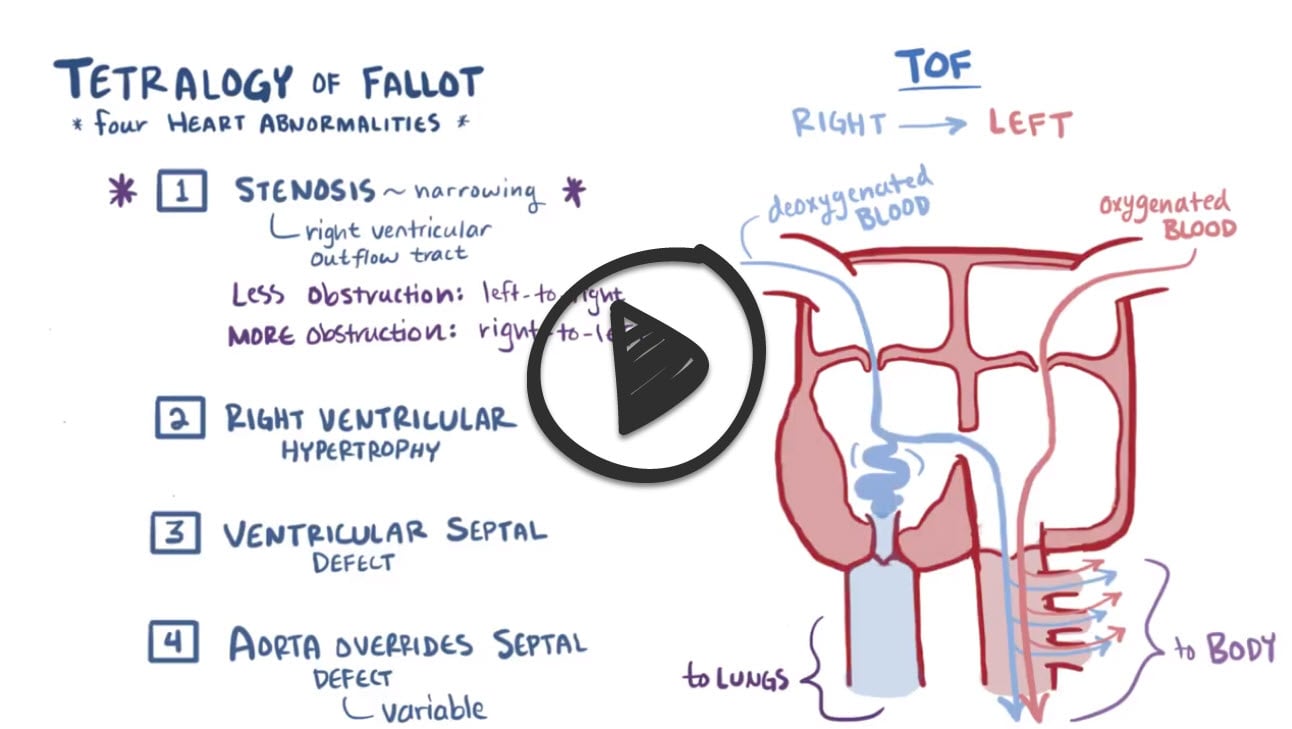 |
Tetralogy of Fallot is a congenital birth defect of the heart leading to cyanosis. It presents with up to 4 different heart defects, and is the most common cause of blue baby syndrome. The four pathologies in this disease are pulmonary infundibular stenosis, right ventricular hypertrophy, overriding aorta, and ventricular septal defect.
Play Video + QuizQuestion 1 |
Pulmonary valve stenosis Hint: See E for explanation | |
VSD Hint: See E for explanation | |
Overriding aorta Hint: See E for explanation | |
Right ventricular hypertrophy Hint: See E for explanation | |
ASD |
Question 2 |
Chest pain Hint: Chest pain is not a feature of tetralogy of Fallot. | |
Cyanosis | |
Convulsions Hint: Convulsions are occasionally seen as part of severe hypoxic spells in infancy rather than a feature of tetralogy of Fallot. | |
Palpitations Hint: Palpitations are uncommon in tetralogy of Fallot. |
|
List |
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate