Patient with a rectal abscess will present as → a 45-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a 3-day history of severe rectal pain, especially during defecation. He also reports fever and malaise. On physical examination, you note a fluctuant, erythematous mass near the anus. The patient is in obvious discomfort.
Patient with an anorectal fistula will present as → a 45-year-old man presents to the clinic with a 3-month history of recurrent perianal abscesses. He reports intermittent drainage of pus and discomfort in the perianal area. On examination, you note a small opening near the anal verge with surrounding erythema. A probe is easily passed through the opening and emerges in the anal canal.
To watch this and all of Joe-Gilboy PA-C's video lessons you must be a member. Members can log in here or join now.
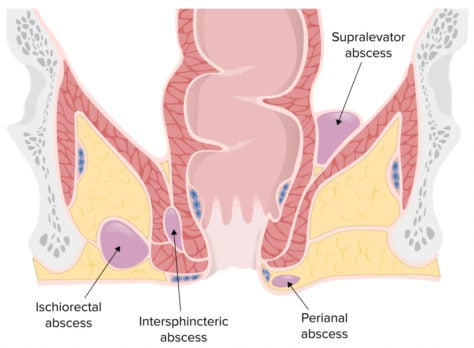
An anorectal abscess is a collection of pus in the area around the anus and rectum and is the result of infection, whereas an anorectal fistula is an abnormal tunnel that connects the anus or rectum to the skin around the anus and is a chronic complication of an abscess.
- Abscesses produce painful swelling at the anus as well as painful defecation. Examination reveals localized tenderness, erythema, swelling, and fluctuance; fever is uncommon.
- Deeper abscesses may produce buttock or coccyx pain and rectal fullness; fever is more likely.
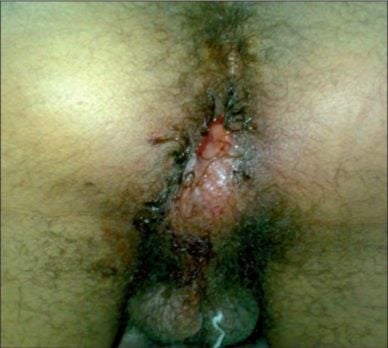
Perianal swelling, erythema, and drainage due to a perianal abscess by the Department of Urology, University Hospital Center, Fez, Morocco. Image - License: CC BY 2.0
An anorectal fistula is an open tract between two epithelium-lined areas and is associated with deeper anorectal abscesses
- Communication between the rectum and perianal skin
- Generally located within 3 cm of the anal margin
- Fistulae will produce anal discharge and pain when the tract becomes occluded
Intraoperative view of the external openings of the fistula in ano (arrowheads) and the upper part of the tract where the foreign material resided (arrow)
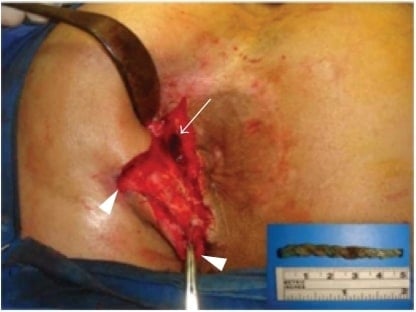
Intraoperative view of the external openings of the fistula in ano (arrowheads) and the upper part of the tract where the foreign material resided (arrow) by Department of General Surgery, Cerrahpasa Medical School, Istanbul University, Cerrahpasa, Fatih 34098, Istanbul, Turkey. Image - License: CC BY 3.0
Treatment of an anorectal abscess requires surgical drainage, followed by warm-water cleansing, analgesics, stool softeners, and a high-fiber diet are prescribed for all patients
- Prompt incision and adequate drainage are required and should not wait until the abscess points. Many abscesses can be drained as an in-office procedure; deeper abscesses may require drainage in the operating room
- Antibiotics are needed for high-risk patients
Anorectal fistulas must be treated surgically
A fistula is a connection or passageway formed abnormally between two epithelium-lined vessels or organs. Causes of enterocutaneous fistulas can be summarized by the mnemonic “FRIEND.” The “FRIENDs” of a fistula include Foreign body, Radiation, Infection, Epithelialization, Neoplasm, and Distal obstruction.
Play Video + QuizQuestion 1 |
Chronic constipation Hint: While it can cause anorectal problems, it is less likely to directly cause abscesses or fistulas. | |
Crohn's disease | |
Hemorrhoidal disease Hint: Primarily involves the venous structures and does not typically lead to fistula formation. | |
Anal fissure Hint: These are superficial tears and do not typically lead to abscesses or fistulas unless they become chronically infected. | |
Diabetes mellitus Hint: While diabetes can predispose to infections due to impaired immunity, it is not a direct cause of rectal abscesses or fistulas. |
Question 2 |
Initiate broad-spectrum antibiotics Hint: Antibiotics are adjunctive to surgical drainage but not a primary treatment. | |
Perform a colonoscopy Hint: This is not indicated acutely in the setting of a suspected abscess. | |
Order an MRI of the pelvis Hint: MRI may be useful in complex cases or to evaluate fistulas but is not the initial step in management. | |
Incision and drainage | |
High-fiber diet and sitz baths Hint: These measures may help in relieving symptoms of hemorrhoids and anal fissures but are not appropriate for an abscess. |
Question 3 |
Topical nitroglycerin Hint: Used for anal fissures, not fistulas. | |
Systemic steroids Hint: These are used in inflammatory bowel disease but not specifically for fistula management. | |
Fistulotomy | |
High-dose antibiotics Hint: While antibiotics may be used to treat acute infections, they do not address the underlying fistula tract. | |
Dietary modifications Hint: Helpful in general bowel health but do not treat a fistula. |
|
List |
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate


 Lecture
Lecture