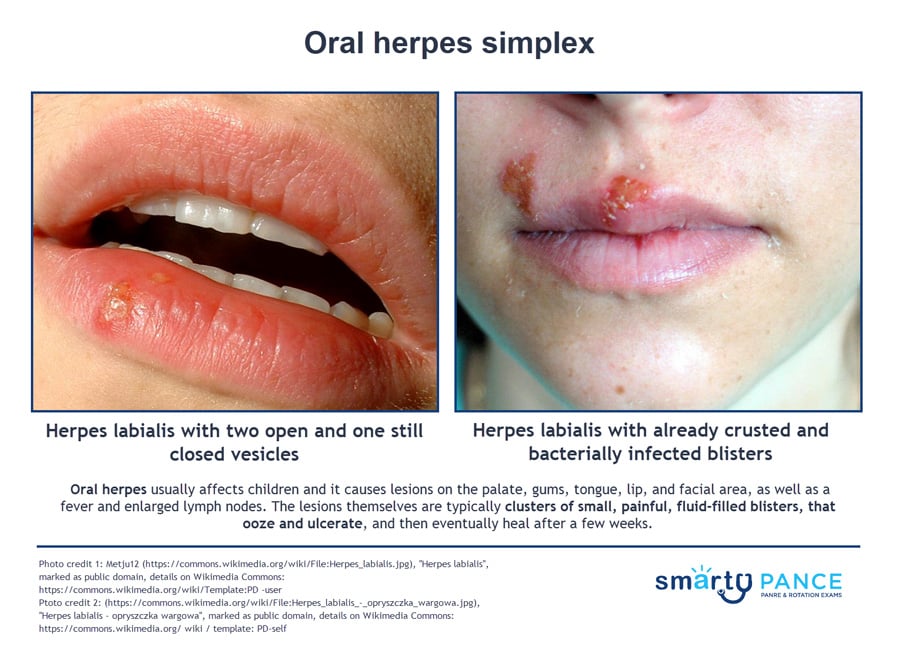
6-year-old with painful vesicle and prodromal discomfort
Patient will present as → a 17-year-old female complaining of a painful rash on her cheek. She says that it has come and gone a few times before and that she usually can feel itching and a tingling discomfort before a break out of the lesions. On physical exam, you observe clusters of small, tense vesicles on an erythematous base.
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is an enveloped double-stranded DNA virus. It exists as two distinct subtypes, HSV-1 and HSV-2, and is responsible for a wide spectrum of illness ranging from fever blisters to genital ulcers and fatal encephalitis. It establishes lifelong latency and can lead to interval episodes of asymptomatic shedding and disease recurrence
- HSV-1 infects 40–80% of the U.S population by young adulthood, and 60–85% by age 60
- Infections “above the waist” are classically due to HSV-1, whereas HSV-2 most commonly causes genital infection. However, both serotypes can cause genital and/or mucocutaneous infection
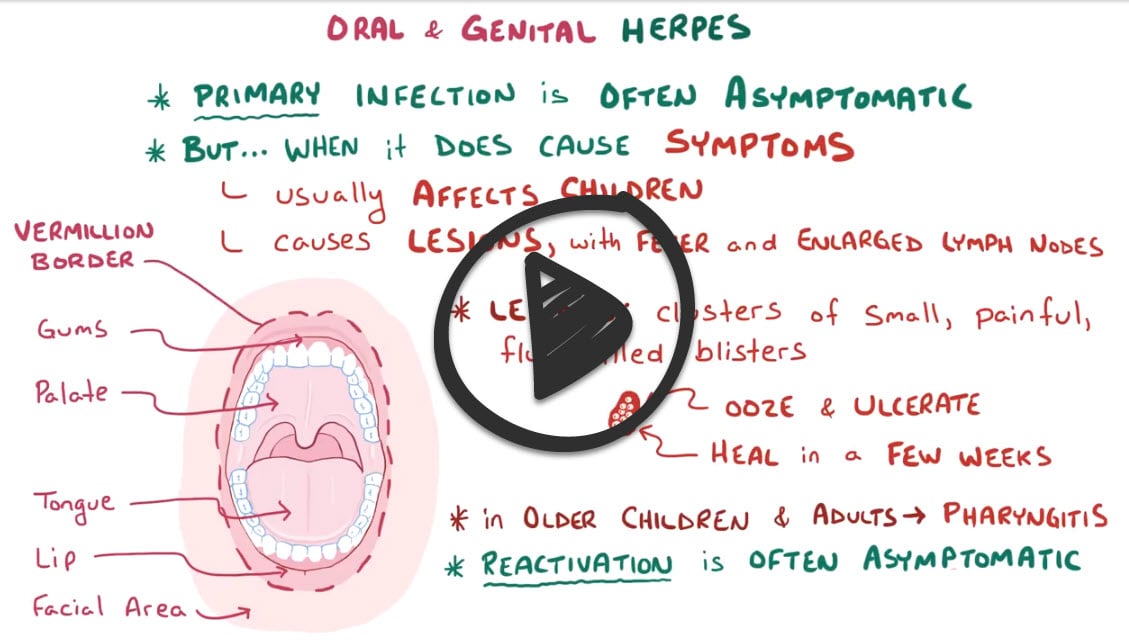
- Primary infection is characterized by fever, irritability, and severe pain/burning of the oral mucosa, with vesicular and ulcerative lesions on the lips, gingiva, and tongue
- Pharyngitis is also common in older children and adolescents
- The illness lasts for 2–3 weeks, with viral shedding continuing for several weeks
Diagnosis of HSV infection is often clinical based on characteristic lesions
- A Tzanck test/smear (a superficial scraping from the base of a freshly ruptured vesicle stained with Wright-Giemsa stain) often reveals multinucleated giant cells in HSV
- Definitive diagnosis is with culture, PCR, and antigen detection
Symptomatic treatment with antipyretics and analgesia (viscous lidocaine or topical benzocaine) is recommended. IV hydration is sometimes needed in cases of decreased oral intake
- First episode:
- Oral acyclovir 400 mg TID x 7-10 days
- peds: (15 mg/kg/dose five times per day for 7–10 days; max 200 mg per dose) may decrease the duration of illness if started within 72 hours at the onset of symptoms.
- Valacyclovir 1 g BID x 7-10 days
- Famciclovir 250 mg TID x 7-10 days
- Oral acyclovir 400 mg TID x 7-10 days
- Recurrent episodes:
- Acyclovir 400 mg TID x 5 days
- Valacyclovir 1 g PO BID x 1 day
- Famciclovir 1 g PO BID x 1 day
- Suppressive therapy
- Acyclovir 400 TID
- Famciclovir 500 mg BID
- Valacyclovir 1 g BID
 Osmosis Osmosis |
|
 |
 Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is a viral disease from the herpesviridae family. This family of viruses is enveloped and has double stranded linear DNA. There are two types of Herpes simplex virus. Type 1 HSV causes oral herpes, commonly called cold sores. Other manifestations include herpetic gingivostomatitis, keratoconjunctivitis, and temporal lobe encephalitis. After the patient begins to produce antibodies, HSV type 1 becomes latent in the trigeminal ganglia and can become reactivated with certain stimuli including stress and UV light exposure. Type 2 HSV is primarily a sexually transmitted infection that can cause clusters of inflamed vesicles on the outer surface of the genitals. Infants that pass through the vaginal canal in a female with an outbreak of genital herpes can lead to neonatal herpes, characterized by multiple vesicular lesions on the skin or involvement of internal organs or the central nervous system. Acyclovir is commonly used as treatment for herpes infections.
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is a viral disease from the herpesviridae family. This family of viruses is enveloped and has double stranded linear DNA. There are two types of Herpes simplex virus. Type 1 HSV causes oral herpes, commonly called cold sores. Other manifestations include herpetic gingivostomatitis, keratoconjunctivitis, and temporal lobe encephalitis. After the patient begins to produce antibodies, HSV type 1 becomes latent in the trigeminal ganglia and can become reactivated with certain stimuli including stress and UV light exposure. Type 2 HSV is primarily a sexually transmitted infection that can cause clusters of inflamed vesicles on the outer surface of the genitals. Infants that pass through the vaginal canal in a female with an outbreak of genital herpes can lead to neonatal herpes, characterized by multiple vesicular lesions on the skin or involvement of internal organs or the central nervous system. Acyclovir is commonly used as treatment for herpes infections.
| Herpes simplex virus (HSV) | Play Video + Quiz |
| Acyclovir (Zovirax) | Play Video + Quiz |
Question 1 |
Highest rate of infection occurs in adolescent children. Hint: Overall, the highest rate of infection occurs during the preschool years. | |
Lesions are usually painless vesicles that form on the tongue, palate, and gingival area. Hint: It typically takes the form of painful vesicles and ulcerative erosions on the tongue, palate, gingiva, buccal mucosa, and lips. Edema, halitosis, and drooling may be present, and tender submandibular or cervical lymphadenopathy is not uncommon. | |
Topical acyclovir is the drug of choice. | |
Recurrent infections are less severe and shorter in duration. | |
Pain associated with lesions typically lasts 2 to 3 weeks. |
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate