Patient will present as→ a 43-year-old male with a “lifelong” history of chronic ear infections and episodic purulent drainage from his right ear canal. The patient currently is without symptoms. Examination of the ear shows a clear external canal, but the tympanic membrane is retracted and there is a pocket of white material and an opacity of the pars flaccida. The Weber test lateralizes to the right and Rinne shows air conduction > bone conduction on the left and bone conduction > air conduction on the right. Preparations are made to undergo a non-contrast computed tomography (CT) scan of the temporal bone.
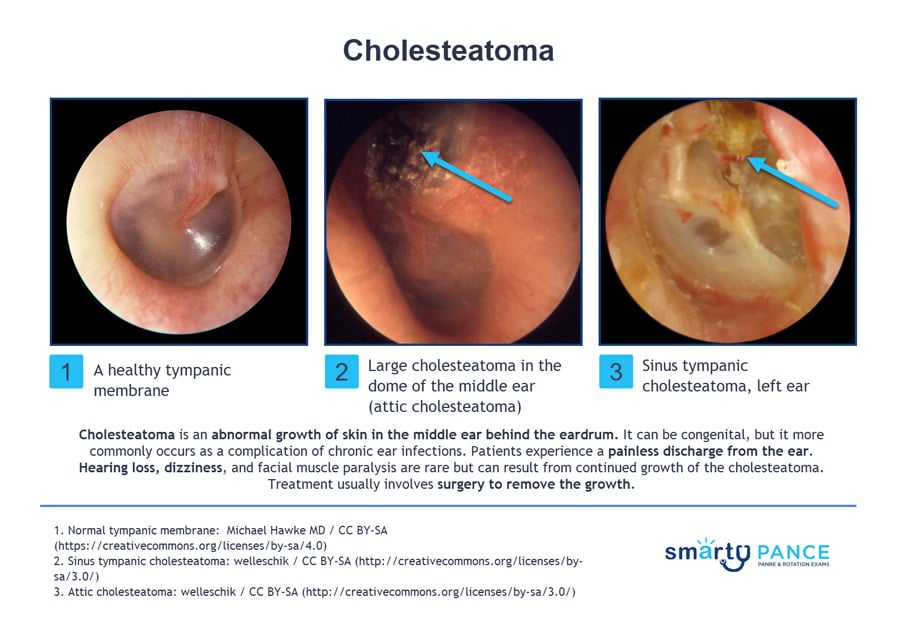
Cholesteatoma is an abnormal growth of skin in the middle ear behind the eardrum.
- Commonly occurs as a complication of recurring ear infections and by chronic eustachian tube dysfunction which results in chronic negative pressure which inverts part of the TM causing granulation tissue that over time, erodes the ossicles and leads to conductive hearing loss.
- Pt will present with painless otorrhea (brown/yellow discharge with strong odor) it may not be bothersome to the patient.
- May also present with hearing loss, tinnitus, dizziness, otorrhea, and cranial nerve palsies.
Management of cholesteatoma includes surgical excision of the debris/cholesteatoma and reconstruction of the ossicles
Question 1 |
Conservative management with regular follow-up Hint: Not appropriate for cholesteatoma as it can lead to complications. | |
Systemic antibiotics Hint: May be used for secondary infections but do not treat the underlying cholesteatoma. | |
Topical antibiotic drops Hint: Useful for controlling discharge but do not address the cholesteatoma itself. | |
Surgical removal of the cholesteatoma | |
Hearing aid fitting Hint: May be needed for associated hearing loss but does not treat the cholesteatoma. |
Question 2 |
CT scan of the temporal bone | |
MRI of the brain Hint: Useful for intracranial pathology but less so for cholesteatoma. | |
Audiometry Hint: Important for assessing hearing loss but does not visualize the cholesteatoma. | |
Tympanometry Hint: Assesses middle ear function but does not provide imaging of cholesteatoma. | |
Ultrasound of the neck Hint: Not relevant for middle ear pathology. |
Question 3 |
History of frequent swimming and ear pain Hint: These symptoms are more indicative of external otitis (swimmer's ear) rather than cholesteatoma. | |
Persistent foul smelling otorrhea and hearing loss | |
Sudden onset of vertigo and tinnitus Hint: While these symptoms can occur in various ear disorders, they are not specifically indicative of cholesteatoma. | |
Intermittent ear fullness and allergic rhinitis Hint: These symptoms are more commonly associated with Eustachian tube dysfunction or allergic conditions, not cholesteatoma. | |
History of head trauma and unilateral tinnitus Hint: While these can be seen in various ear conditions, they do not specifically point towards cholesteatoma. |
|
List |
References: UpToDate