NCCPA™ PANCE EENT Content Blueprint ⇒ Oropharyngeal disorders ⇒ Infectious and inflammatory disorders
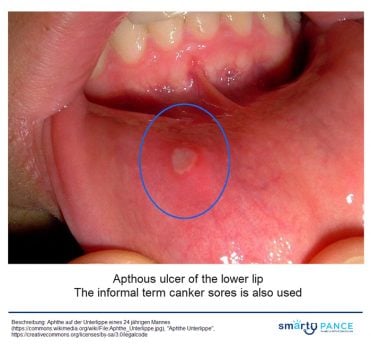
| Aphthous ulcers (ReelDx) | ReelDx Virtual Rounds (Aphthous ulcers)Patient will present as → a 22-year-old complaining of a painful sore for 2 days. He denies any alcohol or tobacco use and otherwise feels fine. The examination is significant for a 2-mm round ulceration with a yellow-gray center surrounded by a red halo on the left buccal mucosa Single or multiple small, shallow ulcers with a yellow-gray fibrinoid center with red halos DX: Diagnosis is made by history and clinical presentation
TX: viscous lidocaine 2–5% applied to ulcer QID after meals until healed |
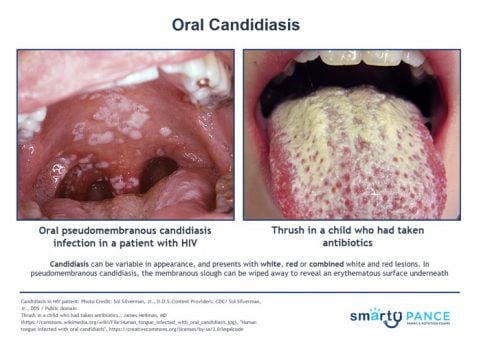
| Candidiasis (ReelDx) | ReelDx Virtual Rounds (Oral Candidiasis)Patient will present as → a 3-week-old infant with decreased appetite and a rash in her mouth. On physical exam, you note white plaques on her tongue that scrape off with a tongue depressor and bleed slightly. Potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation of the scrapings demonstrates budding yeasts with hyphae. Immunocompromised, young patients
DX: Potassium Hydroxide (KOH) prep for diagnosis TX: Antifungals, which are available in several forms (i.e., ketoconazole or fluconazole orally, clotrimazole troches, nystatin liquid rinses) |
| Deep neck infection | Patient will present as → a 51-year-old male patient who underwent extraction of the mandibular right third molar. Seven days after the surgery, the patient developed facial edema, fever, intraoral purulent discharge, and extreme local pain. Infectious cavities in the right and left submandibular, pterygomandibular, and pharyngeal regions were observed on computed tomography scans. Deep neck space infections most commonly arise from a septic focus of the mandibular teeth, tonsils, parotid gland, deep cervical lymph nodes, middle ear, or sinuses
DX: Computed tomography (CT) is the imaging modality of choice for the diagnosis of deep neck space infection
TX: Antibiotics, aspiration or surgical drainage should be performed 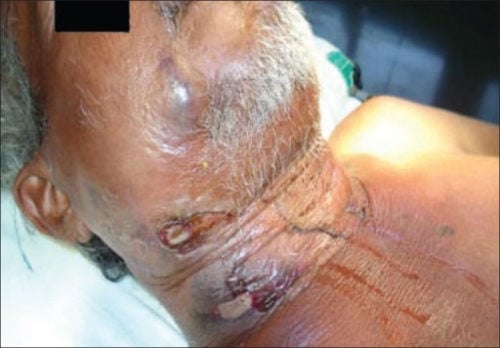 Minor trauma triggering cervicofacial necrotizing fasciitis from an odontogenic abscess. Image by Jain S, Nagpure PS, Singh R, Garg D - CC 2.0 |
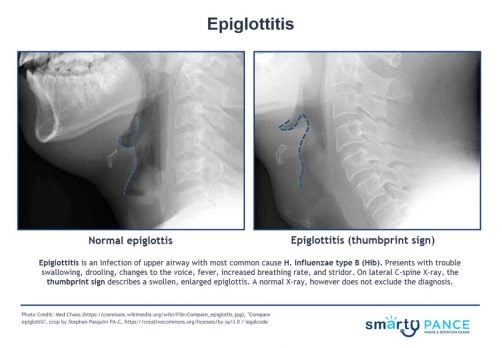
| Epiglottitis | Patient will present as → a 3-year-old who is brought into the emergency room by her parents. The child has had a high fever, sore throat, and stridor. She has a muffled voice and is sitting up on the stretcher, drooling while leaning forward with her neck extended. The patient’s parents are adamantly against vaccinations, claiming that they are a “government conspiracy.” You order a lateral neck x-ray, which shows a swollen epiglottis. The patient recovered following treatment with prednisone and ceftriaxone. Epiglottitis is supraglottic inflammation and obstruction of the airway due to infection with Haemophilus influenzae type B (Hib)
The 3 D's of epiglottitis:
DX: Secure airway, then culture for H.flu
TX: This is a medical emergency! Secure airway, admit, IV Ceftriaxone, and IV fluids |
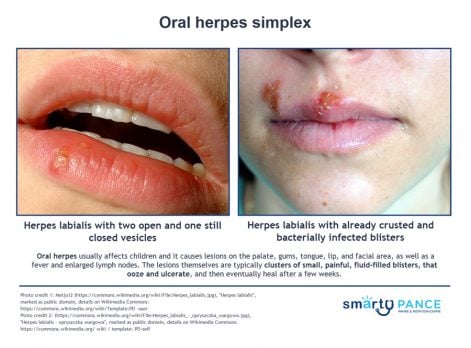
| Oral herpes simplex (ReelDx) | ReelDx Virtual Rounds (Oral herpes simplex)Patient will present as → a 17-year-old female complaining of a painful rash on her cheek. She says that it has come and gone a few times before and that she usually can feel itching and a tingling discomfort before a break out of the lesions. On physical exam, you observe clusters of small, tense vesicles on an erythematous base. HSV type 1, vesicular lesions all in the same stage of development, a prodromal period of tingling discomfort or itching DX: Diagnosis is clinical; laboratory confirmation by culture, PCR, direct immunofluorescence, or serologic testing can be done TX: Symptomatic treatment with antipyretics and analgesia is recommended. IV hydration is sometimes needed in cases of decreased oral intake
|
| Laryngitis | Patient will present as → a 27-year-old mezzo-soprano who states that she developed acute hoarseness 2 days ago. Prior to that, she had a cold, the symptoms of which are improving. There is no history of smoking or other tobacco use. She is very worried as she has an upcoming performance 3 days from now. Almost always viral, hoarseness following a URI
DX: clinical diagnosis ⇒ laryngoscopy is required for symptoms persisting > 3 wk TX: Relax voice (vocal rest), supportive therapy
|
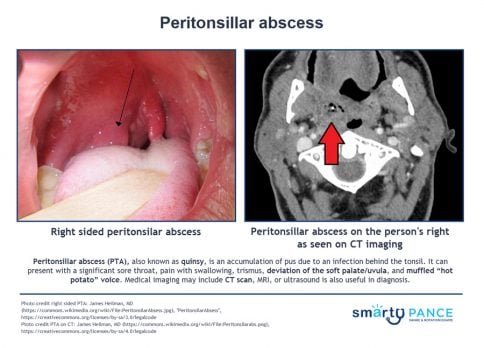
| Peritonsillar abscess (ReelDx) | ReelDx Virtual Rounds (Peritonsillar abscess)Patient will present as → a 19-year-old male who you are seeing for follow-up from the urgent care where he was seen 2 days earlier with a sore throat. The patient is febrile (102°F), has a muffled (hot potato) voice, and extreme difficulty opening his mouth (trismus). He opens it just far enough for you to note uvular deviation. A peritonsillar abscess results from the penetration of infection through the tonsillar capsule and the involvement of neighboring tissue
DX: Xray, CT, or ultrasound of the neck if the diagnosis is in doubt, particularly when the condition must be differentiated from a parapharyngeal infection or other deep neck infection
TX: Aspiration, incision and drainage, and/or antibiotics
|
| Pharyngitis (ReelDx) | ReelDx Virtual Rounds (Acute pharyngitis)Patient will present as → a 7-year-old boy is brought to his pediatrician for evaluation of a sore throat. The sore throat began 4 days ago and has progressively worsened. Associated symptoms include subjective fever, pain with swallowing, and fatigue. The patient denies cough or rhinorrhea. Vital signs are as follows: T 101.4 F, HR 88, BP 115/67, RR 14, and SpO2 99%. Physical examination is significant for purulent tonsillar exudate; no cervical lymphadenopathy is noted. Most cases of pharyngitis are viral - adenovirus is the most common cause
DX: Centor Score for Strep Pharyngitis (MDCalc): 1. Absence of a cough, 2. exudates, 3. fever (> 100.4 F), 4. cervical lymphadenopathy
TX:
|