16 y/o with diaphoresis, weight loss, tremor, palpitations, and neck swelling
Patient will present as → a 37-year-old female with a 2-week history of a painful mass in her neck after having a sore throat and fever for 3 days. The patient reports the mass has slowly been enlarging over that time span and has become more painful to the touch. She also reports feeling hot, even when her coworkers feel cold, and reports loose stools over the past week. The patient’s vital signs are T 98.6F, BP 140/90, Pulse 110 bpm, and SpO2 100%. On exam, you note a diffusely enlarged thyroid that is painful to the touch. TSH is decreased, T4/T3 is elevated, and radioactive iodine uptake and scan at 24 hours reveals an uptake of 3% (normal 8-25%).
Thyroiditis is a general term that refers to inflammation of the thyroid gland and includes a group of individual disorders causing thyroidal inflammation but presenting in different ways
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: an autoimmune form of thyroiditis ⇒ autoantibodies directed against thyroid ⇒ thyroid tissue is destroyed over time ⇒ chronic hypothyroidism
- The most common cause of hypothyroidism in the United States
- Hashimoto's thyroiditis may present similarly to subacute thyroiditis, but the presence of neck tenderness and a recent viral illness should make you think subacute thyroiditis.
- Goiter on PE
- High levels of anti-TPO antibodies
- TX depends on whether hypothyroidism is present
- euthyroid: no treatment
- chronic hypothyroidism: lifelong substitution with T4
Postpartum thyroiditis
- 2-12 months after giving birth
- Immune system diminished during pregnancy ⇒ after childbirth, the immune system is more active and might attack the thyroid
- Hyperthyroid phase 5-7 months after birth, followed by normal thyroid function
Subacute thyroiditis (Quervain's thyroiditis)
- The most common cause of thyroid pain and has a greater incidence in women
- Inflamed, painful thyroid, fever, and muscle aches
- The etiology is often post-infectious and viral in origin
- Usually following symptoms such as fever, myalgia, and pharyngitis
- Early in the course may be hyperthyroid, followed by a period of hypothyroidism
- Increased ESR (60-100)
- Usually causes hyperthyroidism - TFTs (if abnormal) are usually hyperthyroid at presentation - ↓ TSH, ↑ T4, and ↑ T3
Drug-induced: Thyroiditis can also be seen in patients taking certain drugs
- Antithyroid medications: methimazole and propylthiouracil
- Lithium - bipolar disorder
- Amiodarone - antiarrhythmic
- Interferon alpha
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (e.g., Sunitinib) - anti-cancer
- Checkpoint inhibitors (e.g., Nivolumab, Pembrolizumab)
- TSH should be checked every 6-12 months - T4 therapy given right away
Infectious bacterial thyroiditis (rare) is often due to the hematogenous spread of staph or strep
- Its signs are the classic ones of inflammation: fever, heat, pain, redness, and swelling
- ↑ WBC
Summary of thyroiditis:
| Type | Cause | Features | Diagnosis | Duration and resolution |
| Hashimoto’s thyroiditis | Anti-thyroid antibodies, autoimmune disease | Hypothyroidism, rare cases of transient thyrotoxicosis | Thyroid function tests, thyroid antibody tests
↑ anti-TPO antibodies |
Hypothyroidism is usually permanent |
| Subacute thyroiditis (de Quervain’s thyroiditis) | Possible viral cause | Painful thyroid, thyrotoxicosis followed by hypothyroidism | Thyroid function tests, sedimentation rate, radioactive iodine uptake
TFTs (if abnormal) are usually hyperthyroid at presentation - ↓ TSH, ↑ T4, and ↑ T3 |
Resolves to normal thyroid function within 12-18 months, 5% possibility of permanent hypothyroidism. |
| Silent thyroiditis, Painless thyroiditis | Anti-thyroid antibodies, autoimmune disease | Thyrotoxicosis followed by hypothyroidism. | Thyroid function tests, thyroid antibody tests, radioactive iodine uptake | Resolves to normal thyroid function within 12-18 months, 20% possibility of permanent hypothyroidism. |
| Postpartum thyroiditis | Anti-thyroid antibodies, autoimmune disease | Thyrotoxicosis followed by hypothyroidism | Thyroid function tests, thyroid antibody tests, radioactive iodine uptake (contraindicated if the hypothyroid woman is breast-feeding) | Resolves to normal thyroid function within 12-18 months, 20% possibility of permanent hypothyroidism |
| Drug-induced | Drugs include amiodarone, lithium, interferons, cytokines | Either thyrotoxicosis or hypothyroidism. | Thyroid function tests, thyroid antibody tests | Often continues as long as the drug is taken |
| Radiation-induced | Follows treatment with radioactive iodine for hyperthyroidism or external beam radiation therapy for certain cancers. | Occasionally thyrotoxicosis, more frequently hypothyroidism | Thyroid function tests | Thyrotoxicosis is transient, hypothyroidism is usually permanent |
| Acute thyroiditis, Suppurative thyroiditis | Bacteria mainly, but any infectious organism | Occasionally painful thyroid, generalized illness, occasional mild hypothyroidism | Thyroid function tests, radioactive iodine uptake, fine-needle aspiration biopsy | Resolves after treatment of infectious cause, may cause severe illness |
Lab values depend on the cause of thyroiditis and may be euthyroid
- Other possibilities include ↑ ESR (subacute), ↑ WBC count (infectious), ↑ anti-TPO antibodies (Hashimoto's)
- TFTs (if abnormal) are usually hyperthyroid at presentation - ↓ TSH, ↑ T4, and ↑ T3
Ultrasound and radioactive iodine scanning have little value in this setting and are not warranted
- If performed, a radioactive iodine (RAI) scan will reveal diminished uptake
If there is PAIN think:
- Painful subacute - De Quervain's (granulomatous) usually post viral
- Infectious - bacterial mainly - strep or staph most common
- Radiation
- Trauma
If there is NO PAIN, think
- Postpartum - 1-2 months of hyperthyroidism after delivery
- Drug-induced - the most common cause of drug-induced thyroiditis is Lithium or Amiodarone
- Hashimoto thyroiditis
Hashimotos: TX depends on whether hypothyroidism is present
- euthyroid: no treatment
- chronic hypothyroidism: lifelong substitution with T4
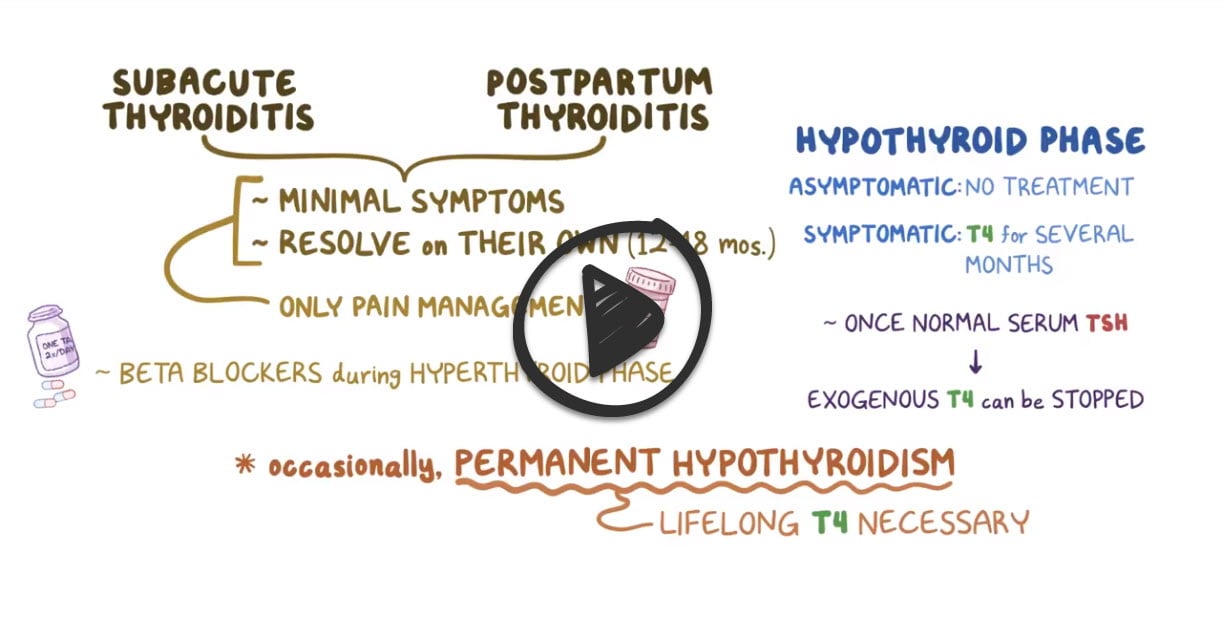
Subacute and postpartum thyroiditis usually resolve on their own after 12-18 months; often only need pain management
- Beta-blockers during hyperthyroid state
- T4 for several months during hypothyroid phase until TSH normalizes then can be stopped
- Occasionally permanent hypothyroidism
- Aspirin for pain and inflammation
Drug-induced: Stop offending drugs *lithium *Amiodarone - will usually return to euthyroid state once the meds are stopped
Infectious bacterial thyroiditis: The treatment is that for any febrile disease, including specific antibiotic drugs if the invading organism has been identified and its sensitivity to the drug established. Surgical drainage if abscess present
Question 1 |
Grave's disease Hint: Graves' disease is an autoimmune disorder that leads to hyperthyroidism. It typically presents with symptoms like weight loss, heat intolerance, and palpitations, and the thyroid is usually not tender. | |
Hashimoto thyroiditis Hint: This is an autoimmune disorder leading to hypothyroidism. While it can cause symptoms like fatigue and weight gain, the thyroid gland is usually not painful. | |
Subacute thyroiditis | |
Papillary thyroid carcinoma Hint: While this is the most common type of thyroid cancer, it typically does not present with a painful thyroid gland or a pattern of symptoms consistent with both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. | |
Thyroid lymphoma Hint: This is a rare form of thyroid cancer and typically presents with a rapidly enlarging, painless goiter. It is not typically associated with a preceding viral infection. |
Question 2 |
Thyroid ultrasound Hint: Thyroid ultrasound is useful in evaluating thyroid nodules but less helpful in acute thyroiditis. | |
Radioactive iodine uptake test Hint: Radioactive iodine uptake test would show low uptake in subacute thyroiditis but is not necessary for diagnosis. | |
Fine-needle aspiration biopsy Hint: Fine-needle aspiration biopsy is more appropriate for evaluating thyroid nodules or suspected thyroid cancer. | |
Anti-thyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO) antibodies Hint: Anti-TPO antibodies are associated with Hashimoto's thyroiditis, not subacute thyroiditis. | |
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) |
Question 3 |
Initiate radioactive iodine therapy Hint: This is not indicated in subacute thyroiditis, as it is typically a self-limiting condition and radioactive iodine is used in the treatment of hyperthyroid states. | |
Start thyroid hormone replacement and monitor thyroid function regularly | |
Reassure and observe without treatment, as the condition is self-limiting Hint: While subacute thyroiditis is often self-limiting, treatment for symptomatic hypothyroidism during its course is necessary to alleviate symptoms. | |
Inform the patient that thyroid function will normalize spontaneously within a few weeks Hint: While thyroid function may eventually normalize, this patient's current symptoms warrant treatment. | |
Order a thyroid ultrasound for further evaluation Hint: While a thyroid ultrasound can be useful in the diagnosis of thyroid conditions, it is not necessary in this case where the diagnosis is clear and the focus is on managing the hypothyroid phase. |
|
List |
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate


 Lecture
Lecture Osmosis
Osmosis