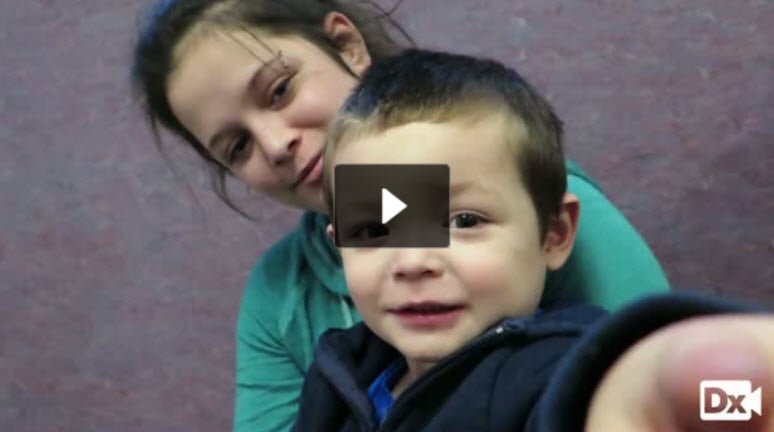
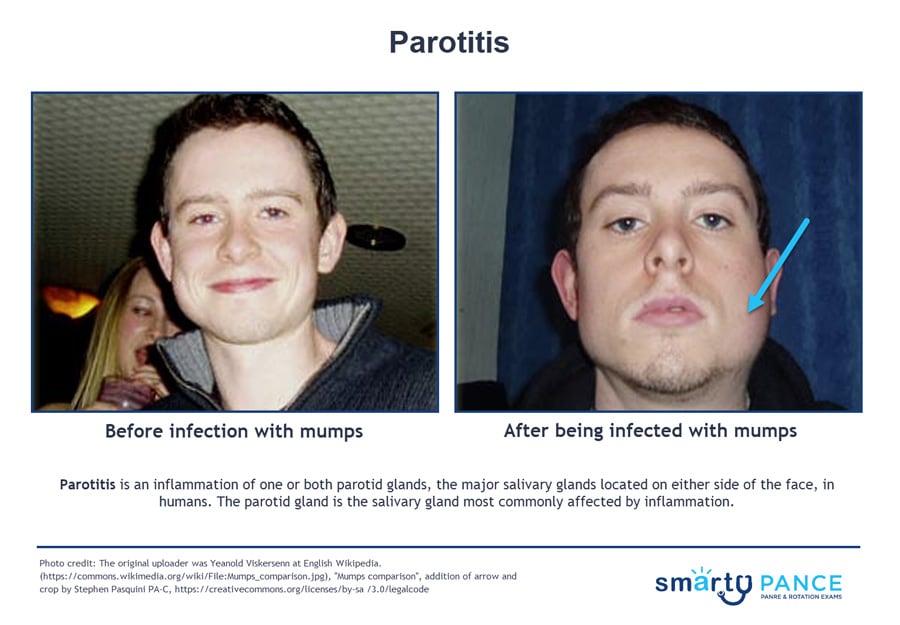
3-year-old with left-sided facial edema
Patient will present as → an 11-year-old boy with malaise and swelling of his face. He has no significant past medical history, but it is documented in his chart that his mother declined the recommended standard immunizations for children because of personal beliefs. Vital signs are stable, with the exception of a mild fever. In addition to the facial swelling, physical exam is also notable for swelling around the testes. There are no rashes.
Parotitis is an inflammation of one or both parotid glands, the major salivary glands located on either side of the face, in humans
- Patients present with fever and chills, periauricular, mandibular pain, and swelling; trismus, dysphagia; purulent drainage
- Viral ⇒ No discharge, prodrome followed by swelling lasting 5–10 days
Causes of parotitis:
- Dehydration is a common, non-infectious cause of parotitis. It may occur in the elderly or after surgery
- Infectious parotitis
- Bacterial parotitis is most often caused by a bacterial infection of Staphylococcus aureus.
- Viral parotitis
- Mumps is the most common viral cause of parotitis is mumps
-
- Caused by the paramyxovirus. Likely in a child without complete vaccination series
- Typically, it begins with a few days of fever, headache, myalgia, fatigue, and anorexia, followed by parotitis; the illness is usually self-limited
- In adult males, look for associated orchitis
- All cases are reported promptly to public health authorities.
-
- Other viral causes associated with parotitis include influenza A virus, parainfluenza, adenovirus, coxsackievirus, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex virus, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus
- Mumps is the most common viral cause of parotitis is mumps
- Autoimmune parotitis:
- Sjögren's syndrome: The syndrome is often characterized by excessive dryness in the eyes, mouth, nose, vagina, and skin
- Sarcoidosis as part of Mikulicz syndrome
- Sialolithiasis, or salivary duct calculus - blockage of the main parotid duct, or one of its branches, is often a primary cause of acute parotitis
"Bulimia nervosa is associated with parotitis, enamel erosion, electrolyte disturbances, metabolic alkalosis, and dorsal hand calluses from induced vomiting also known as Russell sign."
Diagnosis is often clinical
- Sample purulent exudate, ultrasound-guided needle aspiration; culture, Gram stain
- Ultrasound ⇒ increased blood flow through the gland, enlargement, nodules
- CT scan ⇒ extension of inflammation to surrounding tissue
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Serum and urinary amylase rise during the first week of parotitis without underlying pancreatitis
- Viral shows leukocytosis, increased IgM against mumps
Treatment is based on the lab investigation report
- Hydration; IV antibiotics
Mumps is self-limiting - treat with hydration and rest
- Vaccination is effective for prevention - CDC recommends all children get two doses of MMR (measles-mumps-rubella) vaccine, starting with the first dose at 12 through 15 months of age and the second dose at 4 through 6 years of age
- Contagious for 9 days after onset of parotid swelling
 Osmosis Osmosis |
|
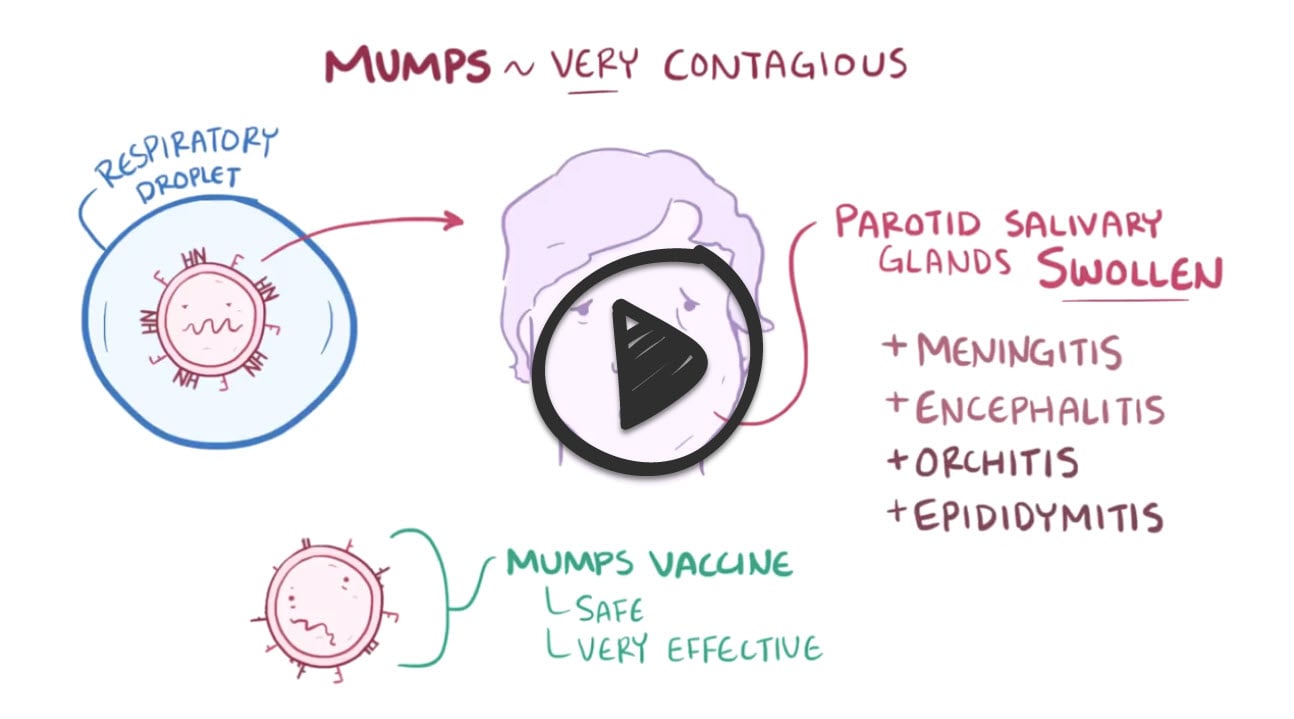 |

Mumps is a viral disease that is part of the paramyxovirus family. It presents with parotitis, orchitis, or aseptic meningitis. The disease is now rare due to vaccination but can be diagnosed with elevated amylase caused by parotitis or testicular pain. In rare cases, the disease can cause pancreatitis.
Play Video + QuizQuestion 1 |
A 5-year-old boy is brought to the clinic by his mother, who states he has had fever and swelling on both sides of his face for two days. She hasn't been able to get him to eat or drink much. He received his first MMR vaccine one year ago. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this child's condition?
Bacterial infection Hint: Bacterial parotitis can present similarly, but is usually unilateral and less common in children than viral causes. | |
Mumps virus | |
Foreign body obstruction Hint: Obstruction typically leads to acute salivary gland swelling but does not cause the same systemic features present here. | |
Autoimmune inflammation Hint: Disorders like Sjögren Syndrome could affect parotid glands, but the timeline and acute nature with other systemic signs support a viral process. | |
Epstein-Barr virus Hint: EBV (associated with infectious mononucleosis) can cause lymph node enlargement but not characteristic parotitis-like swelling. |
Question 2 |
A 24-year-old unvaccinated man presents to the urgent care center with fever, fatigue, and unilateral facial swelling that began two days ago. Physical examination reveals tender swelling of the right parotid gland and decreased salivation. Which of the following laboratory tests would be most helpful in confirming the diagnosis?
Serum amylase level Hint: Elevated amylase can indicate pancreatitis and parotitis but doesn't differentiate the underlying etiology. | |
Mumps IgM antibodies | |
Complete blood count (CBC)
Hint: A CBC might show leukocytosis in viral infections but can also be nonspecific. | |
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) titers Hint: Testing for EBV (Mononucleosis) could be relevant for fever and fatigue but isn't a primary diagnostic tool specifically for parotitis. | |
Salivary gland ultrasound Hint: Can aid in assessing gland structure and abscesses but wouldn't establish an acute viral infection definitively. |
Question 3 |
A 65-year-old woman with mumps parotitis receives appropriate supportive treatment at home. However, five days into her illness, she develops severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. The patient's new symptoms are most suggestive of which of the following complications of mumps?
Meningitis Hint: While mumps can also lead to meningitis (aseptic meningitis being more common), it often presents with headache, stiff neck, and photophobia. It's less likely to manifest primarily with abdominal pain, nausea, | |
Orchitis Hint: Orchitis (testicular inflammation) is a complication of mumps, particularly in post-pubertal males. It might cause lower abdominal pain but usually accompanied by pain and swelling of the testicles. | |
Oophoritis Hint: Mumps oophoritis (ovarian inflammation) can occur in females. While potentially causing pelvic or abdominal pain, the lack of other related symptoms like irregular periods or vaginal discharge make it less likely compared to pancreatitis. | |
Pancreatitis | |
Encephalitis Hint: Encephalitis is a less frequent but severe complication of mumps. Its primary symptoms are neurological – altered mental state, seizures, headaches – differing from the presentation focused on acute abdominal symptoms. |
|
List |
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate