The NCCPA™ PANCE Genitourinary Content Blueprint urethral disorders
| Urethral Prolapse | Patient will present as → a mother of a 3-year-old girl who is concerned because she saw blood in her daughter’s underpants. The patient complains of no pain. Examination demonstrates a complete circular eversion of the distal urethral mucosa. Circumferential protrusion of the distal urethra through the external urethral meatus. It is a rarely diagnosed condition that occurs most commonly in prepubertal girls and postmenopausal women
DX: Diagnosis is clinical and urethral prolapse is often an incidental finding during a routine examination
TX: Treatment includes topical estrogen creams, Vaseline, and sitz baths
|
| Urethral Stricture | Patient will present as → a 56-year-old male with pain during urination, decreased urinary stream, and incomplete bladder emptying. Uroflowmetry demonstrates poor bladder emptying and a low peak rate of urine flow. Narrowing of the urethra caused by injury, instrumentation (TURP), infection (typically with Gonorrhea), and certain non-infectious forms of urethritis
DX: Patients suspected of having a urethral stricture should undergo cystourethroscopy, retrograde urethrogram (RUG), voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG), or ultrasound urethrography to establish the diagnosis TX: Treatments include urethral dilation or stent placement
|


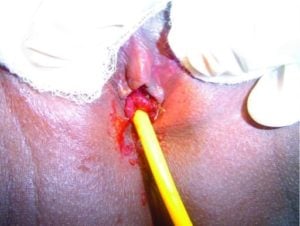
![Bulbar urethral stricture (arrow) bladder diverticula (circle). with an average age of 43.8 years, however the age group most concerned was that of 50 -60 years. Some authors have found an average age of 40 years with extremes of 9 and 78 years, averages between 25 and 55 years and extremes of 0.06 and 90 years [5] [6] [7] [8]. All these studies showed that stenosis appeared](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/333571819/figure/fig2/AS:765707834896385@1559570382875/Bulbar-urethral-stricture-arrow-bladder-diverticula-circle-with-an-average-age-of.png)