The NCCPA™ PANCE Pulmonary Content Blueprint includes two pleural diseases.
| Feature | Pleural Effusion | Pneumothorax |
|---|---|---|
| Etiology | A buildup of fluid in the pleural space due to conditions like heart failure, pneumonia, or malignancies | The presence of air in the pleural space which can lead to partial or complete collapse of the lung. Can be spontaneous or traumatic |
| Symptoms | Dyspnea, vague discomfort or sharp pain that worsens during inspiration | Acute onset ipsilateral chest pain and dyspnea |
| Physical exam findings | Decreased or absent breath sounds over the area of effusion, dullness to percussion, decreased tactile fremitus, pleural friction rub may be present, egophony and bronchial breath sounds if effusion is large | Decreased or absent breath sounds on affected side, hyperresonance to percussion, decreased tactile fremitus, possible subcutaneous emphysema, tracheal deviation towards unaffected side in tension pneumothorax |
| Imaging/lab findings | Chest x-ray shows blunting of the costophrenic angle, fluid layering in the lung periphery, and possible mediastinal shift away from the effusion in large ones.
Differentiate between exudate and transudate - Light's criteria is commonly used
|
Chest x-ray shows the presence of a pleural line and absence of lung markings peripheral to this line. In tension pneumothorax, there can be shift of the mediastinum to the opposite side.
|
| Treatment | Thoracentesis or pleurodesis | Chest tube placement in most cases |
| Underlying medical conditions | Heart failure, pneumonia, cancer | None or underlying lung disease |
| Risk factors | Older adults, underlying medical conditions | Young, tall, thin men, trauma |
 Picmonic
Picmonic
 |
A pleural friction rub occurs near the anterior lateral lung and develops due to rubbing of the pleural surfaces. The sensation of a pleural friction rub is often uncomfortable. This lung sound is prominent during both inspiration and expiration and does not resolve with coughing. Pleural rubs are common in pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, and pleurisy (pleuritis). |
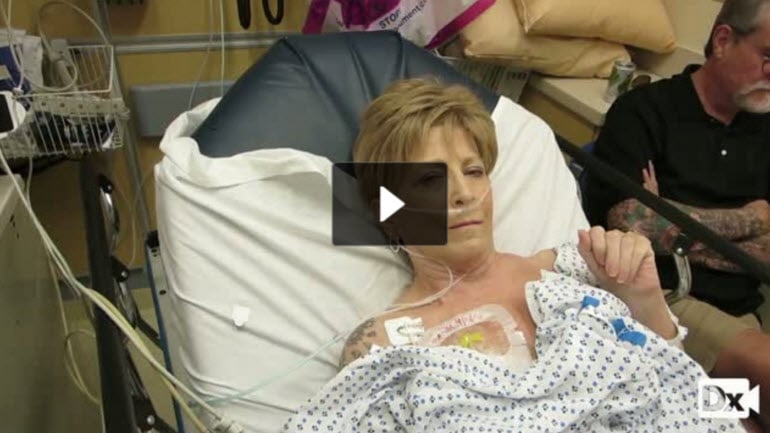
| Pleural effusion (ReelDx) | Patient presents as → a 58-year-old female who returns to the hospital with chest pain and difficulty breathing several weeks after being discharged following a myocardial infarction requiring immediate cardiac catheterization. She has been coughing up frothy sputum for the past three days. The patient complains of a sharp pain that worsens during inspiration. Physical exam reveals decreased tactile fremitus, dullness to percussion, and diminished breath sounds on the left side. Chest X-ray demonstrates blunting of the left costophrenic angle, meniscus sign, obliteration of the left hemidiaphragm, and mediastinal shift. ReelDx Virtual Rounds (pleural effusion)Pleural effusion is the buildup of excess fluid between the layers of the pleura outside the lungs (pleural space)
Differentiate between exudate and transudate with pleurocentesis
Transudate = transient → from changes in hydrostatic pressure: cirrhosis, CHF, nephrotic syndrome, ascites, hypoalbuminemia Exudative = protein ratio ↑, LDH ↑: infection, malignancy, immune; MC cause = pneumonia, cancer, PE, TB Diagnose with lateral decubitus CXR, chest CT, U/S. Thoracentesis is the gold standard
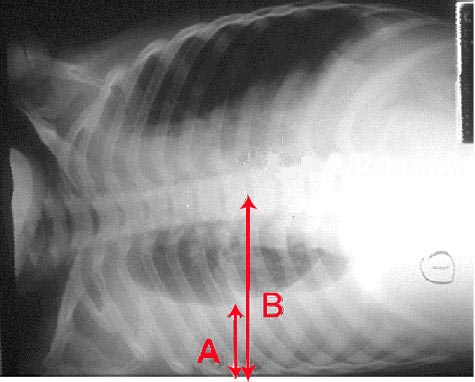 Pleural effusion seen on lateral decubitus chest x-ray. Arrow A shows fluid layering in the right pleural cavity. The B arrow shows the normal width of the lung in the cavity. Treatment is with thoracocentesis
|
 |
Light's Criteria is a diagnostic tool used to determine of the cause of a pulmonary effusion; transudate versus exudate. This relies on a comparison of the chemistries in the pleural fluid to those in the blood. According to Light's criteria, a pleural effusion is likely exudative if at least one of the following exists: The ratio of pleural fluid protein to serum protein is greater than 0.5, the ratio of pleural fluid LDH and serum LDH is greater than 0.6, or the pleural fluid LDH is greater than 0.6 or 2⁄3 times the normal upper limit for serum. |
ReelDx Virtual Rounds (pneumothorax)
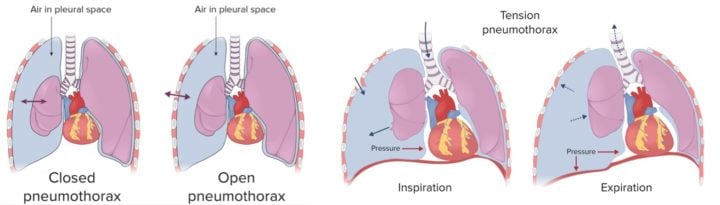
A pneumothorax is a collapsed lung caused by an accumulation of air in pleural space
- Presents with Acute onset ipsilateral chest pain and dyspnea with decreased tactile fremitus, deviated trachea, hyperresonance, diminished breath sounds
Can be spontaneous or traumatic
- Primary: occurs in the absence of underlying disease (tall, thin males age 10-30 at greatest risk)
- Secondary: in the presence of underlying disease (COPD, asthma, cystic fibrosis, interstitial lung disease)
Tension pneumothorax → penetrating injury → air in pleural space increasing and unable to escape
- Mediastinal shift to the contralateral side and impaired ventilation
DX: The diagnosis of pneumothorax is a radiologic one:
-
- Those who are unstable should have rapid bedside imaging with pleural ultrasonography (highly sensitive and specific)
- Those with a stable presentation can wait for confirmation by chest radiography - expiratory chest film reveals pleural air
- CT for those with uncertain dx, suspected to have a loculated pneumothorax, or stable trauma patients who require CT to assess the extent of other injuries
- ABG shows hypoxemia
TX: Treatment depends on the size
- Small - < 15% diameter of hemithorax will resolve spontaneously without the need for chest tube placement
- Large - > 15% diameter and symptomatic pneumothoraces require chest tube placement
- Serial CXR every 24 hours until resolved
- Tension pneumothorax is a medical emergency! Large bore needles to allow air out of the chest; chest tube for decompression