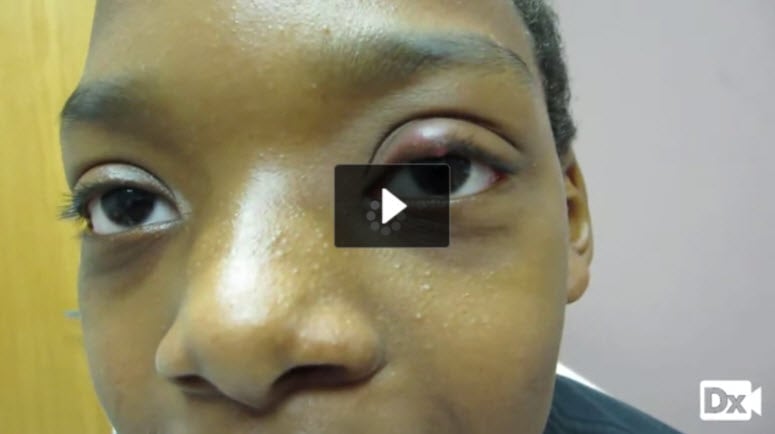
11 y/o with a red, swollen lesion on the eyelid
Patient will present as → a 15-year-old male with pain, redness, and swelling of the upper eyelid for the last 3 days. There are no visual changes or photophobia. Examination reveals a tender, erythematous, and outward-pointing edema of the right eyelid.
To watch this, and all of Joe Gilboy PA-C's fantastic video lessons you must be a member. Members can log in here or join now.
Hordeolum = Stye = Painful and “Hot”- think “H” for Hot = Hordeolum
- The patient will present with a painful, warm (hot), swollen red lump on the eyelid (different from a chalazion, which is painless)
- There may be tearing, photophobia, and a foreign body sensation
- They are usually caused by staphylococcus aureus
- Hordeolum are infections of the glands of the eyelid, while a chalazion is a sterile, chronic inflammation that results from a blocked meibomian gland. A complication of a stye is that it may progress to a chalazion
The diagnosis is clinical
Warm compress and topical antibiotics
- A hordeolum that does not respond to hot compresses can be incised with a sharp, fine-tipped blade
- Systemic antibiotics (e.g., dicloxacillin or erythromycin 250 mg PO QID) are indicated when cellulitis accompanies a hordeolum
Question 1 |
A 25-year-old woman presents with a painful, red swelling on the upper eyelid that developed over the past two days. She reports a similar episode six months ago. Which of the following is the most common causative agent of this condition?
Herpes simplex virus Hint: More commonly associated with ocular herpes, not hordeolum. | |
Staphylococcus aureus | |
Pseudomonas aeruginosa Hint: Not a typical cause of hordeolum. | |
Chlamydia trachomatis Hint: Associated with trachoma and inclusion conjunctivitis, not hordeolum. | |
Candida albicans Hint: Not a common causative agent of hordeolum. |
Question 1 Explanation:
Staphylococcus aureus is the most common causative agent of hordeolum (stye). It typically infects the eyelid margin or lash follicle, leading to the acute onset of a painful, red swelling on the eyelid.
Question 2 |
Which of the following best differentiates between a Chalazion and a Hordeolum?
Chalazion: Acute infection of a meibomian gland, typically painful and located at the eyelid margin Hint: A chalazion results from the blockage and inflammation of a meibomian gland but is typically not as acutely painful as a hordeolum and is often located away from the eyelid margin. | |
Hordeolum (Stye): Chronic granulomatous inflammation of a meibomian gland, usually painless and located away from the eyelid margin Hint: This description incorrectly characterizes a hordeolum as a chronic and painless condition, which is more indicative of a chalazion. | |
Chalazion: Chronic granulomatous inflammation of a meibomian gland, typically painless and located away from the eyelid margin Hint: This is a correct description of a chalazion, but it does not match the patient's presentation of an acutely painful lesion. | |
Hordeolum (Stye): Acute infection of a meibomian gland or Zeis gland, typically painful and located at the eyelid margin | |
Both conditions are essentially the same and differ only in duration Hint: This statement is incorrect as chalazion and hordeolum have distinct clinical features and etiologies. |
Question 2 Explanation:
A hordeolum, commonly known as a stye, is an acute infection of the meibomian gland or Zeis gland, resulting in a painful, red, and swollen lump at the eyelid margin. A chalazion results from the blockage and inflammation of a meibomian gland but is typically not as acutely painful as a hordeolum and is often located away from the eyelid margin.
Question 3 |
A 20-year-old university student presents with an acutely painful swelling on her upper eyelid diagnosed as a hordeolum. What is the most appropriate initial treatment for this condition?
Systemic antibiotics Hint: Typically reserved for cases with significant cellulitis or systemic symptoms. | |
Warm compresses and lid hygiene | |
Steroid injection Hint: Not a standard treatment for hordeolum. | |
Surgical incision and drainage Hint: Considered if the hordeolum does not resolve with conservative treatment. | |
Antiviral medication Hint: Used for viral infections, not applicable for a bacterial infection like a hordeolum. |
Question 3 Explanation:
The most appropriate initial treatment for a hordeolum is warm compresses and lid hygiene. Warm compresses help in promoting drainage and resolution of the stye, while lid hygiene helps in preventing recurrence.
There are 3 questions to complete.
|
List |
References: Merck Manual · UpToDate


 Lecture
Lecture