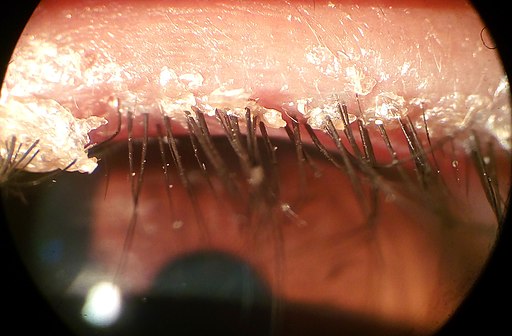
Patient will present as → a 37-year-old male with crusting, scaling, red-rimming of the eyelid, and eyelash flaking along with dry eyes. The patient has a history of seborrheic dermatitis and rosacea.
To watch this and all of Joe Gilboy PA-C's video lessons you must be a member. Members can log in here or join now.
Blepharitis is a clinical diagnosis based on characteristic findings of redness and irritation of the eyelid margin associated with crusting or flakes on the lashes or lid margins
- Slit-lamp examination allows for a more detailed examination; however, is generally not necessary to make the diagnosis.
- Chronic blepharitis that does not respond to treatment may require a biopsy to exclude eyelid tumors that can simulate the condition
Treat with warm compresses, irrigation, lid massage, and topical antibiotics for flare-ups
- Daily lid wash with baby shampoo
Question 1 |
The treatment of choice for blepharitis includes:
Antibiotic ointment (eg, bacitracin/polymyxin B, erythromycin, or gentamicin 0.3% qid for 7 to 10 days) | |
Warm compresses over the closed eyelid | |
Tear supplements during the day | |
Gentle cleansing of the eyelid margin 2 times a day with a cotton swab dipped in a dilute solution of baby shampoo (2 to 3 drops in ½ cup of warm water) | |
all of the above |
Question 1 Explanation:
Chronic disease is treated with tear supplements, warm compresses, and occasionally oral antibiotics (eg, a tetracycline) for meibomian gland dysfunction or with eyelid hygiene and tear supplements for seborrheic blepharitis. Gentle cleansing of the eyelid margin 2 times a day with a cotton swab dipped in a dilute solution of baby shampoo (2 to 3 drops in ½ cup of warm water)
Question 2 |
Which of the following best describes the pathophysiological mechanism of anterior blepharitis?
Autoimmune destruction of meibomian glands Hint: Autoimmune destruction of meibomian glands is more indicative of conditions like meibomian gland dysfunction, not anterior blepharitis. | |
Infection of the eyelid margin by Staphylococcus species | |
Allergic reaction to environmental antigens Hint: Allergic reactions can cause eyelid inflammation but are not the primary mechanism of blepharitis. | |
Blockage of the lacrimal drainage system Hint: Blockage of the lacrimal drainage system leads to conditions like dacryocystitis, not blepharitis. | |
Degenerative changes in the tarsal plate Hint: Degenerative changes in the tarsal plate are not associated with blepharitis. |
Question 2 Explanation:
Anterior blepharitis is commonly caused by infection of the eyelid margin, particularly by Staphylococcus species. This leads to inflammation, redness, and irritation of the eyelid margins.
Question 3 |
A 35-year-old patient presents with red, irritated eyelids and flaky debris at the base of the eyelashes. Which diagnostic feature is most indicative of blepharitis?
Eyelid erythema and scaling at the lash base | |
Painless, firm nodule on the eyelid Hint: A painless, firm nodule on the eyelid is more indicative of a chalazion. | |
Outward turning of the eyelid margin Hint: Outward turning of the eyelid margin describes ectropion, not blepharitis. | |
Inward turning of the eyelid margin Hint: Inward turning of the eyelid margin is characteristic of entropion, not blepharitis. | |
Acute, localized swelling of the eyelid Hint: Acute, localized swelling of the eyelid is suggestive of a hordeolum (stye), not blepharitis. |
Question 3 Explanation:
Eyelid erythema and scaling at the lash base are characteristic findings in blepharitis, often accompanied by irritation and a sensation of burning or grittiness
There are 3 questions to complete.
|
List |
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate


 Lecture
Lecture