Patient will present as → a 25-year-old patient presents with unilateral hearing loss. Weber reveals lateralization to the right ear. Rinne test reveals the following: RIGHT: bone conduction = 10 seconds, air conduction = 5 seconds; LEFT: bone conduction = 5 seconds, air conduction = 10 seconds.
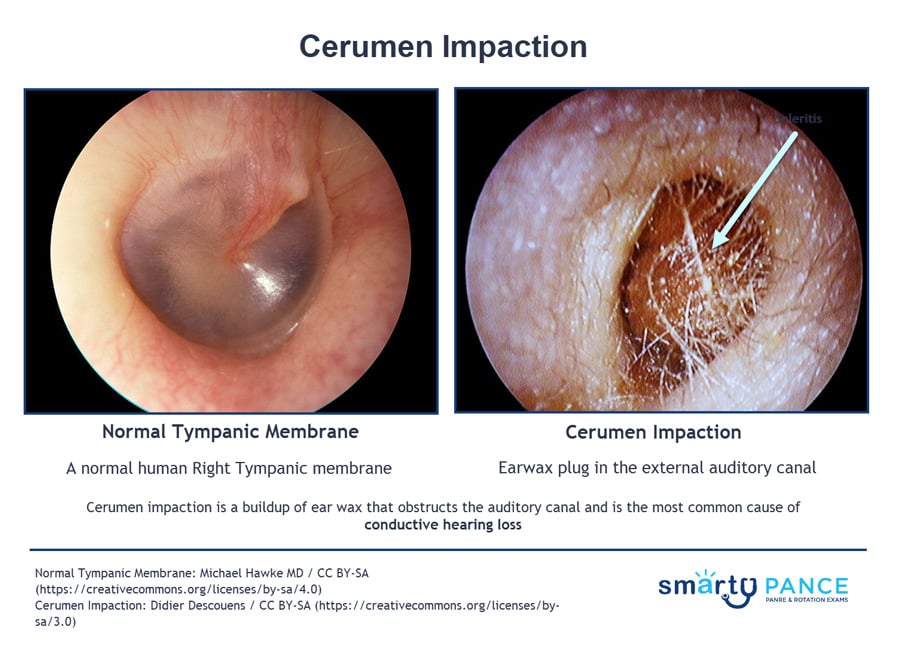
Cerumen impaction—buildup obstructs the auditory canal and is the most common cause of conductive hearing loss
- Cerumen may be pushed further into the ear canal and accumulate during patients' attempts to clean the ear canal with cotton swabs, resulting in obstruction or impaction
Rinne and Weber Tests
Conductive loss
- Abnormal Rinne test—bone conduction is better than air conduction – b/c bone conduction bypasses problems in the external or middle ear
- Weber—sound lateralizes to the affected side (tuning fork is perceived more loudly in the ear with conductive hearing loss) – b/c compensatory neural mechanisms or mechanical factors increase the perceived volume on the side of the conduction problem
Sensorineural loss
- Normal Rinne test—air conduction is better than bone conduction
- Weber—sound lateralizes to the unaffected side
| Rinne Result | Weber Result | |
| Normal | AC > BC in both ears | Midline |
| Conductive hearing loss | BC > AC in the affected ear
AC > BC in the unaffected ear |
Lateralizes to the affected ear |
| Sensorineural hearing loss | AC > BC in both ears | Lateralizes to unaffected ear |
| AC = air conduction, BC = bone conduction | ||
Cerumen impaction is best treated by irrigation after several days of softening with carbamide peroxide (Debrox) or triethanolamine (Cerumenex)
- Carbamide peroxide (Debrox) - apply 5 to 10 eardrops twice daily up to four days, keeping drops in the ear for several minutes by keeping the head tilted and placing cotton in the ear
- In patients with recurrent cerumen impaction and no significant ear disease - a cotton ball dipped in mineral oil and placed in the external canal once per week to help liquefy cerumen and aid the normal elimination mechanism
Question 1 |
A 35-year-old patient presents with unilateral hearing loss. Weber reveals lateralization to the right ear. Rinne test reveals the following: RIGHT: bone conduction = 10 seconds, air conduction = 5 seconds; LEFT: bone conduction = 5 seconds, air conduction = 10 seconds. Which of these other physical exam findings is to be expected?
cerumen impaction in the right ear | |
effusion in the left ear Hint: An effusion or otitis media could potentially cause a conductive hearing loss in the affected ear. The Weber test will lateralize to the left ear and bone conduction will be longer than air conduction in the left ear. | |
otitis media in the left ear Hint: See B. | |
pain on palpation of tragus or mastoid area Hint: Otitis externa and mastoiditis are not associated with hearing loss. |
Question 1 Explanation:
Cerumen impaction will block the ear canal. This would result in lateralization of the Weber test to the affected ear and would also cause bone conduction to be greater than air conduction in the same ear.
Question 2 |
A 42-year-old man presents to your clinic complaining of decreased hearing in his left ear and a sensation of fullness for the past week. On examination, you observe a significant cerumen impaction obstructing the view of the tympanic membrane. What is the most appropriate initial treatment for this patient?
Oral antibiotics Hint: These are not indicated in the treatment of simple cerumen impaction as there is no underlying infection. | |
Topical antibiotic ear drops Hint: Similar to oral antibiotics, these are not necessary for cerumen impaction without evidence of concurrent infection or otitis externa. | |
Manual removal with cerumenolytic agents | |
High-pressure ear irrigation Hint: While irrigation can be used for cerumen removal, high-pressure irrigation is generally avoided due to the risk of tympanic membrane perforation. Gentle irrigation may be considered after softening the cerumen | |
Referral for surgical removal Hint: Surgical intervention is rarely required for cerumen impaction and is reserved for cases where other methods are unsuccessful or contraindicated. |
Question 2 Explanation:
The most appropriate initial treatment for cerumen impaction is manual removal, often facilitated by the use of cerumenolytic agents. These agents help soften the impacted earwax, making it easier to remove either with irrigation or with manual tools like curettes, forceps, or suction devices. This approach is effective, minimally invasive, and can be performed in the outpatient setting.
There are 2 questions to complete.
|
List |
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate