 Patient will present as → a 68-year-old smoker with a 25 lb weight loss over the last three months that is associated with a burning pain deep in the epigastrium after eating, diarrhea, and jaundice. Physical exam reveals an enlarged, palpable, non-tender gallbladder and clay-colored stool. Labs show a total bilirubin of 8, alkaline phosphatase of 450, and an ALT of 150.
Patient will present as → a 68-year-old smoker with a 25 lb weight loss over the last three months that is associated with a burning pain deep in the epigastrium after eating, diarrhea, and jaundice. Physical exam reveals an enlarged, palpable, non-tender gallbladder and clay-colored stool. Labs show a total bilirubin of 8, alkaline phosphatase of 450, and an ALT of 150.
To watch this and all of Joe-Gilboy PA-C's video lessons you must be a member. Members can log in here or join now.
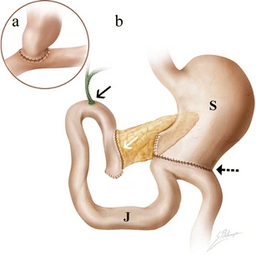
The most common is ductal adenocarcinoma, usually at the head of the pancreas
- Abdominal pain, jaundice, enlarged palpable gallbladder in 40% of patients (Courvoisier's sign), light-colored stools, dark urine, pruritus, weight loss
- Associated with cigarette smoking, pancreatitis, diabetes mellitus, and obesity
Virchow's node (or signal node) is a lymph node in the left supraclavicular fossa (the area above the left clavicle).
- It takes its supply from lymph vessels in the abdominal cavity. Virchow's node is also sometimes coined “the seat of the devil,” given its ominous association with malignant disease
"Pain of pancreatic cancer is often lessened by sitting and leaning forward (just like pancreatitis). This indicated that the lesion had spread beyond the pancreas and is inoperable."
Risk factors: smoking, alcohol, obesity, and chronic pancreatitis.
Diagnose with abdominal CT scan - 75% show tumor at the head of the pancreas, 20% in the body, and 10% in the tail
- Increased amylase (if tumor obstructs ducts)
- Increased direct bilirubin
- Increased CEA
- Glucose intolerance
- ERCP - stenosis or obstruction of pancreatic ducts
- Tumor Marker: CA 19-9 - not diagnostic but can be used to follow response to therapy
Question 1 |
Pancreatic cancer | |
Gastric cancer Hint: Gastric cancer cannot cause pruritus and enlargement of the gallbladder. | |
Gastric ulcer Hint: Gastric ulcer doesn’t present as jaundice and pruritus. | |
Hepatocellular carcinoma Hint: Hepatocellular carcinoma does not cause enlargement of the gallbladder. |
Question 2 |
magnetic resonance imaging scan of the abdomen
| |
gastroscopy | |
dual-phase helical computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen | |
colonoscopy |
Question 3 |
alcohol consumption | |
cigarette smoking | |
high fat intake | |
environmental toxins | |
previous exposure to radiation |
Question 4 |
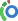
Pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple procedure) | |
Chemotherapy | |
Radiotherapy | |
None of the above |
Question 5 |
Pancreatic carcinoma is the 4th leading cause of cancer death in the US Hint: Cancer of the exocrine pancreas is a highly lethal malignancy. It is the fourth leading cause of cancer-related death in the United States and second only to colorectal cancer as a cause of digestive cancer-related death. | |
Men are affected more often than women Hint: Men are slightly more likely to develop pancreatic cancer than women. This may be due, at least in part, to higher tobacco use in men, which raises pancreatic cancer risk. | |
75% occur in the tail | |
Cigarette smoking, obesity, and physical inactivity are risk factors Hint: The major risk factors for pancreatic cancer include cigarette smoking, high body mass and lack of physical activity. Smoking is one of the most important risk factors for pancreatic cancer. The risk of getting pancreatic cancer is about twice as high among smokers compared to those who have never smoked. Obese people (body mass index [BMI] of 30 or more) are about 20% more likely to develop pancreatic cancer. |
|
List |
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate


 Lecture
Lecture