Patient will present as → a 31-year-old woman who complains of irregular, infrequent menstrual periods. On further questioning, she complains of headaches, fatigue, and breast discharge. She takes ibuprofen only occasionally. The serum prolactin level is 380 μg per L.
Pituitary adenomas are benign tumors of the anterior pituitary that derive from one of the five types of pituitary hormone-producing cells
- Common presentations associated with pituitary adenoma (may involve multiple endocrine abnormalities)
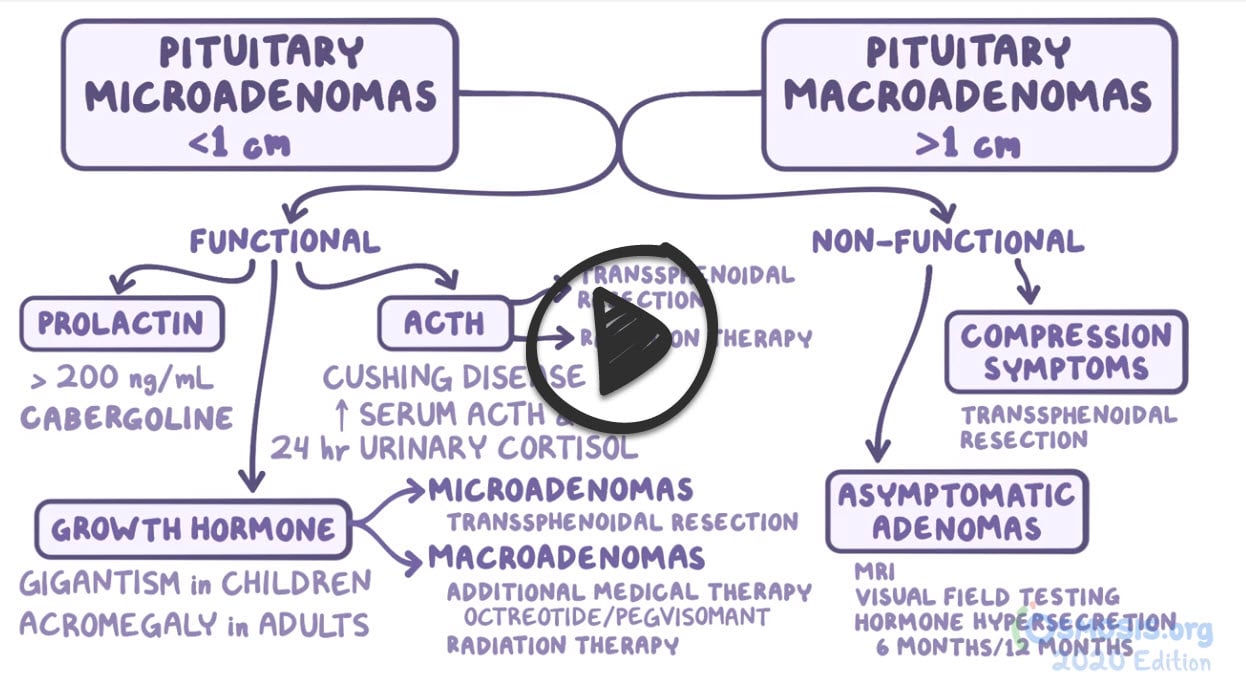
- Pituitary adenomas < 1 centimeter are called microadenomas, whereas those > 1 centimeter are called macroadenomas
| Classification of Pituitary Adenomas | ||
| Tumor Type | Secretory Product(s) | Relative Frequency (%) |
Prolactinoma (Galactorrhea)
|
↑ Prolactin | 50 |
| Somatotroph adenoma (acromegaly & gigantism) | ↑ Growth Hormone (GH) | 10 |
| Corticotroph adenoma (Cushing's disease) | ↑ ACTH | 5 |
| Thyrotroph adenoma (Hyperthyroidism) | ↑ TSH | 1 |
| Gonadotroph adenoma | ↑ LH ↑ FSH | 3 |
| Non-Secreting Adenoma | α alpha -subunit | 34 |
Diagnosis is made by MRI - look for sellar lesions/tumors
- Endocrine studies: Prolactin, GH, ACTH, TSH, FSH, LH
Treatment is often surgical
- Transsphenoidal surgery: management of choice for removal of ACTIVE or compressive tumors
- Medical management is the first line for prolactinomas - Dopamine inhibits prolactin release - Cabergoline or Bromocriptine (dopamine agonists)
- A dopamine agonist drug should usually be the first treatment for patients with hyperprolactinemia of any cause, including lactotroph adenomas (prolactinomas) of all sizes. These drugs decrease serum prolactin concentrations and decrease the size of most lactotroph adenomas. Following the decrease in serum prolactin and adenoma size in patients with macroadenomas, visual and pituitary function often return to normal.
- Transsphenoidal surgery is considered only when dopamine agonist treatment has been unsuccessful or in specific situations, such as a giant lactotroph adenoma in a woman wishing to become pregnant.
- Acromegaly: TSS + Bromocriptine (dopamine decreases GH production)
 Osmosis Osmosis |
|
 |

Prolactinoma is a prolactin secreting tumor of the pituitary gland. This tumor is the most common adenoma of the pituitary gland. These tumors are benign but can cause symptoms due to elevated prolactin levels in the blood or by compression of nearby structures. Prolactin is the hormone that stimulates the breast to produce breast milk. Therefore, elevated prolactin levels are usually seen during pregnancy and after childbirth. Pathologic secretion of prolactin from prolactinomas can cause galactorrhea in women although rare in men because of insufficient breast tissue. Prolactin also inhibits the release of gonadotropin releasing hormone. Normally, GnRH stimulates the release of FSH and LH from the anterior pituitary, which plays an important role in the synthesis of sex hormones. Increased prolactin can therefore cause decreased levels of sex hormone in men and women, leading to impotence and amenorrhea, respectively. Enlargement of the tumor can lead to compression of the optic chiasm resulting in bitemporal hemianopia. Dopamine physiologically suppresses prolactin secretion and is used in the treatment of prolactinomas.
Play Video + QuizQuestion 1 |
Hypothyroidism Hint: While hypothyroidism can cause menstrual irregularities and elevated prolactin levels, it is less likely to present with galactorrhea and does not typically cause decreased libido as a primary symptom. | |
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) Hint: PCOS can cause menstrual irregularities and sometimes galactorrhea, but it is often associated with other symptoms like hirsutism, acne, and obesity, which are not mentioned in this case. | |
Prolactinoma | |
Pregnancy Hint: Pregnancy is a common cause of amenorrhea and galactorrhea, but should be easily ruled out with a pregnancy test. | |
Medication side effect Hint: Certain medications, particularly antipsychotics and antidepressants, can cause hyperprolactinemia and galactorrhea. However, there is no mention of medication use in this patient's history. |
Question 2 |
Serum prolactin level Hint: While elevated prolactin can be indicative of a prolactinoma, a type of pituitary adenoma, it is not the initial diagnostic test for a suspected pituitary adenoma, especially in the presence of visual symptoms. | |
MRI of the brain with focus on the sella turcica | |
CT scan of the head Hint: A CT scan is less sensitive than MRI for detecting pituitary adenomas and does not provide as detailed an image of the sellar region. | |
Serum thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and free thyroxine (T4) levels Hint: These tests assess thyroid function and may be altered by a pituitary adenoma, but they are not initial diagnostic tests for a pituitary adenoma. | |
24-hour urine cortisol level Hint: This test is used to diagnose Cushing's syndrome, which can be caused by a pituitary adenoma, but it is not the initial test for a suspected pituitary adenoma. |
Question 3 |
Transsphenoidal surgery Hint: While surgery is an option for treating prolactinomas, it is generally reserved for patients who are intolerant to medical therapy or have a tumor that is compressing surrounding structures. | |
Cabergoline | |
Radiation therapy Hint: This is typically a third-line treatment for prolactinomas, used when medications and surgery are not effective or feasible. | |
High-dose corticosteroids Hint: Corticosteroids are not used in the treatment of prolactinomas. They are used in the management of other conditions, such as adrenal insufficiency or certain brain tumors, but not for prolactinomas. | |
Bromocriptine Hint: Although bromocriptine is a dopamine agonist used in the treatment of prolactinomas, it is generally considered second-line due to a less favorable side-effect profile compared to cabergoline. |
|
List |
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate



