6-year-old with painless lesions on the gum line
Patient will present as → a 22-year-old complaining of a painful sore for 2 days. He denies any alcohol or tobacco use and otherwise feels fine. The examination is significant for a 2-mm round ulceration with a yellow-gray center surrounded by a red halo on the left buccal mucosa.
To watch this and all of Joe Gilboy PA-C's video lessons you must be a member. Members can log in here or join now.
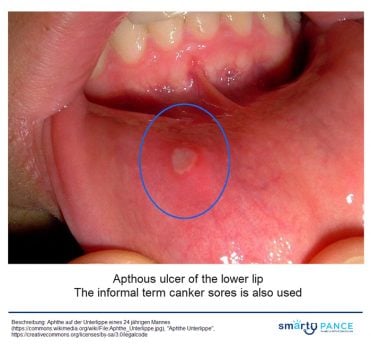
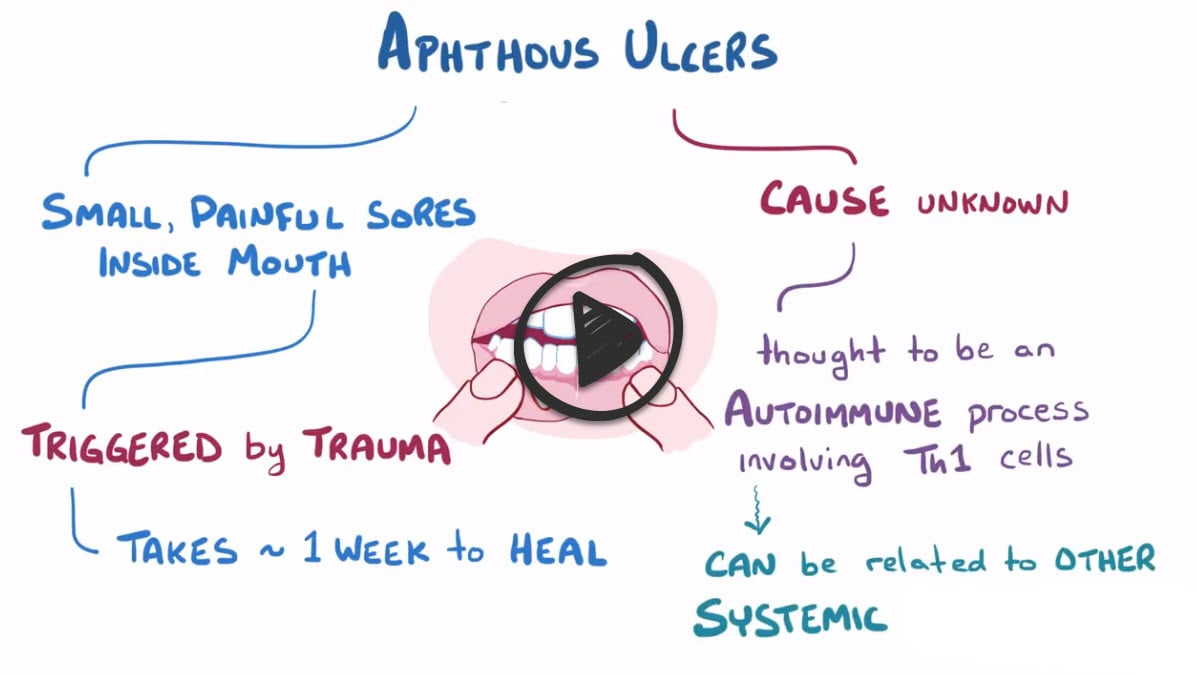
Aphthous ulcers are discrete, painful, ovoid, or round ulcerations on the mucous membranes of the mouth, tongue, or genitals, commonly referred to as “canker sores”
- The lesions are typically 3 to 5 mm, round to oval ulcers with a peripheral rim of erythema and a yellowish, adherent exudate centrally
- The vast majority of aphthous ulcers are benign, self-limited, and usually heal within 7 to 14 days
- Providers must consider the underlying systemic causes of ulcers:
- Inquire about patient or family history of:
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
- Behçet disease
- Reiter disease
- Gluten sensitivity
- Cancer
- HIV
- Inquire about sexual history of syphilis or herpes virus
- Inquire about current medications:
- NSAIDs
- β-blockers
- Inquire about patient or family history of:
Diagnosis is made by history and clinical presentation.
- Biopsy should be considered for ulcers lasting more than 3 weeks
- Rule out an oral manifestation of systemic disease: More likely if it persists >3 wks or is associated with constitutional symptoms. Focus on symptoms of eyes, mouth, genitalia, skin, GI tract, allergy, diet history, and physical exam
The severity and duration of symptoms guide treatment. The goal is for symptomatic pain relief and reduction of inflammation.
- Mild to moderate disease:
- Avoid oral trauma/acidic foods
- Topical anesthetic
- Magnesium hydroxide/diphenhydramine hydrochloride 5 mg/5 mL in 1/1 mix swish and spit
- Viscous lidocaine 2–5%: Applied to ulcer QID after meals until healed
- High-potency topical corticosteroids (e.g., dexamethasone elixir 0.5 mg/5 mL to swish and spit three to four times per day) are the first-line treatment for patients with recurrent aphthous stomatitis
- Monitor PO status (especially in small children)
- PO NSAIDs
- Referral to a specialist if an underlying disease is suspected
Question 1 |
Prescribe topical corticosteroids | |
Initiate oral acyclovir therapy Hint: Oral acyclovir is used for treating herpes simplex virus (HSV) infections, which can cause oral ulcers. However, the description of the ulcers and the absence of systemic symptoms do not suggest HSV, making acyclovir an inappropriate choice. | |
Order a biopsy of the ulcer Hint: While biopsy can be helpful in diagnosing uncertain cases or when malignancy is suspected, it is not typically necessary for the initial management of classic recurrent aphthous stomatitis, especially in the absence of alarming features. | |
Start systemic corticosteroids Hint: Systemic corticosteroids are reserved for severe cases of RAS or when topical therapy is ineffective. Given the lack of systemic involvement and the patient's description of localized ulcers, systemic corticosteroids would not be the most appropriate next step. | |
Recommend avoidance of spicy and acidic foods Hint: While avoiding spicy and acidic foods may help reduce irritation and discomfort associated with oral ulcers, this recommendation alone does not constitute adequate management for recurrent aphthous stomatitis. Topical treatment aimed at reducing inflammation and promoting healing is necessary. |
Question 2 |
Biopsy of the lesions Hint: Not necessary given the classic appearance. Aphthous ulcers are a clinical diagnosis. | |
Blood cultures Hint: There are no systemic symptoms to indicate an underlying infection. | |
HIV screening Hint: May be considered in high-risk patients, but is not routinely warranted. | |
Oral antiviral therapy Hint: Antivirals are not used to treat aphthous ulcers. | |
Reassurance and symptomatic treatment |
|
List |
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate


 Lecture
Lecture Osmosis
Osmosis