NCCPA™ PANCE EENT Content Blueprint ⇒ ear disorders ⇒ other abnormalities of the ear
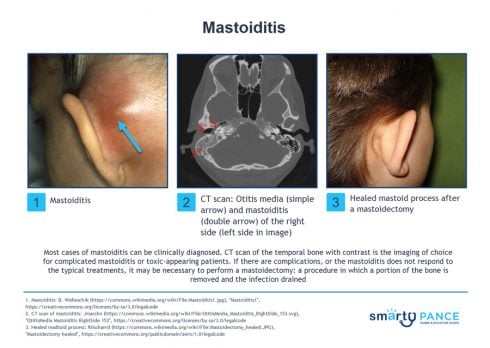
| Mastoiditis (ReelDx) | ReelDx Virtual Rounds (Mastoiditis )Patient will present as → a 10-year-old boy with otalgia, worsening over the last 5 days and associated with nasal congestion. The patient is afebrile with a temperature of 98 ° F. Examination reveals edema of the external auditory canal, producing an anterior and inferior displacement of the auricle with percussion tenderness posteriorly. Suppurative infection of mastoid air cell ⇒ usually a complication of acute otitis media
DX: Clinical; CT scan temporal bone with contrast for complicated/toxic appearing TX: Simple = Oral antibiotics or IV antibiotics (ceftriaxone)
|
| Meniere disease | ReelDx Virtual Rounds (Foreign body in ear)Patient will present as → 41-year-old female with intermittent episodes of vertigo, tinnitus, nausea, and hearing loss over the past week. Ménière syndrome is a disorder of the endolymphatic compartment with the classic triad of episodic vertigo, unilateral low-frequency sensorineural hearing loss, and tinnitus. "Meniere's disease is associated with EPISODIC vertigo and NOT associated with viral infections. This differentiates it from Labyrinthitis, which is associated with CONTINUOUS vertigo along with hearing loss +/- tinnitus and is usually associated with an upper respiratory infection." DX: Although audiometric testing is a required part of the diagnostic evaluation, there is no specific diagnostic test for MD
A clinical diagnosis of MD is made based on the following criteria:
TX: Low salt diet, diuretics (HCTZ + triamterene) to reduce aural pressure |
| Tinnitus | Patient will present as → a 70-year-old female who states that her children and grandchildren have asked her to seek medical attention as she seems to be losing her hearing. She also describes an occasional ringing, buzzing, and hissing sound. She is in generally good health, and her only medications are a multivitamin along with calcium and vitamin D. You examine her ears and find the external auditory canals to be free of cerumen and the tympanic membranes to be normal in appearance. A perceived sensation of sound in the absence of an external acoustic stimulus is often described as ringing, hissing, buzzing, or whooshing.
DX: All patients with significant tinnitus should be referred for comprehensive audiologic evaluation to determine the presence, degree, and type of hearing loss.
TX: No pharmacologic agent has been shown to cure or consistently alleviate tinnitus
|