Patient will present as → a 6-month-old infant is brought to the clinic for a routine check-up. The parents express concerns about the child's recent irritability and noticeable decrease in responsiveness. The infant, born at term with no complications, initially had normal development. However, the parents note that over the past two months, the child has shown delayed milestones, particularly in social engagement and motor skills. The infant's diet consists mainly of formula milk. On examination, the child has a fairer complexion compared to siblings, with a musty odor. There's also mild microcephaly and hypotonia. The initial blood work shows elevated phenylalanine levels. Given these findings, a diagnosis of Phenylketonuria (PKU) is considered, and genetic testing is recommended to confirm the diagnosis. Dietary modifications with phenylalanine-restricted formula are initiated. The parents are counseled about the importance of strict dietary adherence to prevent further neurological damage and to promote normal development.
To watch this and all of Joe-Gilboy PA-C's video lessons you must be a member. Members can log in here or join now.
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is an autosomal recessive disorder and inborn error of metabolism involving absent or virtually absent phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) enzyme activity
- Phenylalanine and its metabolites accumulate in the central nervous system, causing mental retardation and movement disorders
- Infants are normal at birth - after a few months, mental retardation is evident
- Presents as blond, blue-eyed, with fair skin, mental retardation, eczema, and a musty, mousy body odor of phenylacetic acid
- Neonates are screened for PKU 24 to 48 h after birth
Routine neonatal screening
- In the US and many developed countries, all neonates are screened for PKU 24 to 48 hours after birth with one of several blood tests; abnormal results are confirmed by directly measuring phenylalanine levels.
- Phenylketonuria is said to be present when plasma phenylalanine levels exceed 20 mg/dl.
Treatment is lifelong dietary phenylalanine restriction and increasing dietary (amino acid) tyrosine intake
- All-natural protein contains about 4% phenylalanine. Therefore dietary staples include low-protein natural foods (e.g., fruits, vegetables, and certain cereals)
- The sweetener aspartame can act as poison for people with phenylketonuria
 Osmosis Osmosis |
|
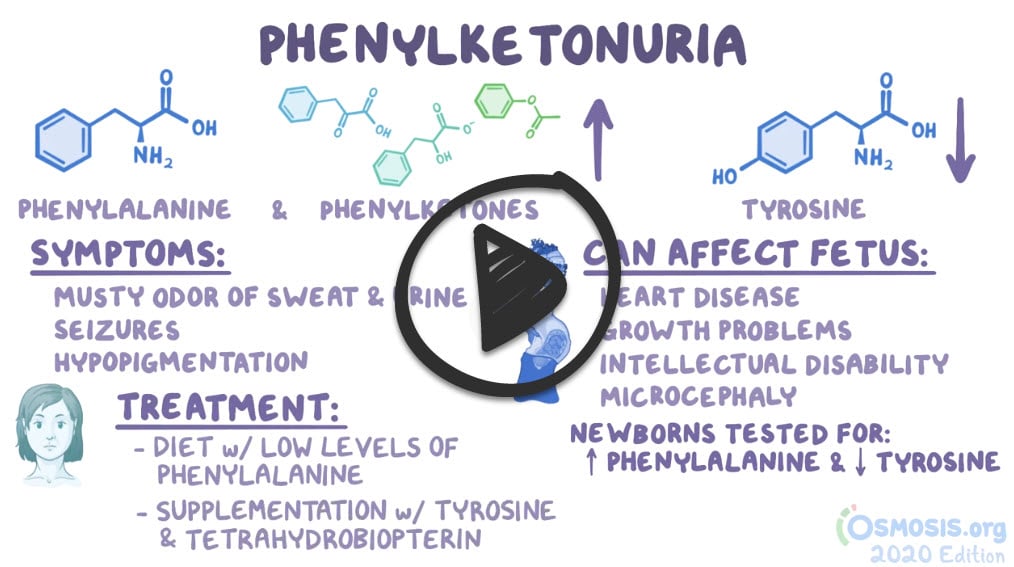 |
Phenylketonuria or PKU is a metabolic disorder caused by decreased levels of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase, or alternatively decreased levels of its tetrahydrobiopterin cofactor. Phenylketonuria is inherited in an autosomal recessive fashion. For affected patients, tyrosine becomes an essential amino acid. Treatment requires avoiding phenylalanine intake from the diet, which is found in products containing aspartame, such as Nutra Sweet. Clinically, patients’ urine will have a musty or mousy body odor. They can also exhibit growth retardation, seizures, mental retardation, and skin hypopigmentation.
Play Video + QuizQuestion 1 |
It is an autosomal dominant disorder | |
It is almost always associated with intellectual disability Hint: See A for explantion | |
Incidence in the US is 350 cases per 1 million live births Hint: See A for explantion | |
It is due to deficiency of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase Hint: See A for explantion |
Question 2 |
Fair skin and hair Hint: See C for explanation | |
Atopic dermatitis | |
Psoriasis | |
Scleroderma like plaques |
Question 3 |
5 mg/dl Hint: See D for explanation | |
10 mg/dl Hint: See D for explanation | |
15 mg/dl Hint: See D for explanation | |
20 mg/dl |
Question 4 |
24 weeks gestation | |
24 to 48 h after birth | |
48 to 72 h after birth | |
at the first well child visit |
Question 5 |
Weekly | |
Twice a week Hint: for neonates | |
Monthly Hint: for children older than age 2 up till adulthood. | |
Biweekly Hint: for toddlers |
|
List |
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate


 Lecture
Lecture


